Protective foam for electronics packaging is specialized material that safeguards your sensitive electronic components during storage and shipping. You'll find these foams in different types – including anti-static, conductive, and static dissipative varieties – each with specific surface resistivity levels to prevent electrostatic damage. The foam's shock-absorbing properties protect against impacts and vibrations, while its non-abrasive surface keeps delicate device finishes scratch-free. You can get custom-cut foam inserts that provide a snug, precise fit for your equipment, meeting essential industry standards like EIA-541. Understanding the specific properties of each foam type will help you choose the best protection for your electronics.
Understanding Electronics Packaging Foam Essentials

When you're shipping or storing electronic devices, choosing the right protective foam isn't just an option – it's essential for safeguarding your valuable equipment.
The key to effective electronics packaging lies in understanding the fundamental properties that make protective foam indispensable. Pink anti-static foam is most common, but it can be manufactured in various other colors while maintaining the same protective qualities.
You'll need to focus on anti-static protection first, as electronic components are highly susceptible to damage from electrostatic discharge. The foam you select must provide reliable shock absorption to protect against impacts and vibrations during transit. Additionally, you'll want to guarantee the material is non-abrasive to prevent scratches on sensitive surfaces.
Your choice of foam should align with your specific needs. If you're packaging smaller, delicate items, open-cell polyurethane foam will serve you well. For larger electronics, closed-cell polyethylene foam offers better support. You'll find both types available with anti-static properties that meet industry standards like EIA-541.
Don't overlook the importance of moisture resistance and customization options. You can have the foam cut to precisely fit your device, guaranteeing it stays firmly in place during shipping.
This custom fit, combined with the foam's protective properties, creates a superior packaging solution for your electronic equipment.
Types of Protective Foam Materials
Now that you understand the basics of electronics packaging, let's examine the main types of protective foam materials available for your needs. You'll find four primary options: Polyethylene (PE), Polyurethane (PU), Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), and Anti-Static/Conductive foams, each serving specific protection requirements.
| Foam Type | Best Used For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| PE Foam | Heavy electronics, computers | Durable, moisture-resistant, custom-formable |
| PU Foam | Delicate components, circuits | Lightweight, anti-static variants, void-filling |
| EPS Foam | Appliances, medical equipment | Cost-effective, rigid support, thermal insulation |
PE foam's closed-cell structure makes it ideal for moisture-sensitive items, while PU foam's flexibility works well for fragile components. If you're working with static-sensitive devices, you'll need to take into account anti-static foam variants that meet EIA-541 standards. While EPS foam offers cost-effective protection, it is crucial to be aware of its static electricity concerns. For maximum protection of sensitive electronics, you'll find anti-static and conductive foams particularly valuable, as they create Faraday cage effects and prevent electrostatic discharge damage. These specialized materials provide superior customization options through precise cutting and shaping to ensure devices remain firmly in place during transit.
Key Properties of ESD Foam

Every ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) foam possesses distinct electrical, physical, and chemical properties that make it essential for electronics protection. You'll find these foams are made from various materials like PE, EVA, EPE, and PU, each incorporating special additives such as carbon particles to enhance their static-dissipative capabilities.
When you're selecting ESD foam, you'll need to take into account its surface resistance, which typically ranges from 10^3 to 10^9 ohms. The foam's ability to dissipate static charges safely protects your sensitive electronic components from damage. Most ESD foam products are manufactured to meet IEC61340-5-1 standards for reliable protection.
While some ESD foams offer permanent anti-static properties, others, like PU foam, maintain effectiveness for about six months.
You'll notice ESD foams come in either black or pink colors and feature different densities. PE foam, for instance, offers densities of 45kg/m^3 or 67kg/m^3.
The cell structure varies too – you can choose between open-cell PU foam or closed-cell PE foam, depending on your needs. These foams are highly customizable and can be fabricated into specific shapes and sizes to match your packaging requirements while providing both static and physical protection during transport and storage.
Electronics Industry Foam Applications
When you're working with sensitive electronics, you'll need specialized foam solutions for precision equipment storage, including anti-static foam inserts for testing equipment and custom-cut compartments for calibration tools.
You can maximize shipping protection by combining PE foam for impact resistance with conductive foams for EMI shielding, ensuring your electronic components arrive safely. Carbon-based materials make these protective foams significantly lighter than metal alternatives while maintaining excellent conductivity.
During assembly processes, you'll find PE and PU foam workstation organizers invaluable for keeping components organized while protecting them from physical damage and electrostatic discharge.
Precision Equipment Storage Solutions
Modern electronics manufacturing demands precision equipment storage solutions that protect valuable devices throughout their lifecycle. To meet these demands, you'll find custom foam solutions designed specifically for storing and transporting sensitive electronic equipment.
When you're working with precision devices, you'll need tailored foam inserts that provide a snug, secure fit for your equipment. These custom-cut foam solutions distribute pressure evenly around your devices, preventing damage during storage and transport.
The foam-lined boxes and cases incorporate specialized padding layers that absorb vibrations and minimize impact damage, ensuring your equipment stays protected. Storage with proper foam protection helps maintain cleanroom conditions by preventing dust and particle accumulation.
For ideal protection against electrical damage, you'll want to use anti-static foam solutions. These specialized materials minimize the risk of electrostatic discharge, which can severely damage sensitive electronic components.
The foam's protective properties work in conjunction with your existing ESD protection systems to create a thorough safeguard for your valuable equipment.
Shipping Protection Best Practices
Building on proper storage solutions, shipping electronics requires carefully selected protective foam materials to guarantee safe delivery. You'll need to match the foam type to your specific electronic components, considering factors like size, weight, and static sensitivity. For maximum security during transit, use high-quality packing tape to thoroughly seal all foam packaging.
| Protection Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Static Foam | Circuit Boards, Chips | Prevents ESD, Available in PE/PU |
| Closed-Cell Foam | Computers, Monitors | Rigid, Vibration Resistant |
| Conductive Foam | Sensitive Components | EMF Blocking, Static Protection |
For maximum protection, you'll want to guarantee your packaging meets EIA-541 standards when shipping static-sensitive items. Choose polyethylene foam for heavier electronics like monitors and computers, while polyurethane foam works better for delicate components. Don't forget to include moisture barriers and maintain humidity levels between 40% and 80% during transit.
When packaging valuable electronics, wrap them in non-abrasive foam to prevent surface scratches. You should also consider using static shielding bags as an additional protective layer. For maximum protection, combine different foam types – for example, using conductive foam for inner packaging and closed-cell foam for outer shock absorption.
Component Assembly Foam Uses
The versatility of foam in electronic component assembly extends far beyond basic protection. You'll find foam materials performing critical functions in thermal management, moisture resistance, and shock absorption while providing essential static protection for sensitive components.
When you're assembling electronic devices, you can customize these materials to fit any configuration, ensuring maximum stability and protection. The foam materials meet strict industry standards for quality and safety, similar to those applied in automotive and aerospace sectors.
Different foam types serve specific purposes in your assembly process. You'll want to use polyethylene foam when you need durability for heavy electronics, while polyurethane foam works best for delicate components requiring gentle cushioning. For static-sensitive parts, you should opt for anti-static variants available in both PE and PU forms.
You can leverage foam's properties in various electronic applications, from improving energy efficiency through thermal management to creating smart materials for sensing and monitoring. It's particularly useful in printed circuit board assembly, where foam hybrid via processes offer mechanical support and physical separation.
When you implement foam solutions in your component assembly, you're not just protecting your electronics – you're enhancing their performance, ensuring cost-effectiveness, and maintaining design flexibility throughout the manufacturing process.
Selecting the Right Foam Protection
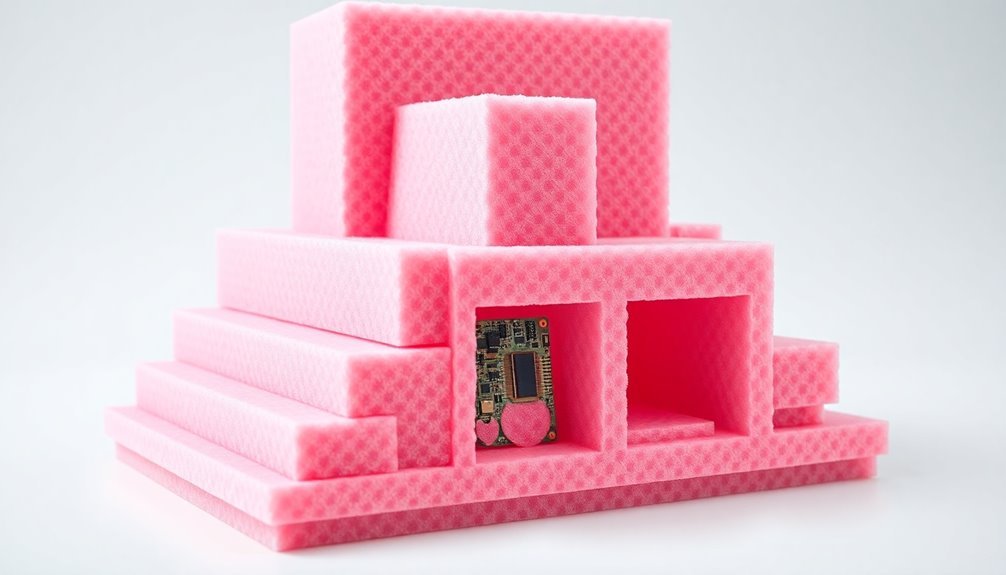
When you're choosing protective foam for electronics packaging, you'll need to match key properties like density, shock absorption, and cell structure to your specific product requirements.
You should weigh the initial cost against the foam's expected lifespan, as higher-quality materials often provide better long-term value despite higher upfront expenses.
If you're packaging static-sensitive components, you'll want to prioritize anti-static foam varieties over standard options, even though they typically cost more.
Properties Vs Product Type
Selecting appropriate protective foam requires careful matching of material properties to specific electronic product requirements.
You'll need to take into account both the size and sensitivity of your electronic items when choosing between foam types. For smaller, delicate components, polyurethane foam offers the lightweight, soft protection you're looking for, while cross-linked polyethylene works better for heavier, bulkier equipment.
The level of static protection your product needs will determine whether you should use conductive, anti-static, or static dissipative foam. If you're packaging components sensitive to electromagnetic fields, you'll want conductive foam that creates a Faraday cage.
For items that need protection from static buildup, anti-static foam with a surface resistance of 10^6-10^9 ohms is ideal. When sudden discharge is a concern, static dissipative foam provides controlled charge release.
You'll also need to decide between open-cell and closed-cell structures based on shock absorption requirements. Remember to verify that your chosen foam meets EIA-541 standards and has the appropriate non-abrasive properties for your specific electronic components.
For consistent protection, ETHAFOAM products with built-in anti-static additives offer reliable performance across various applications.
Material Cost and Lifespan
Many cost-conscious manufacturers find polyethylene foam to be their go-to choice, offering superior moisture resistance and durability at just $0.01 to $0.10 per sheet. You'll find even greater savings through bulk purchase discounts, making it a cost-effective solution for large-scale electronics packaging needs.
When you're selecting foam materials, consider their lifespan and reusability. High-density closed-cell polyethylene foam delivers exceptional resistance to vibration and compression, allowing for multiple uses.
While expanded polystyrene (EPS) provides an economical option for less sensitive components, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) offers premium protection for delicate electronics at a higher price point.
To maximize your investment, you'll want to match the foam type to your specific requirements. If you're packaging heavier electronics, opt for denser polyethylene foam that guarantees stability and protection.
For items requiring EMI shielding or anti-static properties, you'll need specialized foam sheets that may cost more but provide essential protection.
Remember that recyclable polyethylene foam offers an environmentally conscious choice, as you can send it to recycling centers after its useful life ends.
Anti-Static Vs Standard
The critical difference between anti-static and standard foam lies in their ability to protect against electrostatic discharge. While standard foam offers physical protection, anti-static foam provides both physical and electrostatic safeguards through its specialized chemical treatment. You'll find that anti-static foam's surface resistance of 10^9 – 10^12 ohms effectively dissipates static charges that could otherwise damage sensitive electronics.
| Feature | Anti-Static Foam | Standard Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Static Protection | Yes – dissipates charges | No protection |
| Cost | Higher due to treatment | More economical |
| Applications | Electronics, circuits, chips | General packaging |
When you're packaging electronic components, selecting the right foam type is vital. Anti-static foam, typically pink in color, comes in various forms like sheets, boxes, and custom-cut inserts. While it's more expensive than standard foam, it's essential for protecting static-sensitive devices during shipping and storage. You'll need to take into account that anti-static foam isn't reusable, but its ability to prevent damage and reduce product returns makes it a cost-effective choice for electronics packaging. The combination of impact absorption and static dissipation guarantees your sensitive components arrive safely at their destination.
Foam Packaging Benefits and Impact
Modern foam packaging delivers thorough protection for electronics through its versatile cushioning properties and environmental benefits. You'll find that foam materials excel at absorbing shocks, dampening vibrations, and protecting your delicate electronic items from impacts during shipping and handling.
When you're considering foam packaging options, you'll discover various types designed for specific needs. Polyethylene foam offers durability for heavier electronics, while polyurethane foam provides lightweight protection with customizable densities. For static-sensitive components, you'll want to use anti-static foam variants that prevent harmful electrostatic discharge.
You're making an environmentally conscious choice when using recyclable foam packaging. It contributes to lower carbon emissions during production and supports a circular supply chain through reuse and reprocessing.
The minimal VOC emissions during manufacturing also help maintain better air quality.
From a practical standpoint, you'll appreciate foam packaging's cost-effectiveness. Its lightweight nature reduces shipping expenses and fuel consumption.
You can maximize efficiency with custom foam inserts that create precise fits for your electronic components, ensuring ideal protection while minimizing wasted space in your packaging solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Protective Foam Packaging Typically Last Before Needing Replacement?
You'll need to replace standard pink ESD foam regularly as it degrades unpredictably. However, high-quality antistatic foams can last over three years if you're storing them in controlled temperature and humidity conditions.
Can Protective Foam Be Safely Cleaned Without Damaging Its Anti-Static Properties?
You can clean protective foam using gentle, non-abrasive methods like air blowing or mechanical removal. Avoid solvents and detergents that'll damage anti-static properties. Always test conductivity after cleaning to verify effectiveness.
What Temperature Ranges Can Different Types of Protective Foam Withstand?
You'll find that Neoprene-based and EPDM/CR/SBR blend foams can withstand temperatures from -65°F to 250°F. While EPP and EPE foams' specific ranges aren't listed, they're engineered for general protective packaging applications.
Is It Possible to Repair Damaged Foam Inserts for Electronics Packaging?
Yes, you can repair damaged foam inserts using Plasti Dip and shoe glue. You'll need to reattach loose pieces first, then apply heavy coats of Plasti Dip while wearing a mask for safety.
How Much Weight Can Different Densities of Protective Foam Safely Support?
You'll find that foam density directly affects weight capacity. Standard PE foam (4-6 lbs/ft³) can support 2-4 lbs/in², while high-density PU foam (6+ lbs/ft³) safely handles up to 8 lbs/in².
In Summary
You'll find protective foam packaging essential for safeguarding your valuable electronics during storage and transport. By choosing the right type of foam with proper ESD protection, density, and cushioning properties, you're ensuring your devices stay secure from physical damage and static electricity. Remember to take into account your specific needs, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness when selecting foam packaging solutions for your electronics.




Leave a Reply