Electronic components need static-free shipping bags because they're extremely vulnerable to static electricity damage. When you handle or ship electronics, even a tiny static discharge of 100 volts can permanently destroy sensitive semiconductors and circuits that operate on much lower voltages. Static buildup happens easily during shipping through friction, vibration, and dry conditions below 40% humidity. Anti-static bags protect your components by creating a protective barrier that safely dissipates static charges and prevents direct electrostatic discharge. They also shield against moisture and environmental factors. Understanding the full scope of static protection can save you significant costs from damaged electronics.
Understanding Electronic Component Sensitivity
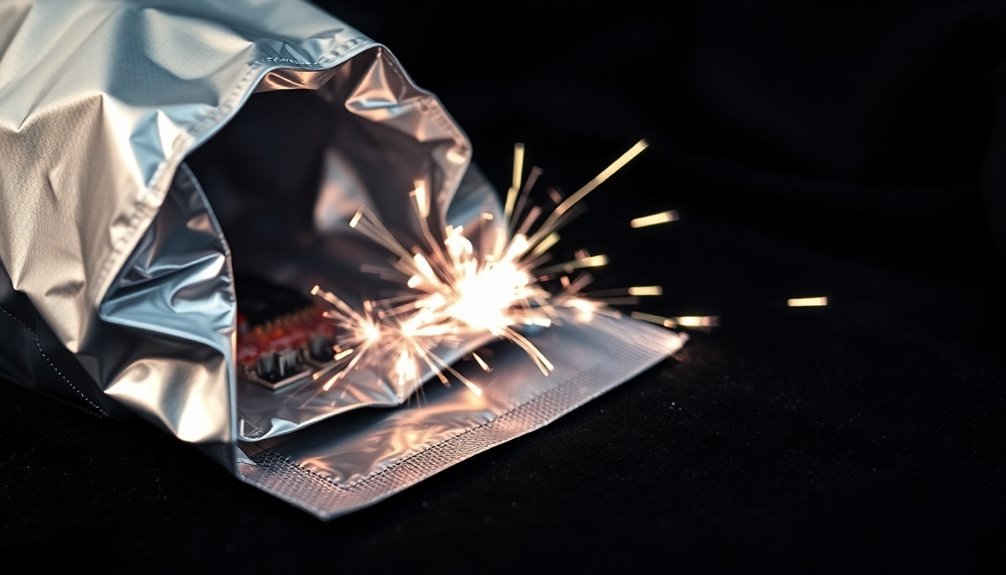
The proper handling of electronic components requires a deep understanding of their sensitivity to electrostatic discharge (ESD). When you're working with electronic components, you'll find that many devices are highly susceptible to static damage.
Thin and thick film resistors can experience immediate failure or degraded performance when exposed to static electricity, while electrolytic and ceramic capacitors become more vulnerable as their applied voltage increases. Many sensitive components can be damaged by static charges below 100V.
MOSFETs are particularly delicate, as they can suffer from multiple types of damage, including insulation breakdown and thermal overstress. You'll need to pay special attention to these components, as they're prone to metallization failure and material migration when exposed to static charges.
Electronic devices are typically classified by their withstand voltage, and their susceptibility depends on both energy levels and peak current exposure. You'll notice various failure modes in sensitive components, from contact damage to burnouts.
In integrated circuits, ESD can create holes in chips and increase heat generation. That's why it's vital to identify the most ESD-susceptible items in your electronic assembly and safeguard them properly during handling and shipping.
The Static Electricity Threat
Understanding component sensitivity is only part of the battle – you'll need to know exactly what you're protecting against. Static electricity builds up when objects contact and separate from each other, transferring electrons and creating charge differences. In dry conditions, especially below 40% humidity, this buildup becomes more severe and dangerous.
Anti-static bags made from 100% virgin polyethylene are essential for preventing static buildup during transportation. You'll find static electricity particularly threatening during shipping, where constant vibration causes materials to rub against each other through tribocharging. When these charges finally discharge through electrostatic discharge (ESD), they can devastate your electronic components. Even a single shock can fry motherboards, damage MOSFET transistors, and destroy sensitive CMOS devices.
Modern electronics face greater risks than ever because they're built with increasingly smaller components and thinner protective layers. The threat doesn't end with shipping – static electricity can remain built up in products and discharge later during unloading or while sitting on shelves.
Through electrostatic induction, charged items can even affect nearby conductive materials, creating a chain reaction of potential damage. In worst-case scenarios, high levels of static electricity can ignite flammable materials, posing fire risks beyond just component damage.
How Anti-Static Bags Work

Inside modern anti-static bags, three specialized layers work together to shield your electronics from dangerous static electricity. The inner layer, made of dissipative polyethylene plastic, provides a soft cushion for your components while preventing static buildup.
In the middle, an aluminum layer acts as a conductor, safely grounding any static discharges. The outer polyester layer, coated with dissipative material, adds another barrier against electrostatic charges. These bags are specifically designed to meet IEC protocols for safe electronic component storage.
When you handle electronic components, these bags create what's known as a Faraday cage effect, completely protecting your devices from direct electrostatic discharge. The multi-layer design doesn't just block static—it actively dissipates it. The conductive layer grounds the charges, while the dissipative layers slow down their flow, ensuring your electronics remain safe during shipping and handling.
You'll find different types of anti-static bags for various needs, including dissipative bags, static-shielding bags, and metallized options. Remember, though, that these bags only work effectively when they're properly sealed and handled. You should always open them at static-free workstations and minimize handling to maintain maximum protection for your sensitive electronic components.
Types of Protective Packaging
When choosing protective packaging for your electronics, you'll find various anti-static solutions including EPS foam, PE foam, and specialized packing peanuts that prevent static discharge.
Static shield bags with moisture-proof properties offer an additional layer of protection by combining conductivity control with water resistance.
You can enhance your packaging strategy by pairing these materials strategically—for example, using anti-static bubble wrap inside a static shield bag for sensitive components. Primary layer packaging helps protect electronics while displaying essential product and safety information.
Anti-Static Bag Varieties
Dissipative bags are your simplest option, made from polyethylene terephthalate with special additives that prevent static buildup. While they're available in various colors and work well for basic storage, they won't protect your components from external static discharge.
For better protection, you'll want to think about conductive anti-static bags. These bags feature multiple layers, including a conductive material like carbon or aluminum, plus a static dissipative inner layer. Static electricity can remain until product unloading, making proper storage essential throughout the shipping process.
They're particularly useful in oxygen-rich environments where sparks could be dangerous, as they effectively conduct static charges away from sensitive parts.
The highest level of protection comes from metallized anti-static bags, which create a Faraday cage effect using an aluminum layer. While these bags offer superior shielding for your most sensitive components, they're more fragile and have a limited shelf life.
You'll need to handle them carefully to maintain their protective properties.
Each type can be customized to fit specific products, whether you're shipping hard drives, motherboards, or electronic chips.
Static Shield Solutions
Building upon these basic bag varieties, static shield solutions offer multi-layered protection through specialized construction. You'll find these bags are engineered with three distinct layers: an inner dissipative polyethylene layer that prevents static buildup, a middle metal or carbon layer that grounds charges, and an outer polyester layer with a static-dissipative coating that disperses external charges. These bags can be designed with heat sealable edges for maximum protection during shipping.
You can choose between two main types of static shield bags: metal-in and metal-out configurations. Metal-in bags are more cost-effective and durable, with their protective metal layer buried within the structure.
If you need superior protection, metal-out bags position the conductive layer closer to the surface for faster static dissipation, though they're typically more expensive.
When you're shipping sensitive electronics like circuit boards, processors, or memory cards, these bags create a Faraday cage effect that shields your components from electromagnetic radiation and static discharge. They're particularly vital in supply chain operations where your products might encounter various static risks during transit and storage.
Each layer works together to guarantee your electronic components arrive safely, meeting industry standards for ESD protection.
Moisture-Proof Package Options
The moisture barrier bags you'll need for electronics shipping combine multiple protective features into a single 3.6 mil thick package. These specialized bags incorporate high-performance barrier materials that provide superior ESD and EMI shielding while meeting EIA Std. 583, Class 1 requirements. The bags provide excellent protection with a proven tensile strength of 7800 PSI.
You'll find they're completely waterproof, vapor-proof, and greaseproof, offering essential protection against moisture and humidity.
When you're choosing moisture-proof packaging options, you'll want to think about the aluminum film layer that controls the Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR). The bags' polyester (PET) construction delivers exceptional puncture resistance, while their heat-sealable design allows for vacuum packaging.
You can also opt for moisture barrier films in ESD roll format if you need custom sizes for specific applications.
For additional protection, you might think about combining moisture barrier bags with protective foams. However, you'll need to be cautious with EPS and PE foams, as they can generate static electricity.
While these foams offer excellent shock absorption and thermal insulation, they're particularly useful when you're shipping electronics through challenging environments, such as maritime routes where humidity poses a significant risk.
Cost Benefits of Static Prevention

Static damage costs the electronics industry a staggering $5 billion annually, making prevention a critical financial consideration. When you consider that up to 33% of electrical product losses stem from static and that it causes 25% of electronics part failures, investing in proper protection becomes essential for your bottom line.
Anti-static packaging offers significant cost benefits across multiple areas. By preventing static buildup and discharge, you'll reduce damaged goods, which directly cuts your repair and replacement expenses.
You'll also minimize returns and reverse logistics costs, saving on handling time and preserving your company's reputation with customers.
While anti-static bags may represent an upfront investment, they're typically less expensive than static shielding alternatives. When you weigh the cost of packaging against potential damage to electronics, the long-term savings become clear.
You'll benefit from improved operational efficiency, reduced handling of returned goods, and increased customer satisfaction due to fewer damaged items. By choosing right-sized anti-static packaging, you can optimize your packing costs while maintaining effective protection.
The result is a more streamlined operation with lower overall expenses and higher customer retention.
Environmental Impact on Electronics
Dark clouds of pollution hover over electronics manufacturing, contributing a staggering 6.1 million metric tons of CO2 emissions annually. This environmental impact extends far beyond air pollution, as improper disposal and handling of electronic devices create lasting damage to our ecosystems through soil and water contamination.
When you don't protect your electronics with static-free shipping bags, you're contributing to a larger environmental problem. Static damage leads to premature device failure, which adds to the growing e-waste crisis.
Here's how static damage and improper handling affect our environment:
- Damaged devices end up in landfills, where toxic chemicals leach into groundwater
- E-waste incineration releases harmful pollutants into the air
- Replacement of damaged electronics increases manufacturing emissions
- Soil contamination occurs when e-waste isn't properly managed
You can help reduce this environmental impact by using anti-static bags for shipping and storage. These protective measures don't just save your devices – they're part of a larger solution to minimize e-waste. When you prevent static damage, you're extending the life of electronic components and reducing the need for replacements, which ultimately helps decrease manufacturing emissions and environmental contamination.
Industry Standards for Static Protection

You'll need to comply with key standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340-5-1 when selecting static-free shipping bags for your electronic components.
Your packaging must pass rigorous testing and certification processes to guarantee it meets the required static discharge protection levels.
These regulations require specific protective qualities in your shipping materials, including proper static shielding and controlled dissipative properties that align with EPA guidelines.
Key Compliance Requirements
When protecting sensitive electronic components, compliance with industry standards is crucial for effective static control. You'll need to follow key requirements from standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20, IEC 61340-5-1, and JEDEC JESD625B to guarantee your electronic components remain safe during shipping and handling.
To meet these critical compliance requirements, you must focus on:
- Personnel grounding and training – Your staff needs proper training on ESD control practices and must use appropriate grounding equipment when handling sensitive components.
- Environmental controls – You'll need to maintain suitable humidity levels and implement ionization systems to neutralize charges on non-conductive surfaces.
- Proper packaging materials – Your shipping materials must include static shielding bags and anti-static materials that meet specific standards for different sensitivity levels.
- Regular verification – You must conduct ongoing compliance checks of your personnel, equipment, and procedures to maintain protection standards.
These requirements aren't just bureaucratic hurdles – they're essential safeguards that protect your electronic components from damage. By implementing these measures within your Electrostatic Protected Areas (EPAs), you'll substantially reduce the risk of ESD-related failures and guarantee your products reach customers in prime condition.
Testing and Certification Standards
Since protecting electronic components requires strict adherence to industry standards, it's critical to understand the three major testing and certification frameworks: ANSI/ESD S20.20, IEC 61340-5-1, and JEDEC JESD625B.
ANSI/ESD S20.20, which has replaced MIL-STD-1686, focuses on three core principles: grounding conductors, using ionization systems, and enclosing sensitive items in protective materials.
You'll need to comply with both administrative requirements, like training plans, and technical specifications for grounding and handling.
The European standard IEC 61340-5-1 provides detailed guidelines for creating electrostatic protective areas (EPAs).
You'll find extensive requirements for workstations, flooring, and environmental controls, including humidity management and ionization systems.
For semiconductor manufacturing, JEDEC JESD625B sets specific requirements to protect sensitive devices during production.
Testing methods include ANSI/ESD STM11.31 for evaluating packaging discharge shielding, and the Human Body Model (HBM) and Charged Device Model (CDM) for device robustness.
Your static-free shipping bags must pass these tests, demonstrating their ability to shield against static discharge through metalized layers and dissipative coatings.
Protective Packaging Regulations
In accordance with strict industry guidelines, protective packaging regulations establish essential requirements for safeguarding electronic components from electrostatic discharge (ESD). You'll need to guarantee your packaging meets ANSI/ESD S541 and ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards, which specify the necessary properties for static-dissipative and antistatic materials.
To comply with these regulations, your packaging must meet specific criteria:
- All materials must demonstrate verifiable ESD protection properties, including proper conductivity and static dissipation levels.
- Packaging designs must effectively shield electronics from electrostatic fields while preventing triboelectric charging.
- Materials must undergo rigorous testing to validate their protective capabilities and meet standardized performance requirements.
- Your company's internal specifications must meet or exceed industry standards for ESD protection.
You'll need to implement continuous monitoring and improvement processes to maintain compliance. This includes regular audits, staff training on proper handling procedures, and staying current with evolving industry standards.
Compliance isn't optional – it's a legal requirement for companies handling electronic devices, and it's essential for protecting both your products and your liability exposure.
Best Storage and Handling Practices
Through proper storage and handling practices, you can substantially reduce the risk of electrostatic discharge damaging your sensitive electronic components. Always use appropriate anti-static bags for storing and shipping items like hard drives, CPUs, GPUs, RAM cards, and motherboards.
You'll want to handle these components in designated ESD Protected Areas (EPAs) to prevent external static charges from compromising their integrity.
When you're working with electronic components, make sure you're using grounded equipment to dissipate any static charges effectively. Don't remove items from their anti-static packaging until you're ready to install them, and store unused components in their original bags or new anti-static containers.
You'll find different types of bags available, including metal-in film, metal-out film, and static dissipative options – choose the one that best suits your specific component's needs.
If you're managing a team, guarantee they're properly trained in ESD handling procedures. This includes understanding how to use anti-static bags correctly, recognizing when packaging needs replacement, and following proper grounding protocols.
Remember that proper storage extends beyond ESD protection – these bags also guard against moisture and dust, which can cause corrosion and short circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Anti-Static Bags Be Reused Multiple Times for Shipping Electronics?
You can reuse anti-static bags several times, but you'll need to check them for damage before each use. Don't reuse bags with tears or excessive wrinkles, as they won't protect your electronics effectively.
How Long Does the Anti-Static Protection Last in Storage Bags?
You'll find that anti-static bags maintain protection for 1-2 years under proper conditions. However, if you're using static shielding bags, they'll last longer – up to 5 years with minimal handling and controlled storage.
Are Household Aluminum Foil Bags Suitable Alternatives for Anti-Static Bags?
No, you shouldn't use aluminum foil bags as alternatives. They're too conductive, can pierce easily, and risk damaging your electronics through rapid discharge. Proper anti-static bags are specifically designed for safe component storage.
What Temperature Ranges Can Anti-Static Shipping Bags Safely Withstand?
You'll need to keep your anti-static bags between 21°C and 23°C for storage, though they can withstand up to 150°C briefly. Don't expose them to temperatures outside these ranges to maintain effectiveness.
Should Anti-Static Bags Be Used for Transporting Already-Assembled Consumer Electronics?
Yes, you should use anti-static bags for assembled electronics. They'll protect your devices from static damage during shipping and handling, even after assembly. This is especially important for items containing sensitive circuit boards.
In Summary
Static-free shipping bags are essential to protect your valuable electronics from damaging electrostatic discharge. You'll want to keep using these specialized bags for storage and transport, as they prevent costly component failures and extend your devices' lifespan. By following proper anti-static handling procedures and maintaining appropriate packaging, you're safeguarding your electronic investments against invisible but destructive static electricity threats.





Leave a Reply