For ideal PCB protection, you'll need a multi-layered approach using industry-standard anti-static materials. Start with static shielding bags that create a Faraday Cage effect, then add ESD foam inserts custom-cut to your PCB dimensions. Consider metallized packaging for additional EMI shielding and thermal management, especially for sensitive components. Pink polyethylene laminates work well for non-sensitive parts, while ESD bubble wrap bags offer both static and physical protection during shipping. Proper handling procedures and regular staff training are essential for maintaining ESD protection. Understanding the complete spectrum of available solutions will help you make the most cost-effective choices for your specific needs.
Understanding PCB Static Sensitivity
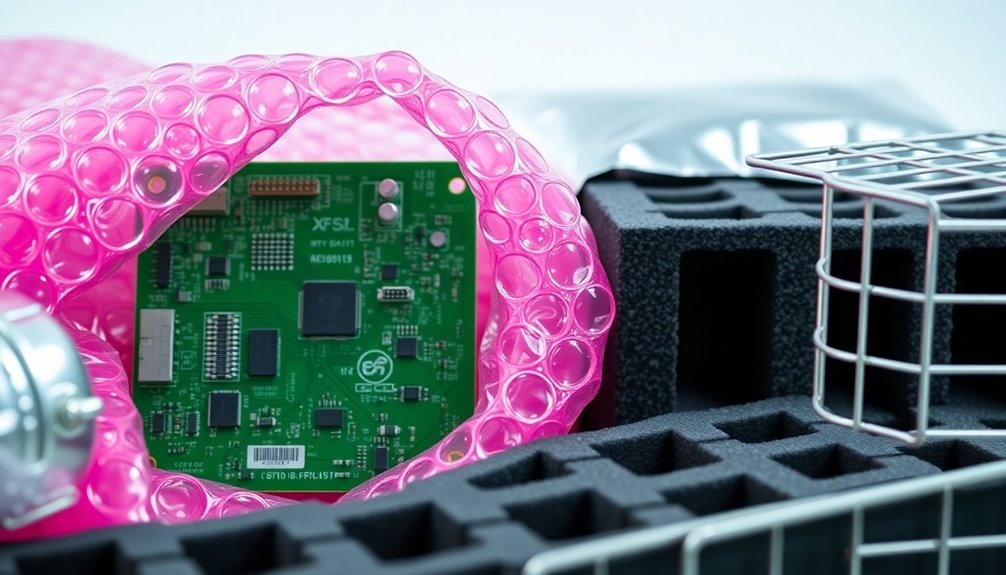
Nearly all modern PCBs are highly sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can occur when static electricity discharges into circuit components.
You'll generate static electricity through triboelectric charging – when materials exchange electrons by touching and separating. Your body alone can store between 500-2500 volts of static electricity, which you won't feel but can severely damage electronic components. The discharge process resembles miniature lightning bolts, rapidly flowing through paths of least resistance.
The risks don't stop there. When you're working with PCBs, everyday activities like walking on carpet, using plastic materials, or operating fans near your workspace can generate harmful static charges. Air movement and airflow can create charge accumulation even without direct contact with components.
These charges can cause two types of damage: catastrophic and latent. While catastrophic damage immediately destroys components and is detectable during testing, latent damage is more insidious. It won't cause immediate failure but gradually degrades your PCB's performance and reduces its lifespan.
You'll find this particularly concerning because ESD can char the insulation layer between PCB tracks, leading to partial degradation.
In the electronics industry, these issues contribute to losses of up to 33%, making ESD one of the most expensive forms of damage in PCB manufacturing and handling.
Types of Anti-Static PCB Bags
In the world of PCB protection, you'll encounter four main types of anti-static bags, each designed for specific applications.
Anti-static bags, made of pink polyethylene laminates, work well for non-sensitive parts within ESD-protected areas but won't shield against external static charges. These bags are designed to have a maximum resistance range of 1005 – 1015 ohms/sq. You'll want to use these primarily for basic components like nuts and bolts.
When you need thorough protection for your sensitive PCBs, static shielding bags are your best choice. These metallized bags create a Faraday Cage effect, protecting your components from both internal static build-up and external discharges. Selecting quality-certified bags with proper material traceability ensures maximum protection for your components.
For enhanced protection with UV resistance, consider conductive bags, which offer quick static discharge through their conductive copolymer construction.
If you're shipping delicate PCBs that need both static and physical protection, ESD bubble wrap bags provide the ultimate solution. They combine static dissipative properties with cushioning protection against impacts and vibrations.
You'll find these particularly useful when transporting sensitive electronics through challenging environments where both static discharge and physical damage are concerns.
Choose your packaging based on your PCB's sensitivity level and the environmental conditions it'll face during storage or transport.
ESD Foam Protection Solutions
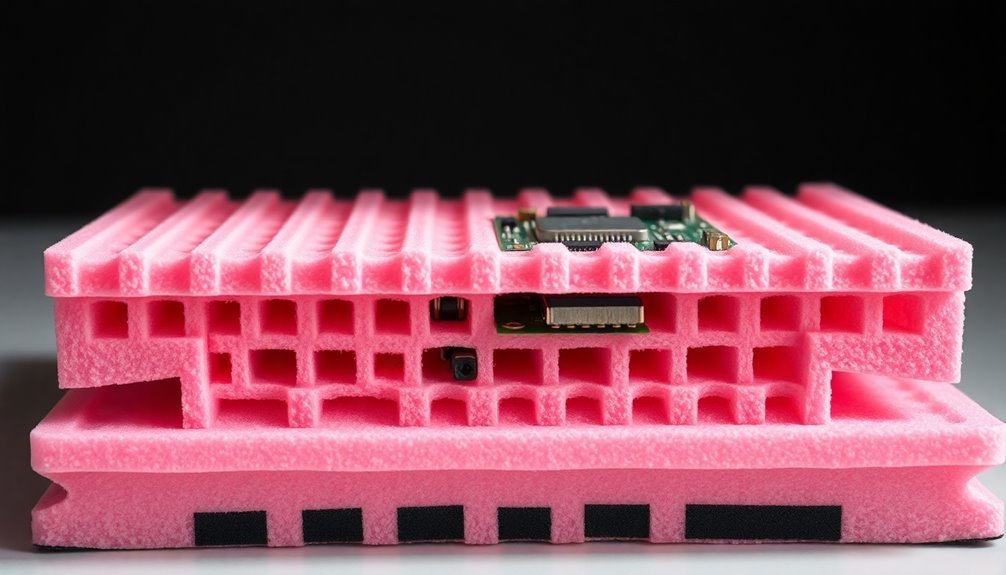
Beyond anti-static bags, ESD foam protection offers another powerful layer of defense for your sensitive PCBs. You'll find several types of ESD foam materials, each designed for specific protection needs. Polyethylene foam provides exceptional durability and vibration dampening, while polyurethane foam excels in shock absorption and quick shape recovery. All materials undergo cushioning requirement calculations to ensure optimal protection levels. Our high-impact polypropylene materials deliver superior moisture resistance for sensitive electronics.
| Material Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Tear-resistant, supports heavy items |
| Polyurethane | Quick recovery, easily customizable |
| EPE | Lightweight, moisture-proof |
| Convoluted | Custom-fit, ideal shock protection |
When you're packaging PCBs, you can choose from pink anti-static or black conductive options, depending on your specific requirements. These foams effectively protect against static discharge, physical damage, and environmental factors during shipping and storage. You'll find they're particularly valuable for long-term storage solutions, as they maintain their anti-static properties over extended periods.
For maximum protection, you can opt for custom-cut foam inserts that perfectly match your PCB dimensions. These tailored solutions guarantee your boards remain secure and protected against impacts, vibrations, and static charges throughout handling and transportation processes.
Metallized Packaging for PCBs
You'll find that metallized packaging offers multiple protective layers, combining static discharge prevention with EMI shielding and thermal management capabilities.
Your PCB components receive thorough protection through the package's conductive metal layers, which efficiently channel static electricity away while maintaining a controlled environment. The metal film dissipation feature ensures consistent static protection throughout the shipping process. Similar to how aluminum core substrates provide superior heat dissipation in MCPCBs, metallized packaging effectively manages thermal conditions during transport.
The initial investment in metallized packaging pays off through reduced component damage, extended product life, and decreased need for additional protective measures like separate heat sinks or EMI shields.
Multi-Layer Protection Features
Modern PCB protection relies on sophisticated multi-layer packaging systems that combine metallized films with various protective elements.
You'll find these systems incorporate multiple protective layers, each serving a specific purpose in safeguarding your PCBs during storage and transport.
The protective layers start with cushioning materials like bubble wrap and foam sheets that absorb impacts and vibrations.
You'll need to add immobilization elements, such as plastic trays and specialty tapes, to prevent your PCBs from shifting during handling.
The critical metallized film layer provides essential static dissipation and barrier protection against moisture and oxygen.
When you're implementing multi-layer protection, you can choose from several metallized film grades including F-UHB-M, F-LLP-M, and F-HSP-M, ranging from 12-23 μm in thickness.
These films work with other protective elements to create a thorough shield. The high bond strength of metallized films, measuring at least 600 gm/25mm, ensures reliable protection throughout the packaging lifecycle.
Following proper IPC standards ensures consistent quality and reliability in PCB packaging processes.
You'll want to confirm your outer container is rigid and properly labeled to maintain the integrity of all internal layers.
Static Discharge Prevention Methods
Building on the multi-layer protection concept, effective static discharge prevention requires specific metallized packaging materials and handling protocols.
You'll need to use metallized bags with aluminum or carbon coatings as your primary defense, as they create a Faraday cage effect that shields your PCBs from external static charges.
Don't rely solely on pink or blue anti-static bags, as they only protect against friction-induced charges. Instead, combine static shielding bags with carbon-loaded materials like Blackstat for thorough protection.
You'll want to ascertain your packaging system includes proper grounding measures – always use ESD straps when handling PCBs and maintain a static-free environment during packaging.
For maximum protection during shipping, you should use static shielding boxes made from carbon-loaded plastics alongside your metallized bags.
Remember to avoid standard bubble wrap and cling film, as they generate static electricity. Instead, opt for ESD-safe bubble wrap for physical protection, but always use it in conjunction with static shielding materials.
Don't forget to apply ESD warning stickers to alert handlers that the contents require special handling procedures.
Cost-Benefit Performance Analysis
When analyzing the cost-benefit ratio of metallized PCB packaging, the initial investment in premium materials delivers substantial long-term returns. While you'll face higher upfront costs for metallized materials, you'll see significant savings through reduced damage rates and fewer replacement requirements.
The enhanced protection against static discharge can lower your repair and rework expenses by up to 99%, making it a financially sound decision for your PCB manufacturing process.
Your investment in metallized packaging yields measurable benefits across multiple areas:
- Regulatory Compliance: You'll meet industry standards for static-sensitive components while ensuring adherence to aerospace and defense requirements, reducing potential liability costs.
- Performance Benefits: You'll achieve better thermal management with metal-core PCBs and improve overall manufacturing efficiency through reduced component failures.
- Long-term Savings: You'll minimize material waste from repairs, decrease shipping damage rates, and reduce the need for replacement components.
PCB Storage and Handling Requirements

Safe storage of PCBs requires strict adherence to regulated protocols and conditions. You'll need to implement specific storage measures when handling PCBs in concentrations of 50 mg/kg or more, particularly for quantities exceeding 100 L for liquids or 100 kg for solids.
| Storage Requirement | Specification |
|---|---|
| Physical Barriers | 1.83m high wire fence or enclosed structure |
| Surface Type | Non-absorbent (steel or concrete) |
| Containment Capacity | 125% for single container, 25% total volume for multiple |
| Security | Locked entrances, authorized access only |
Your storage facility must be positioned away from sensitive locations like drinking water treatment plants and childcare centers. You'll need to guarantee proper containment measures, including curbing that can hold either twice the volume of your largest container or 25% of total stored PCB liquid volume.
Monthly inspections are mandatory, and you must maintain detailed records of these checks. Don't exceed the maximum storage periods: one year for on-site and transfer facilities, two years for destruction facilities. You're required to keep fire suppression equipment and PCB cleanup materials readily available and in good condition. Any damage to storage infrastructure demands immediate repair and decontamination.
Industry Standards for ESD Protection
To protect your PCBs from electrostatic discharge, you'll need to follow established testing protocols outlined in ANSI/ESD S20.20 and ANSI/ESD S541 standards.
The IPC/JEDEC J-STD-001 and IPC-A-610 standards provide essential guidelines for handling and protecting electronic assemblies from ESD damage.
Military specifications MIL-STD-883 and MIL-PRF-81705 set stringent requirements for ESD protective materials and testing methods that you can apply to guarantee maximum protection for your sensitive components.
ESD Testing Protocols Required
Industry standards for ESD protection rely on rigorous testing protocols that manufacturers must follow up on to confirm product compliance and reliability.
You'll need to conduct both contact and air discharge tests using specialized ESD generators that simulate human body and machine model discharges. These tests must align with key standards like IEC 61000-4-2, which specifies test levels ranging from 2kV to 8kV for contact discharge and up to 15kV for air discharge.
To confirm your PCB packaging meets ESD protection requirements, you'll need to implement these critical testing procedures:
- Pre-compliance testing to identify potential vulnerabilities early in the development phase, saving time and resources before final certification.
- Annual verification of your ESD simulators' voltage and current waveforms using calibrated voltmeters or voltage dividers.
- Compliance testing according to specific industry standards that match your product's application (medical EN 60601-1-2, automotive ISO 10605, or aerospace RTCA DO-160).
Your testing protocols must include proper documentation of simulation results, assessment of product response to discharges, and verification that all protective measures meet the specified standards.
Remember to maintain your ESD testing equipment and keep detailed records of all test results for compliance purposes.
Essential IPC/JEDEC Standards
The extensive IPC/JEDEC standards form the backbone of modern ESD protection requirements for PCB manufacturing and handling.
You'll need to understand three key standards: J-STD-609A for component marking and labeling, J-STD-020E for moisture sensitivity classification, and J-STD-033D for handling moisture-sensitive devices.
To comply with these standards, you'll need to implement specific packaging solutions. You must use vacuum-sealed moisture barrier bags (MBB) for storing your PCBs, along with desiccant packs and humidity indicator cards to control and monitor moisture levels.
It's vital that you use proper anti-static packaging materials to protect against ESD damage.
You'll also need to guarantee your personnel are properly trained in ESD and moisture protection techniques. This includes following standardized handling procedures and maintaining detailed records of storage conditions.
Your compliance efforts should include continuous monitoring of packaging conditions and proper documentation of all handling processes.
Remember that these standards aren't just guidelines – they're critical requirements that help prevent costly component failures.
Military ESD Protection Specs
Several critical military specifications govern ESD protection standards, with MIL-STD-1686 serving as the Department of Defense's primary framework for ESD control programs.
When you're working with military contracts or defense sector projects, you'll need to guarantee your ESD protection measures align with these stringent requirements. MIL-STD-1686 covers electrical and electronic parts, assemblies, and equipment while mandating thorough ESD control program plans and handling procedures.
To effectively implement military ESD protection standards, you'll need to focus on these key elements:
- Establish documented ESD control programs that address both your internal operations and subcontractor controls, guaranteeing continuous protection throughout the supply chain.
- Classify all ESDS parts according to their sensitivity levels using Human Body Model (HBM), Machine Model (MM), and Charged Device Model (CDM) testing.
- Implement proper handling procedures and maintain regular training and audit programs to verify compliance.
While the DoD has adopted ANSI/ESD S20.20 as an alternative standard, MIL-STD-1686 remains relevant and covers devices from 0 to 15,999 volts HBM.
You'll need to tailor these requirements to your specific acquisition needs while maintaining strict compliance throughout your operation.
Cost-Effective Anti-Static Packaging Options

Through careful selection of cost-effective anti-static packaging materials, you can protect your PCBs while maintaining budget constraints. Corstat conductive corrugated materials offer an economical solution for short-term and one-way shipments, while conductive fluted plastic provides a more durable option for long-term shipping cycles.
You'll find significant cost savings by implementing reusable packaging systems and custom-designed die-cut foam inserts. These solutions not only protect your PCBs but also optimize shipping efficiency and reduce long-term expenses.
Consider using Evolon, which combines strength and softness in a compact fiber structure, making it ideal for delicate electronic components.
For maximum cost efficiency, you can combine different economical materials. Start with static shielding bags as your primary protection, then add cushioning using anti-static foam or bubble wrap.
Black conductive circuit board shipping boxes with pink anti-static foam offer a complete solution that's both protective and budget-friendly. When you're shipping in bulk, consider Protektive Pak products and conductive containers, which provide reliable protection while keeping costs manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Anti-Static Bags Be Reused, and How Many Times Safely?
You shouldn't reuse pink or blue anti-static bags due to their quick degradation. If you need to reuse ESD packaging, opt for permanent ESD bags instead, as they're specifically designed for multiple safe uses.
What Temperature Ranges Can Different Anti-Static Packaging Materials Withstand?
You'll find most standard anti-static bags work between -40°C to 80°C, but specialized materials can handle wider ranges. Basic EPE foam tops out at 70°C, while premium solutions can withstand up to 100°C.
How Long Does the Anti-Static Protection Last in Unused Packaging?
You can expect your unused anti-static packaging to last 12-24 months when properly stored. However, it's vital that you maintain ideal storage conditions and regularly inspect the materials to guarantee they're still effective.
Are There Specific Cleaning Procedures for Maintaining Anti-Static Packaging?
You'll need to clean anti-static packaging using soft, lint-free cloths and deionized water. Don't use harsh chemicals, and always wear anti-static gear while cleaning. Remember to store cleaned materials in static-free environments.
Can Regular Plastic Bags Be Converted Into Anti-Static Packaging?
You can't effectively convert regular plastic bags into anti-static packaging. The process would be impractical and costly, as these bags lack essential conductive properties. It's better to purchase purpose-made anti-static bags instead.
In Summary
Protecting your PCBs from static damage isn't optional – it's essential for maintaining product quality and reliability. You'll need to combine proper anti-static bags, ESD foam, and metallized packaging while following industry standards to guarantee complete protection. Don't compromise on ESD safety measures; instead, choose cost-effective solutions that meet your specific requirements. Remember, prevention is always cheaper than replacing damaged components.





Leave a Reply