Place your anti-static mats in key areas where you handle sensitive electronic components. You'll want them at workstations, assembly lines, and entrances between carpeted and non-carpeted areas. Position them directly on workbenches where employees handle electronics, and verify each mat has its own ground connection. Don't forget high-traffic areas where staff movement can generate static electricity. For maximum protection, install mats at storage areas and equipment testing stations. Proper placement combined with regular maintenance will substantially reduce the risk of static damage, but there's much more to take into account for complete ESD protection.
Understanding Anti Static Mat Basics
Three key components make up an anti-static mat's essential construction: a static dissipative top layer, a conductive middle layer, and an anti-skid bottom layer.
These mats are typically made from vinyl or rubber materials that can withstand chemicals, mechanical wear, and temperature extremes. The three-layer construction provides support and stress absorption through its inner foam layer. You'll notice they're usually black due to their carbon content, which makes them conductive.
When you're working with anti-static mats, you'll need to understand their core function: they dissipate static electricity from both people and objects by directing it to ground.
You can ground your mat by placing it on a conductive surface or connecting it to an electrical outlet using a grounding cable.
The mat's top surface provides static dissipative properties with resistance between 1 x 10^6 and 1 x 10^12 ohms, while the bottom surface offers conductivity with less than 1 x 10^6 ohms resistance.
To guarantee proper functionality, you'll need to test your mat's resistance using RTT (top-to-top) and RTG (top-to-ground) measurements.
These measurements must comply with ANSI/ESD S4.1 standards, making the mat an effective part of your complete ESD safety setup.
Critical Placement Locations
Strategic placement of anti-static mats is essential for effective ESD protection in your facility. You'll need to focus on two primary locations: entrance points and workstations. At entrances, these mats help dissipate static electricity from personnel before they interact with sensitive equipment, especially when moving between carpeted and non-carpeted areas. The proper placement helps create a safe working environment by preventing potential hazards.
| Location Type | Primary Purpose | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Entrances | Static Dissipation | Ground Connection |
| Workstations | Component Protection | Individual Grounding |
| Assembly Lines | Worker & Product Safety | Regular Testing |
| Storage Areas | Overall ESD Control | Maintenance Schedule |
For workstations, you'll want to place mats directly at individual work areas where employees handle sensitive electronics. Each mat requires its own ground connection – don't daisy-chain them together. In industrial settings like manufacturing floors and logistics warehouses, you'll need thorough coverage at assembly lines and handling areas.
Manufacturing Floor Best Practices
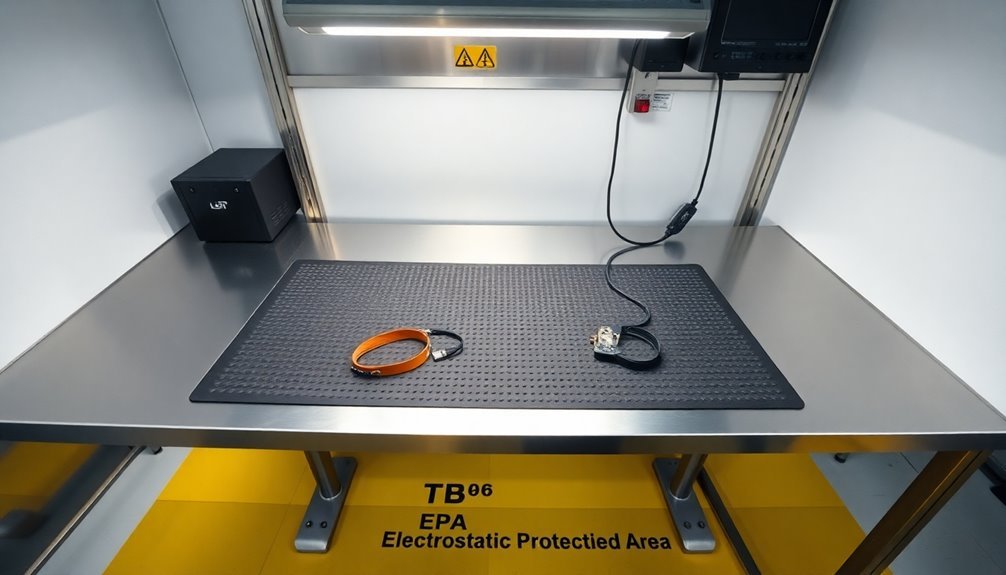

On manufacturing floors, proper anti-static mat implementation follows specific protocols to guarantee consistent ESD protection. You'll need to verify your mats are properly grounded and positioned to create an effective static-free environment for sensitive electronic components and assembly processes.
Using approved cleaning solutions and regular maintenance helps prevent surface resistance degradation that could compromise ESD protection.
For superior protection in your manufacturing facility, follow these essential practices:
- Lay all table mats completely flat with snaps facing the operator, and connect them to a common point ground cord using either the left or right snap – this creates a reliable path for static dissipation.
- Install floor mats in assembly areas and connect them to the building's ground point using the designated green wire, verifying they're not isolated by insulating materials like carpet.
- Test all newly installed workstations using a surface resistivity meter to verify proper grounding and compliance with ANSI/ESD S6.1 standards.
- Maintain regular testing schedules to check both top-to-top (RTT) and top-to-ground (RTG) resistance measurements, verifying continuous effectiveness of your static control system.
Remember to integrate your anti-static mats with other ESD control measures like heel grounders and wrist straps for thorough protection against static damage.
Electronics Lab Setup Requirements
Your electronics lab's workbench needs proper grounding through an ESD mat connected to a verified ground point.
With all essential equipment positioned within arm's reach, you'll want to place your bench power supply, multimeter, and soldering station on the right side of your workspace if you're right-handed (or left side if left-handed) for ideal access. Using precision hand tools in your setup ensures accurate and delicate component handling.
Position these tools close to AC power outlets while maintaining clear paths to your component storage and ensuring your hot glue gun stays away from sensitive electronic equipment.
Workbench Grounding Best Practices
Proper workbench grounding serves as the foundation for any electronics lab setup, protecting sensitive components from costly ESD damage.
You'll need to verify your workbench has a complete path-to-ground through conductive surfaces and properly installed ESD mats. It's crucial to connect these mats to electrical outlets using grounding cables and maintain them regularly to guarantee their effectiveness. Ensure your mats have a surface resistance between 10^4 and 10^6 ohms for optimal protection.
- Start by installing your ESD mat on a clean, flat surface – any bumps or debris underneath can compromise its functionality. Make sure you're using proper snaps and grounding cables to create a reliable connection to your electrical ground point.
- You'll need to ground all your equipment and tools properly, using only ESD-safe tools in your workspace. Position everything strategically to maintain continuous contact with grounded surfaces.
- Test your grounding system regularly to catch any potential issues early. Don't forget to check the conductivity between your mat and grounding point periodically.
- Watch out for common mistakes like using insulating materials without proper grounding measures or neglecting regular maintenance checks. Remember, even small oversights in your grounding setup can lead to significant damage to sensitive electronics.
Essential Equipment Placement Guidelines
Setting up an electronics lab requires careful attention to equipment placement, starting with the strategic positioning of ESD mats around your workspace.
You'll need to cover your entire work surface with ESD mats in areas where you handle static-sensitive components, verifying they're properly grounded to prevent electrostatic discharge.
Place your ESD mats on clean, flat surfaces, and position them near workbenches and assembly areas where you frequently handle electronic components. Using ESD-safe cleaners regularly will maintain optimal mat performance.
Make sure they're easily accessible to all personnel and consider your workspace's size and layout when selecting mat locations. Don't forget to position mats in high-traffic areas where staff movement could generate static electricity.
You'll want to install your ESD mats in conjunction with other anti-static equipment, like wrist straps and ESD-safe bags, for complete protection.
Connect each mat to a verified ground point and test the connection regularly with a continuity tester. Consider your lab's humidity levels when choosing mat placement, as low-humidity environments may require additional coverage.
Remember to maintain clear pathways and avoid creating tripping hazards when positioning your mats.
Regular cleaning and maintenance will verify your ESD mats continue to provide effective static protection.
Workspace Coverage Guidelines
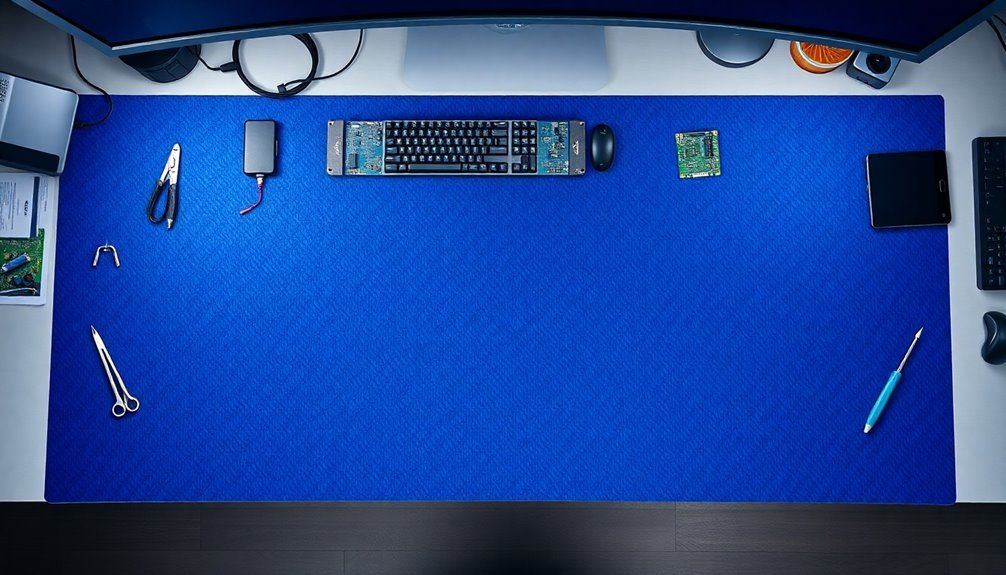

Effective workspace coverage starts with a thorough approach to static protection. You'll need to guarantee your anti-static mats cover all critical areas where you handle sensitive electronic components.
Your goal is to create a thorough ESD-protected zone that safeguards both equipment and personnel from potentially damaging static discharge. Ensure all surfaces maintain a consistent vinyl or rubber material depending on whether you're performing general assembly or soldering work.
- Start by measuring your entire work area, including workbenches and floor spaces where you'll handle static-sensitive devices. You'll want mats that fully cover these surfaces without leaving gaps or exposed areas.
- Select mats that match your workspace's specific needs, considering both table and floor coverage. You'll need to account for equipment placement and personnel movement patterns.
- Position your mats strategically around high-voltage machinery and electronic devices, guaranteeing you've created a complete protective barrier against static discharge.
- Consider combining different mat types for maximum protection – table mats for workstations and floor mats for standing areas. You'll want to maintain continuous coverage wherever static-sensitive components are present.
Remember to choose mats with appropriate thickness and conductivity levels that meet industry standards for your specific application. Your mat selection should balance protection requirements with practical workspace considerations.
Safety Standards For Mat Installation
You'll need to ground your anti-static mat properly using either an electrical outlet or conductive work surface to meet essential safety requirements.
Your mat's resistance levels must fall between 1 x 10e6 and 1 x 10e12 ohms to comply with industry standards for static dissipation.
Regular testing of your mat's resistance-to-ground and top-to-top measurements will guarantee continued protection against static discharge in your workspace.
Each anti-static mat requires its own dedicated connection to the ground point without daisy-chaining multiple mats together.
Grounding Requirements and Testing
Proper grounding stands at the heart of any anti-static mat installation's success. You'll need to connect your mat to a reliable ground source, typically through a standard US electrical outlet using a grounding cable with a #10 ring terminal.
For maximum protection, each mat requires its own dedicated grounding cable with a resistance of 1 megohm ± 20%, and you shouldn't daisy chain multiple mats together.
When installing your anti-static mat, follow these essential requirements:
- Position the mat flat on your work surface with the snap connectors facing the operator's position, ensuring direct contact with the grounding point.
- Connect your grounding cables to both table and floor mats, leading them to a common building ground point through an AC outlet.
- Test the entire setup for continuity using a surface resistivity meter to verify proper grounding across all components.
- Implement regular testing protocols, ideally checking your wrist straps and mats daily for maximum performance.
You can enhance your protection by adding heel grounders to your setup and installing real-time monitors to alert you of any grounding failures. Remember to use ESD resistance meters specifically designed for testing anti-static mat dissipation layers.
Resistance Level Compliance
Understanding resistance level compliance stands as a critical element when installing ESD mats in your workspace. You'll need to verify that your mats meet the ANSI/ESD S6.1 and STM 4.1-2017 standards, which specify resistance requirements for different applications.
For electronics manufacturing environments, your ESD mats should maintain a resistance level of less than 1 x 10e9 ohms. You'll want to conduct regular resistance top-to-ground (RTG) tests to verify proper conductivity.
Remember that conductive materials have less than 1 x 10e6 ohms resistance, while static dissipative materials range between 1 x 10e6 and 1 x 10e12 ohms.
You should perform resistance testing using an ESD Resistance Meter, placing one electrode on the floor and measuring to ground. Don't forget to account for environmental factors like temperature and humidity, as they can affect your mat's conductivity.
If you're working in communications facilities, your floor should measure between >1 x 10e6 and <1 x 10e9 ohms. For custom requirements, you might consider mats enhanced with copper layers to meet specific safety standards while maintaining flexible protection options.
Workspace Coverage Guidelines
Building on the resistance level standards, effective workspace coverage requires strategic placement of anti-static mats throughout your facility. You'll need to guarantee thorough protection by covering both floor areas and workbench surfaces in sensitive environments like data centers, medical facilities, and manufacturing spaces.
To achieve proper workspace coverage, follow these essential guidelines:
- Start by laying your anti-static mats flat at room temperature for at least four hours before installation, guaranteeing they'll conform properly to your workspace surfaces.
- Cover your entire floor area in sensitive environments, including manufacturing zones and clean rooms, while guaranteeing workbenches have complete mat coverage for assembly and repair tasks.
- Install ground cables by snapping them to each mat and connecting them to a common ground point, making sure to include the required 1 megohm resistor for controlled discharge.
- Maintain continuous protection by using heel grounders when moving between mats and implementing regular testing protocols to verify compliance with ANSI/ESD S6.1 and IEC 61340-2-3 standards.
Don't forget to extend coverage to specialized areas like operating rooms and computer repair stations where sensitive equipment requires consistent static protection.
To ensure comprehensive coverage, consider the following:
- Covering the entire floor area in sensitive environments, including manufacturing zones and clean rooms.
- Ensuring workbenches have complete mat coverage for assembly and repair tasks.
- Using heel grounders when moving between mats to maintain continuous grounding.
- Implementing regular testing protocols to verify compliance with relevant standards.
Regular testing and maintenance are crucial to maintaining the effectiveness of your anti-static mats. This includes testing the resistance to ground from the mat surface and ensuring all ground cables are properly connected to a common ground point.
Common Placement Mistakes

Placing anti-static mats incorrectly can sabotage your ESD protection efforts and put sensitive components at risk. If you don't properly prepare your work surface by cleaning it thoroughly and ensuring it's flat, you'll compromise the mat's ability to dissipate static effectively. Dirt, bumps, or debris under the mat can substantially reduce its performance.
You'll also need to pay close attention to grounding practices. If you're not connecting your mat to a verified ground point or using appropriate grounding cables, you're virtually rendering the mat useless. Make sure you're regularly checking for damaged cables and loose connections.
Don't make the mistake of partial coverage – your mat should protect the entire work area where you handle static-sensitive components.
You'll want to avoid placing mats near moisture sources or in areas with high humidity. Additionally, if you're not maintaining your mats properly, you're reducing their effectiveness. Regular cleaning with compatible products is crucial, and you should inspect the mat frequently for signs of wear and tear.
When you notice considerable deterioration, replace the mat immediately to maintain proper static protection.
Commercial Vs Industrial Placement
When choosing between commercial and industrial anti-static mat placement, you'll need to take into account distinct requirements for each environment.
Commercial settings like computer repair shops and medical offices typically require smaller, more specialized mats designed for specific workstations. Industrial environments, on the other hand, demand larger, more durable mats that can withstand heavy traffic and provide thorough protection in manufacturing facilities and laboratories.
- Commercial mats like the Apachestat Soft Foot Mat work best in limited spaces behind cash registers or in medical procedure rooms, where they provide targeted protection for sensitive equipment.
- Industrial settings benefit from heavy-duty options like Stat-Zap Matting, which offers superior static dissipation through materials like Zedlan Foam.
- You'll find commercial mats often include ergonomic features for worker comfort, while industrial mats focus on durability and large-scale protection.
- Both environments require proper grounding and regular maintenance, but industrial settings typically need more robust cleaning routines due to higher traffic and exposure to various contaminants.
Remember to think about your space's specific needs, traffic patterns, and the type of equipment you're protecting when selecting between commercial and industrial anti-static mats.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Anti-Static Mats Be Replaced?
You'll need to replace your anti-static mats every 3-6 months in harsh environments or with heavy use. However, if you're using them in gentler conditions and maintain them properly, they can last several years.
Can Anti-Static Mats Be Stacked on Top of Each Other?
You shouldn't stack anti-static mats on top of each other. It creates safety hazards like slips and falls, causes postural instability, and prevents proper grounding. Use single mats directly on conductive surfaces instead.
Do Anti-Static Mats Work in High Humidity Environments?
Yes, your anti-static mats will work in high humidity, but they're less essential since humidity naturally reduces static buildup. Above 60% RH, you'll see minimal static charges, making the mats less necessary.
What Cleaning Solutions Are Safe to Use on Anti-Static Mats?
You'll want to use specialized ESD mat cleaners like ACL Mat & Table Top Cleaner or StaticCARE. Avoid products with alkali, ammonia, or isopropyl alcohol. Always use non-abrasive, residue-free solutions to maintain effectiveness.
Can Anti-Static Mats Lose Effectiveness if Exposed to Direct Sunlight?
Yes, your anti-static mats can lose effectiveness when exposed to direct sunlight. UV radiation degrades the mat's electrical properties over time, so you'll want to keep them away from windows and direct sun exposure.
In Summary
You'll get the most value from your anti-static mats by placing them in high-traffic areas where static-sensitive components are handled. Make sure you've covered workstations, assembly areas, and equipment access points. Don't forget to properly ground each mat and check connections regularly. By following proper placement guidelines and safety standards, you're protecting both your valuable electronics and your workspace investment.





Leave a Reply