Anti-static mats and wrist straps protect your electronics differently in three key ways. First, mats offer extensive workspace protection across entire surfaces, while wrist straps focus on protecting just you and your immediate work area. Second, mats use carbon-rubber compositions that cover large areas, whereas wrist straps employ conductive materials designed for skin contact. Third, you'll need to place and ground mats on work surfaces, but wrist straps require direct body contact and proper grounding for effectiveness. Understanding these differences helps you create the most thorough ESD protection strategy for your needs.
Coverage Area and Protection Scope
Anti-static mats and wrist straps differ considerably in their coverage capabilities and protective functions. When you're working with electronics, you'll find that mats provide broad workspace protection, covering entire surfaces to prevent static electricity buildup. In contrast, wrist straps focus solely on protecting you as an individual, with a limited range that's specific to your immediate work area.
Wrist straps, while more limited in scope, come with built-in grounding mechanisms and directly address the static discharge from your body to a grounded point.
When you're handling sensitive electronics, it's important to understand that mats primarily control environmental static, while wrist straps prevent you from transferring harmful charges to components.
For maximum protection in high-risk environments, you'll want to take into account using both solutions together, as they complement each other to provide thorough ESD safety. This combined approach guarantees both your workspace and your body remain static-free during sensitive operations.
Construction and Materials
Beyond their protective scope, understanding the physical makeup of these ESD solutions reveals significant differences in their design. Anti-static mats typically feature a carbon and rubber composition that creates static dissipative or conductive properties. You'll find these mats in single-layer homogenous polymer or two-layer constructions, with thicknesses around 0.094 inches. These specialized mats maintain performance across a wide temperature range from -20°F to 160°F. In contrast, wrist straps use conductive materials specifically chosen for direct skin contact and continuous wear. The mats require proper grounding connections every 5 feet to maintain their effectiveness.
| Feature | Anti-Static Mats | Wrist Straps |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Materials | Carbon, rubber, vinyl | Carbon fibers, metal fibers |
| Construction | Single or dual layer | Single layer with skin contact |
| Thickness | ~0.094" ± 0.010" | Thin, flexible design |
| Surface Properties | Static dissipative/conductive | Conductive for skin contact |
| Durability Focus | Floor/bench wear resistance | Repeated flexing, skin contact |
When you're selecting these ESD protection tools, you'll need to take into account their distinct material requirements. Anti-static mats must meet surface resistivity standards of no more than 1 x 10^9 ohms/square, while maintaining durability for constant surface contact. Wrist straps, however, prioritize materials that guarantee reliable skin contact and flexibility for comfortable, extended wear.
Application and Usage Methods
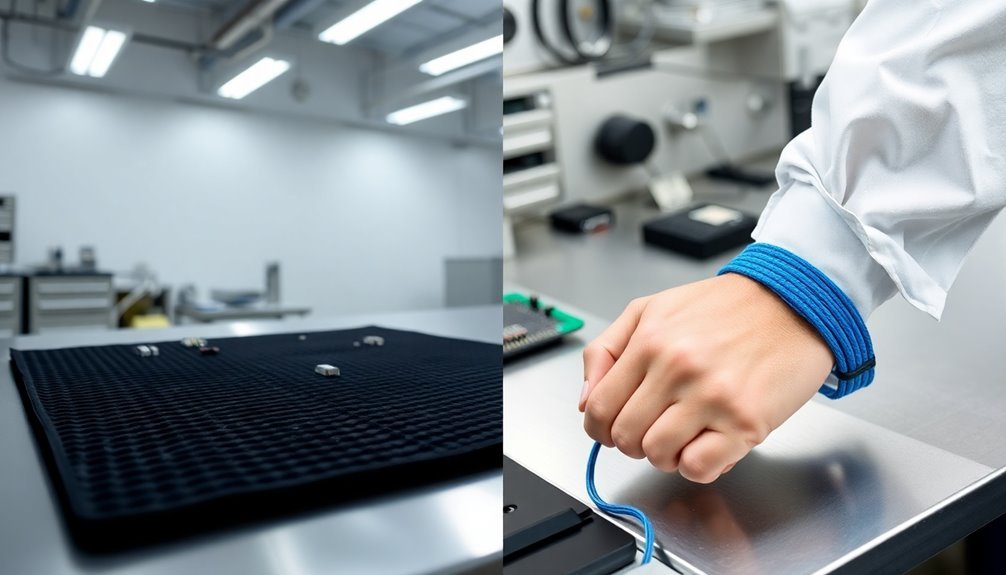

Deploying ESD protection effectively requires understanding the distinct applications of both anti-static mats and wrist straps. You'll need to place your anti-static mat on the work surface and connect it properly to a grounding source. For maximum protection, you should integrate wrist straps with your mat setup, especially when handling sensitive electronic components.
When you're working in high-risk environments like electronics manufacturing or labs, you'll want to use both protective devices simultaneously. Your anti-static mat provides broad area protection for components and tools, while your wrist strap guarantees you're consistently grounded during handling operations. Static charge equalization occurs instantly when touching components, making comprehensive protection critical. The most common mat materials are rubber and vinyl, providing reliable static dissipation.
Remember that environmental factors, such as humidity levels, can affect the performance of both devices.
You'll need to maintain your ESD protection system properly. This means regularly cleaning your anti-static mat to preserve its static-dissipative properties and checking your wrist strap's connection daily.
When you're setting up your workstation, verify your mat is properly grounded to prevent shock hazards, and connect your wrist strap to a verified ground point.
Don't forget that different components may require varying levels of protection, so adjust your setup accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Anti-Static Mats and Wrist Straps Be Replaced?
You'll need to replace anti-static mats every 2-5 years based on usage and conditions. For wrist straps, plan on replacement every 1-3 years, but replace either immediately if they show damage or fail testing.
Can These Devices Be Damaged by Cleaning Products or Chemicals?
Yes, your anti-static mats and wrist straps can be severely damaged by harsh chemicals and cleaning products. You'll want to stick to mild soap and water or specialized cleaners designed for ESD equipment.
Do Temperature Changes Affect the Effectiveness of Anti-Static Protection Equipment?
Yes, temperature changes can affect your anti-static protection equipment's effectiveness. You'll notice changes in conductivity, material properties, and static dissipation rates when temperatures fluctuate. It's important to monitor environmental conditions carefully.
What Happens if the Grounding Connection Fails During Use?
If your grounding connection fails, you'll lose static dissipation protection, risking damage to electronic components. You're also exposed to potential electrical shock hazards, and static charges will accumulate on your work surface.
Are There Specific Storage Requirements to Maintain the Effectiveness of These Items?
You'll need to store your ESD items in a dry area away from sunlight. Keep mats rolled, not folded, and store wrist straps flat. Don't expose them to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures.
In Summary
You'll find both anti-static mats and wrist straps essential for ESD protection, but they serve distinct purposes. While mats provide broad workspace coverage and protect components placed on them, wrist straps focus solely on grounding you. Understanding their unique materials, application methods, and protection scope helps you choose the right solution – or better yet, use both for extensive ESD protection in your workspace.





Leave a Reply