Anti-static wrist straps are your primary defense against electrostatic discharge (ESD) when you're working with sensitive electronic components. You'll need to wear one while handling computer parts, circuit boards, or semiconductors to prevent static electricity from damaging these delicate devices. The strap connects your body to a ground point through a coiled wire with a built-in resistor, safely channeling static away from sensitive equipment. Even minor static discharges under 25 volts can destroy electronic components, making these straps essential in professional electronics work. There's much more to understand about proper grounding techniques and industry standards for maximum protection.
Understanding Anti Static Wrist Straps
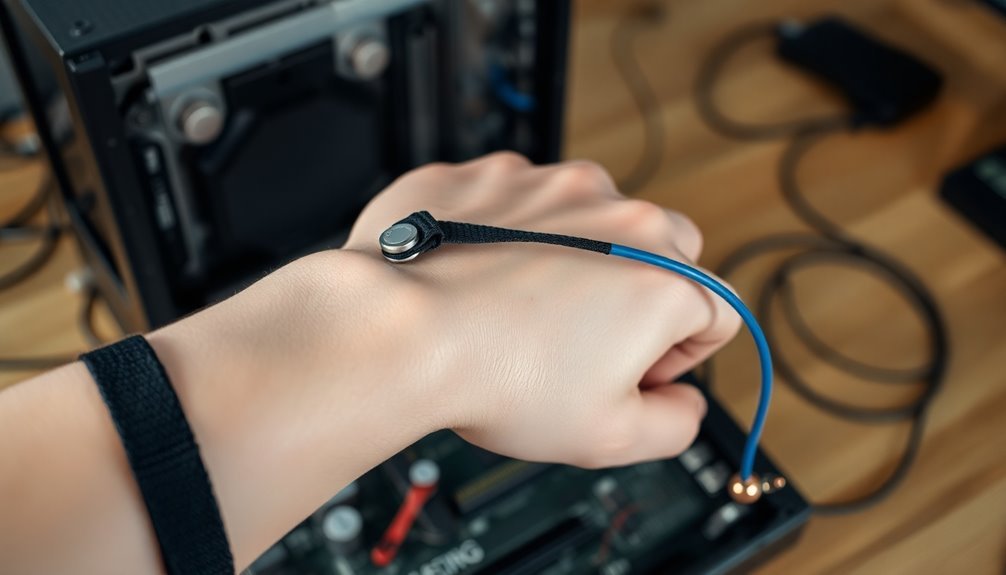

Don't be tempted by wireless options – they've been proven ineffective and don't meet ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
These wireless versions can allow dangerous voltage buildup exceeding 500 volts and won't effectively drain accumulated charge.
Instead, stick to traditional wired anti-static wrist straps, especially in ESD-controlled areas where you're handling critical mission hardware.
Direct grounding path helps prevent costly damage to sensitive electronic components during maintenance and repairs.
Remember to verify your ESD grounding system periodically to guarantee it's functioning correctly and maintaining proper protection.
Metal or metal-coated fabrics enhance the effectiveness of proper grounding in anti-static wristbands.
Essential Components and Design Features
A well-designed anti-static wrist strap comprises several critical components that work together to protect sensitive electronic equipment.
You'll find conductive materials like steel or metal-coated fabric in the band's construction, while rubber or plastic elements serve as conductors between your skin and the device surfaces. Regular testing ensures the wrist strap functionality remains effective.
The wrist strap's core features include a highly elastic PVC coil cord that can withstand over 30,000 uses, and a stainless steel crocodile clip for secure grounding. Conductive gauze yarn weaves throughout the band to ensure consistent static discharge.
A built-in 1MΩ resistor guarantees safe, controlled discharge of static electricity. The adjustable band is designed to fit snugly against your wrist, incorporating anti-static yarns in inner layers and regular yarns in outer layers.
You'll notice these straps come in both wired and wireless variants, with the wired versions typically featuring a 6-foot grounding cord for mobility.
The design meets or exceeds IBM and US military static control standards, offering options for different grounding connections, including 10mm snap connectors.
Whether you're choosing a bright-colored band for visibility or a standard design, you'll need to verify it's properly connected to a grounding source, such as an antistatic mat or grounded equipment.
Proper Grounding Methods
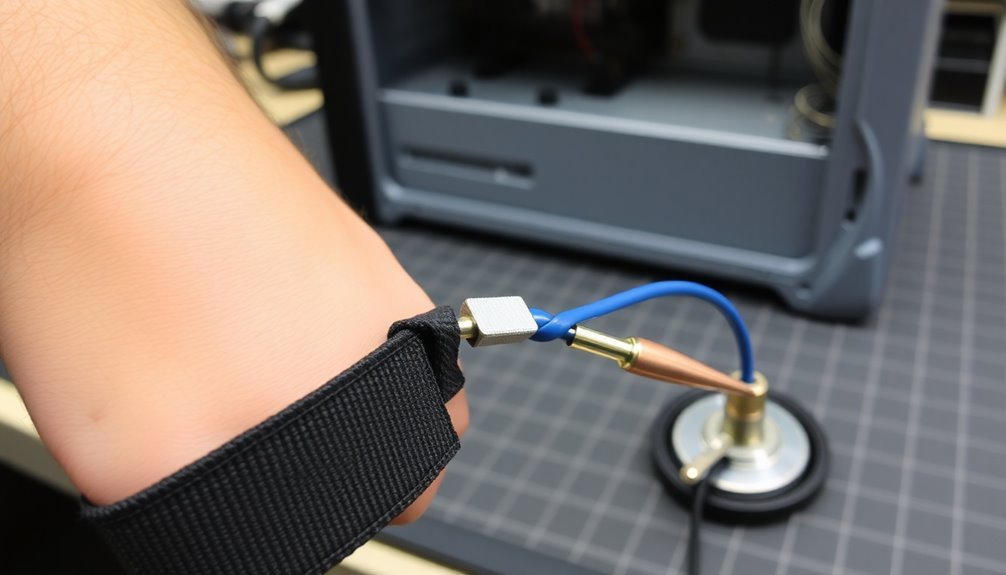
Through proper grounding methods, you'll guarantee your anti-static wrist strap effectively dissipates static electricity. You must connect your wrist strap to a designated grounding source using either 10 mm press studs, coiled cords, or removable crocodile clips. You can find suitable grounding points on anti-static mats, workstations, or directly on the equipment you're working with.
You'll need to secure the wrist strap snugly against your skin while ensuring it remains comfortable. The coil cord contains 1 megohm resistor to safely control discharge. Don't let the strap become loose or dirty, as this can interrupt the grounding path and risk ESD damage. Using an anti-static wrist strap provides a high resistance path to prevent static buildup. Even if you're using ESD footwear, you should keep the strap on while seated.
Maintaining the integrity of your grounding path is essential. You'll want to regularly inspect your wrist strap for signs of wear or damage, replacing it when necessary. The grounding path must remain continuous and unbroken to effectively dissipate static electricity.
You can use multiple grounding points for added security. By following these proper grounding methods, you'll create a reliable path for electrostatic discharge and protect sensitive electronic components from damage.
Common Applications in Industry
When you're working in electronics manufacturing, you'll find anti-static wrist straps to be essential tools for protecting sensitive components from electrostatic discharge.
You must wear them properly while handling circuit boards, semiconductors, and other ESD-sensitive devices to prevent costly damage and production failures. Even minor static discharges of 25 volts or less can cause significant damage to sensitive electronics. These reliable wrist straps feature a 0.1 second discharge time to quickly neutralize static electricity.
In clean room environments, you'll need to follow strict protocols that include wearing these straps as part of a thorough ESD protection system, along with specialized clothing and footwear.
Electronics Manufacturing Essentials
Modern electronics manufacturing relies heavily on anti-static wrist straps as vital safety equipment for protecting sensitive components. When you're assembling electronic devices, these straps provide a safe path for static discharge, preventing potential damage that could render components useless. You'll need to guarantee proper grounding by connecting your strap to a verified ground point while working with sensitive electronics.
| Component Type | ESD Risk Level | Protection Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Microprocessors | Very High | Always Required |
| Memory Chips | High | Always Required |
| Circuit Boards | Moderate | Recommended |
| Power Supplies | Low | Situational |
You'll find these straps particularly essential when handling microprocessors, memory chips, and other static-sensitive devices. They're designed to incorporate specific resistance levels that allow high-voltage charges to safely leak to ground without causing sudden discharges. For peak protection, you should wear the strap on your non-dominant hand and regularly verify its functionality through resistance testing. Remember that wireless alternatives don't meet ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards, so stick to properly grounded wrist straps to guarantee component safety and maintain quality control in your manufacturing process.
Clean Room Work Protocols
Safety protocols in clean room environments demand rigorous adherence to anti-static wrist strap procedures. You'll need to wear these essential devices whenever you're handling sensitive electronic components or working in areas where static discharge could cause damage or safety hazards.
Clean rooms require proper grounding through wrist straps connected to standardized points using 4mm plugs or 10mm press studs, ensuring static electricity dissipates safely through controlled resistance levels.
- You must maintain proper static control through wrist straps with resistance levels between 10^5 to 10^8 ohms to prevent shock hazards.
- You'll need to verify your wrist strap's effectiveness regularly, as wireless alternatives don't meet industry standards.
- You should consider using ankle or heel straps for increased mobility when working in surgical rooms or areas requiring frequent movement.
When you're working with sensitive electronics or in explosive environments, you can't afford to skip proper ESD protection. Your wrist strap serves as your primary defense against costly damage and safety risks.
Remember that compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20-2014 standards isn't optional – it's a vital requirement for maintaining professional standards and protecting valuable equipment in clean room environments.
Safety Guidelines and Best Practices
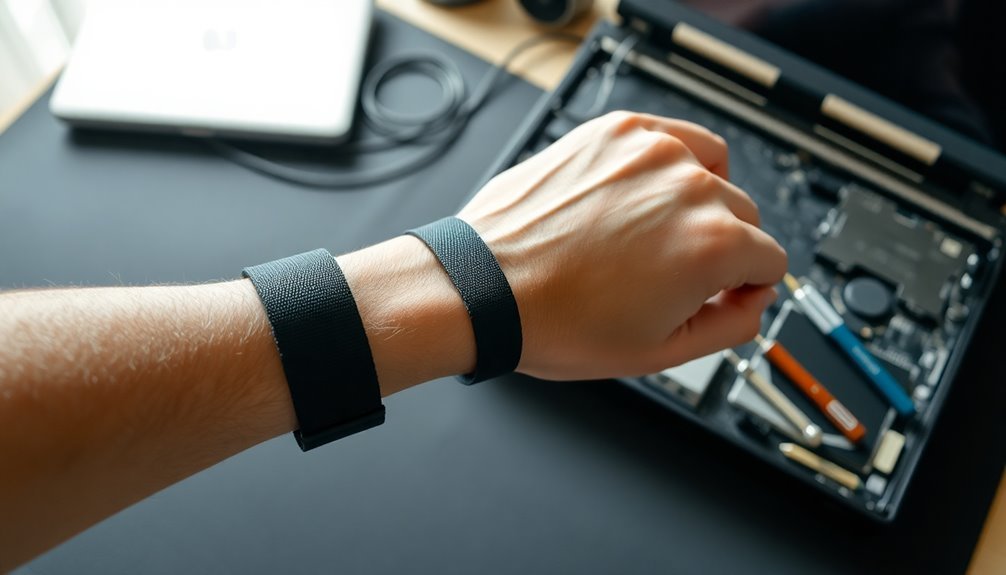

You'll need to verify your anti-static wrist strap is properly connected to a reliable ground point, such as an unpainted metal surface or designated ESD grounding terminal.
It's crucial to test your wrist strap daily with an impedance tester to verify it's functioning correctly and maintaining proper conductivity.
Position the strap snugly against your skin, about one inch above your wrist bone, making sure the metal contact plate maintains consistent skin contact throughout your work session.
Proper Grounding Connection Methods
For ideal protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD), proper grounding connection is vital when working with sensitive electronic components. You'll need to connect your wrist strap to bare, unpainted metal surfaces, as painted metals can insulate and prevent effective grounding. Common connection points include power supply screws or fan grilles, guaranteeing they're free from non-conductive materials.
- Always wear the strap snugly on your dominant hand, positioning it for easy access to your work area.
- Connect the alligator clip directly to exposed metal, verifying a secure connection.
- Consider relocating the grounding point to reduce cord interference while you work.
When you're setting up your grounding connection, remember that wireless wrist straps aren't acceptable substitutes in ESD-controlled environments.
You'll want to establish a common ground point that guarantees both you and the device maintain the same electrical potential. This creates a safe, conductive path for static electricity to dissipate.
If you need to adjust your position, you can move the grounding point to the opposite side, but never work on sensitive components without a properly grounded wrist strap, as ESD events can cause immediate or latent damage to electronic devices.
Regular Testing and Maintenance
After establishing proper grounding connections, maintaining your anti-static wrist strap requires consistent attention to detail and regular testing.
You'll need to perform regular visual inspections, checking for any signs of wear, damage, or fraying in the strap material, cord, and grounding points. Make sure the strap fits snugly on your wrist and the alligator clip remains firmly attached.
Testing the functionality of your wrist strap is essential for safety and effectiveness. Use a wrist strap tester to verify proper grounding and check that the resistance maintains approximately 1 megaohm.
You should also confirm that your wrist strap works correctly with your specific workspace setup, including ESD mats and various grounding points.
When using the wrist strap, only wear it while working with static-sensitive electronics, and always disconnect it when not in use. Don't use it near flammable materials or during non-static-sensitive tasks.
Store your wrist strap in a dry place when not in use, and replace it immediately if you notice any damage. Keep track of your testing and replacement history to maintain proper safety standards.
Correct Strap Positioning Guidelines
Proper positioning of an anti-static wrist strap directly impacts its effectiveness in preventing static discharge. You'll need to wear the strap snugly around your wrist, guaranteeing it maintains consistent contact with your skin while remaining comfortable.
While most users wear their straps on the wrist, you can also position them on your ankle in specific environments like surgical rooms or clean labs.
The strap you choose should have an insulative outer surface for your safety, and you'll need to connect it to a proper grounding point to make it effective. Whether you wear it on your left or right wrist depends on your preference and the location of your grounding point.
- Always guarantee your strap is connected to a common grounding point, such as your workstation's Earth bonding point
- Keep the strap clean and check regularly for signs of wear to maintain consistent grounding
- Use the strap even when wearing ESD footwear for maximum protection
Remember that proper positioning isn't just about comfort – it's about maintaining a reliable path to ground. You should adjust the band to fit your wrist size perfectly, as loose straps won't provide consistent protection against static discharge.
Maintenance and Testing Procedures
Regular maintenance and testing of anti-static wrist straps play an essential role in preventing ESD damage to sensitive electronics.
You'll need to inspect your wrist straps daily for signs of wear, damage, or contamination that could compromise their effectiveness. Clean them regularly to maintain proper conductivity and store them in a dry, clean environment away from static sources.
You must test your wrist straps daily using a continuity tester or resistance meter to guarantee they're functioning correctly. Measure the resistance between the wrist strap and grounding point, and verify that it meets ESD standards. If you notice any issues with conductivity or find damage, replace the wrist strap immediately.
When troubleshooting, check your grounding points for proper connection and integrity. If you're experiencing frequent device failures, conduct an ESD audit to identify potential risks in your work environment.
Don't forget to maintain proper training for all users on correct wrist strap usage and maintenance procedures. Always verify your wrist strap is properly connected to a grounding point before handling sensitive electronics, and keep your work area ESD-controlled to prevent static buildup.
Benefits of ESD Protection
With proper maintenance practices in place, you'll want to understand the significant advantages of ESD protection in your workspace. Anti-static wrist straps offer extensive protection against electrostatic discharge, helping you prevent damage to sensitive electronic components while guaranteeing workplace safety and efficiency.
- You'll minimize the risk of costly repairs and component failures by safely grounding yourself during electronic handling tasks.
- You can maintain a continuous workflow without frequent interruptions for manual grounding.
- You'll meet industry compliance standards while protecting your investment in electronic equipment.
The benefits extend beyond basic protection. You'll find these straps are designed with your comfort in mind, featuring adjustable fits and hypoallergenic materials that won't interfere with your work.
The high-quality construction, including carbon-filled conductive fibers and stainless steel clasps, guarantees reliable performance throughout your workday.
Plus, you'll appreciate the versatility these straps offer, as they're compatible with various grounding systems and can be used across multiple industries, from electronics manufacturing to aerospace applications.
With controlled resistance and verified performance standards, you're investing in a solution that protects both your equipment and your bottom line by preventing immediate and latent ESD damage.
Professional Standards and Regulations
Throughout the electronics industry, professional standards and regulations govern the use of anti-static wrist straps to verify consistent ESD protection. Organizations like ANSI/ESD and IEC develop these standards, with ANSI/ESD S1.1 providing essential test methods and performance requirements that you'll need to follow.
When you're using anti-static wrist straps, they must meet specific resistance requirements. Your wrist strap shouldn't exceed 35 megohms in resistance, while maintaining at least 750K ohms to verify proper functioning of the safety resistor. You'll need to test your wrist straps regularly using an ESD Test Station to confirm they're working correctly.
You'll find that professional standards require wrist straps to connect to ground through a coiled cable with a 1 megohm resistor. These standards also specify that you should integrate wrist straps with anti-static mats or static-dissipating workbench surfaces for complete protection.
If you're working in specialized industries, you'll need to comply with additional standards. For instance, military contractors must follow MIL-STD-1686, while facilities can pursue certification under ANSI/ESD S20.20 or IEC 61340-5-1 standards to demonstrate their commitment to ESD control.
Selecting the Right Wrist Strap

Choosing an effective anti-static wrist strap involves careful consideration of materials, design features, and fit options to ascertain reliable ESD protection.
- Common materials include rubber, plastic, and metal-coated fabric, with conductive fibers woven into the straps.
- Hypoallergenic options made from nylon or stainless steel are available for those with sensitive skin.
- Adjustable bands with coiled cords provide flexibility and mobility while maintaining proper grounding.
When selecting your wrist strap, you'll want to confirm it fits snugly against your skin while remaining comfortable for extended wear. The strap should include a removable coiled cord and crocodile clip for connection to grounding points. You can choose to wear it on either wrist, depending on your workspace setup and personal preference.
Consider the durability of materials and consistent contact requirements in your work environment. If you're sharing a workspace, you'll need to account for multiple users accessing grounding points.
For temporary projects, disposable options are available, though quality shouldn't be compromised. Remember, your chosen strap must provide reliable static discharge protection while meeting professional quality standards, regardless of whether you're working in a lab, clean room, or field environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Anti-Static Wrist Straps Be Worn While Working With Live Electrical Circuits?
You should never wear an anti-static wrist strap while working with live electrical circuits. It's extremely dangerous as the conductive strap creates a direct path to ground, putting you at risk of shock or electrocution.
How Often Should Anti-Static Wrist Straps Be Replaced?
You should replace your anti-static wrist strap annually for standard use, or more frequently with heavy use. Replace it immediately if you notice any damage, wear, or loss of elasticity in the strap.
Do Anti-Static Wrist Straps Work Through Clothing or Gloves?
No, anti-static wrist straps won't work effectively through clothing or gloves. You'll need direct skin contact to create a proper conductive path to ground. Insulating materials block the static discharge function.
What Happens if You Accidentally Disconnect the Ground Wire While Working?
If you disconnect the ground wire, you'll immediately risk static buildup on your body. This can cause dangerous electrostatic discharge, potentially damaging sensitive electronics and creating latent failures in components you're handling.
Can Multiple People Share the Same Grounding Point Simultaneously?
Yes, you can safely share a grounding point with multiple people simultaneously. Just guarantee your ESD mat has enough grounding snaps and each person's wrist strap maintains proper resistance for safe static dissipation.
In Summary
You'll find that anti-static wrist straps are essential tools for protecting sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge damage. By wearing one properly and following safety guidelines, you're safeguarding valuable equipment and ensuring successful repairs or assembly work. Don't forget to regularly test your wrist strap and maintain proper grounding connections. When you're working with electronics, it's always better to prevent ESD damage than to fix it.




Leave a Reply