You can test your anti-static wristband's performance in seven reliable ways to guarantee proper ESD protection. Start with single-wire resistance measurements using capacitance technology for basic verification. Perform daily checks at a test station to confirm resistance levels stay between 750K and 35 megohms. Use combo testers to verify both wristband and ground connections simultaneously. Install continuous monitoring systems for real-time alerts. Conduct regular visual inspections of straps and cords. Utilize portable battery-powered testers for on-the-spot checks. Finally, implement data logging analysis to track performance trends. Understanding these testing methods will strengthen your ESD protection strategy.
Single-Wire Resistance Measurement

Testing specialists rely on single-wire resistance measurement to monitor anti-static wrist straps through capacitance technology. The system works by sending a signal down a single wire to your wrist strap, detecting the mass at the end of the coil cord to confirm you're wearing it. Rather than measuring resistance directly, it uses your body's parasitic capacitance to ground and monitors waveform distortions to verify circuit completion. Work surface grounding is essential for preventing charge build-up during testing procedures. A successful test is indicated by a green LED light when resistance falls between 800 kΩ to 9 MΩ.
You'll need to be aware of several limitations when using single-wire monitoring. It's less accurate than dual-wire systems and can be fooled by dry skin conditions since it doesn't verify proper electrical connection. You might encounter false positives if there's a break in the circuit or poor contact, and some models can cause skin irritation due to constant DC voltage.
When you're testing anti-static wristbands, remember that standards like ANSI/ESD S1.1-2021 require resistance less than 3.5 x 10^7 ohms, while IEC 61340-5-1 specifies impedance below 35 megohms.
For sensitive applications, you'll want to take into account switching to dual-wire monitors, as they provide direct resistance measurement and more reliable verification of your ground connection.
Daily Test Station Operation
When you arrive at your workstation, you'll need to properly connect your wrist strap to the test station's metal touch plate and press the test button firmly.
You must maintain contact until the test station displays either a pass or fail indication through its LED lights or digital readout.
For optimal ESD safety, less than 3.5 megohms is the acceptable resistance range for properly functioning wrist straps.
Industry standards recommend conducting daily wrist strap tests at least twice daily to ensure continuous ESD protection.
If you receive a fail result, check your strap's fit, cleanliness, and cord connections before retesting, as these are common causes of test failures.
Basic Test Station Setup
A proper test station setup forms the foundation of your daily ESD protection routine. You'll need several key components to guarantee accurate and reliable testing of your anti-static wristbands. The main element is the wrist strap test station itself, which provides clear pass/fail indications based on the resistance measurements of your wrist strap system. Daily testing is absolutely critical for maintaining effective ESD control programs.
Your test station should include a standard banana jack connector for attaching the wrist strap's coil cord. This connector guarantees a secure connection between your wrist strap and the testing equipment. The ideal resistance range for proper antistatic performance falls between 10^6 and 10^9 ohms.
The station's indicator system typically uses color-coded lights to display results clearly, making it easy to determine if your wrist strap passes or fails the resistance test.
Many modern test stations also include data logging capabilities, which you'll find useful for maintaining testing records and meeting quality control requirements.
When setting up your station, verify it's positioned in an easily accessible location and properly connected to ground. You'll want to verify that the station can detect both high resistance failures (above 35 megohms) and low resistance failures (below 750 kilohms) to maintain compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
Operating Test Station Controls
The daily operation of test station controls requires consistent attention to detail and proper sequencing. You'll need to test your wrist straps and footwear daily as part of your quality process audit, following manufacturer specifications to guarantee accurate results. Regular testing ensures effective protection against electrostatic discharge events.
To operate the test station, you'll first plug in your wrist strap and foot grounder to the designated ports. Make sure you've secured your wrist strap properly before initiating the test. The station will display results through a color-coded system – green for pass and red for fail. Many advanced stations can log your test data directly to a computer for documentation.
You'll need to verify that your wrist strap's resistance falls within specific limits. The resistance should be less than 35 megohms to comply with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards but above 750K ohms for safety. If you're using a continuous monitoring system, you'll receive immediate alerts if your connection to ground fails.
Your testing frequency may vary depending on your company's requirements. Some facilities require testing at the start of each shift, while others mandate multiple daily checks to maintain consistent ESD protection throughout your workday.
Interpreting Pass/Fail Results
During daily test station operation, you'll encounter both high and low fail results that require proper interpretation.
When you get a high fail reading (above 35 megohms), it typically means your wrist strap's resistance is too high, which can lead to ESD damage. Common causes include high skin resistance, soiled or poorly fitted wristbands, and damaged coil cords.
Low fail results (below 750,000 ohms) indicate your wrist strap's 1 megohm resistor isn't working correctly, creating a serious safety risk. You might get these readings if your coil cord has a shorted resistor or if you're touching additional grounded surfaces during testing. Low fails are particularly dangerous as they could allow excessive current to flow through your body.
To address failures effectively, you'll need to take immediate action. If you're getting high fails, try using electronics-approved lotion to reduce skin resistance or check your wrist strap for proper fit and wear.
For low fails, you'll need to replace the wrist strap or coil cord immediately. Don't continue working with a failed wrist strap, as it compromises both ESD protection and personal safety.
Combo Tester Ground Checks

Modern combo testers serve as essential checkpoints for ESD safety, combining both wrist strap and footwear verification in a single unit. You'll find these devices strategically placed at entrances to ESD-protected areas, where they provide immediate feedback on your grounding equipment's effectiveness.
- Tests both wrist straps and footwear simultaneously
- Uses color indicators for quick pass/fail determination
- Measures resistance within industry-standard thresholds
- Provides results within 5 seconds of testing
When you're using a combo tester, it'll check if your wrist strap maintains resistance below 35 megohms while guaranteeing your footwear falls within 750 kilohms to 100 megohms. The test voltage, typically set at 10 volts, helps identify potential issues like high skin resistance or damaged coil cords that could compromise your ESD protection.
To maintain compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards, you'll need to perform these tests regularly. The combo tester's dual-testing capability streamlines your verification process, making it easier to guarantee you're properly grounded before entering sensitive work areas.
If you receive a fail indication, you'll need to investigate whether it's due to equipment failure or improper wearing of your ESD protection gear.
Continuous Wristband Monitoring Systems
You'll find continuous wristband monitoring systems offer immediate alerts through real-time warning mechanisms that detect grounding issues or equipment failures.
Built-in data logging features help you track and document ESD incidents while maintaining compliance records for quality assurance. Both single and dual wire monitors are available to match your specific workplace safety requirements.
Remote monitoring capabilities let you oversee multiple workstations from a central location, ensuring consistent ESD protection across your facility.
Real-Time Warning Systems
Real-time warning systems have revolutionized how we monitor anti-static wristbands in sensitive electronic environments. These sophisticated monitoring systems provide immediate feedback on your wrist strap's performance and the static control worksurface's status, eliminating the need for time-consuming periodic testing.
Key features you'll find in modern warning systems include:
- Visual and audible alarms that trigger instantly when a failure occurs
- Continuous monitoring that catches even split-second intermittent failures
- Dual-wire monitoring that maintains ground connection even if one conductor fails
- Fail-safe designs that guarantee reliable static protection throughout your shift
You'll find these systems available in various configurations, from single-user to multi-user setups, with options to monitor both wrist straps and ESD worksurfaces simultaneously.
You can install them on your ESD mat, bench, or under the workstation, depending on your needs. Whether you're using single-wire impedance monitors for basic applications or dual-wire resistance monitors for critical operations, you'll receive instant notifications if any component fails.
This real-time monitoring helps you maintain compliance with static control regulations while greatly reducing maintenance downtime and improving your productivity.
Data Logging Capabilities
Building upon the advantages of real-time monitoring, continuous wristband monitoring systems now offer extensive data logging capabilities that transform how you manage ESD protection.
These systems automatically store test data, eliminating the need for manual record-keeping while ensuring compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20 and other standards.
You'll find multiple connectivity options, including USB, Ethernet, and Wi-Fi, making it easy to transfer and store thousands of test records.
The systems integrate seamlessly with ESD management software and offer both LCD displays and LED indicators for real-time monitoring.
You can set custom test frequencies, whether you need checks at the start of each shift or continuous monitoring throughout the day.
To implement these systems effectively, you'll need to perform initial calibration and regular maintenance checks.
You should also train your team on proper system operation and troubleshooting procedures.
The software may require periodic updates to maintain compatibility with evolving ESD standards.
Remote Monitoring Solutions
Through modern continuous monitoring systems, remote supervision of ESD wristband performance has become more sophisticated and reliable than ever. You'll find these systems offer real-time monitoring capabilities that instantly detect and alert you to any wristband or worksurface failures, ensuring continuous protection of sensitive electronic components.
- Instant visual and audible alerts notify you immediately when a failure occurs
- Both single-wire and dual-wire configurations are available to match your needs
- Systems can be mounted on, under, or near your ESD workstation
- Real-time detection catches even split-second failures that periodic testing might miss
You can greatly reduce downtime and improve efficiency by eliminating the need for manual testing before each shift. These systems comply with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards and work seamlessly with your existing ESD equipment.
When selecting a remote monitoring solution, you'll find options from trusted brands like SCS, Desco, and Binary, each offering customizable configurations for single or multiple users. The systems integrate easily with your workstation and provide continuous protection without interrupting your workflow.
You'll save on long-term costs by avoiding regular testing procedures while maintaining superior protection against ESD damage.
Visual Inspection Methods
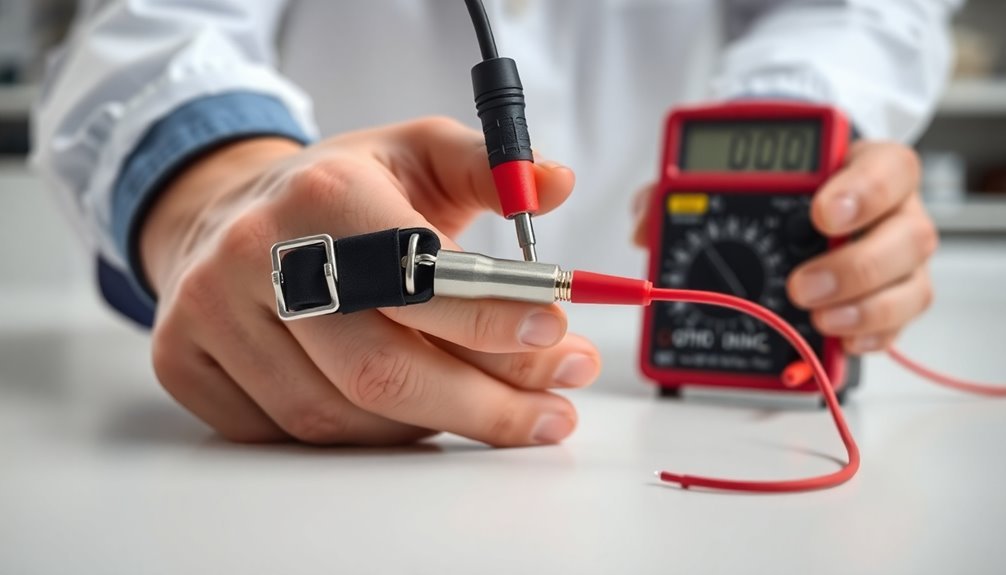
Before using any anti-static wristband, a thorough visual inspection guarantees the device's reliability and safety. You'll need to systematically examine three main components: the band itself, the strap, and the cord with its connectors.
Start by checking the wristband for any obvious damage, loose parts, or improper fitting. You should look carefully for signs of wear and tear, and note if someone's made any unauthorized modifications to the device.
When examining the strap, focus on identifying cuts, tears, or unusual stretching that might compromise its effectiveness. Don't forget to verify the strap's electrical integrity and watch for indicators of misuse.
The cord and connector inspection is equally essential. You'll want to examine the cord for any breaks or fraying, while ensuring the connectors are free from corrosion and dust buildup. Check that all connections to grounding points are secure.
During your inspection, use a wrist strap tester while wearing the device to include skin resistance in your assessment. Make sure to document your findings, including any failures or concerns, and maintain regular testing records for future reference.
Battery-Powered Portable Testing
After completing a visual inspection, you'll need reliable testing equipment to verify your wrist strap's performance. Battery-powered portable testers offer a convenient solution for checking your anti-static wristband's resistance levels. These compact devices typically run on a 9V battery and can quickly determine if your wrist strap falls within the acceptable range of 750 kilohms to 35 megohms.
- Green LED indicators confirm proper functioning within the safe resistance range
- Red LEDs and audible alarms alert you to dangerous resistance levels
- Operating temperature range of 0-40°C guarantees reliable testing in most workplace environments
- Test voltage of 3-4 VDC with currents as low as 6uA for safe operation
To test your wrist strap, simply plug the coiled cord into the tester's banana jack and touch the metallic surface. The device will instantly evaluate the ground resistance through your wrist strap system.
If you're experiencing high-resistance readings, dry skin might be the culprit – apply a moisturizing lotion to improve conductivity.
Remember that these portable testers need annual calibration to maintain accuracy, and you should always follow the manufacturer's specific testing procedures for reliable results.
Data Logging Performance Analysis

Data logging capabilities take anti-static wristband testing to the next level. With digital test stations, you'll get immediate notifications of any wrist strap failures and can track performance trends over time.
You can connect advanced testing equipment to your computer, allowing for detailed analysis and thorough compliance reporting that meets ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
You'll find various data logging technologies available, including constant monitors and digital test stations like the WST200 and GTS600K. These devices don't just test your wrist straps; they maintain detailed records of performance metrics and failure instances.
Some systems even offer wireless connectivity for remote monitoring and easier data management.
To maximize your data logging effectiveness, you'll need to implement standardized testing procedures and maintain consistent record-keeping practices.
Make sure you're conducting regular tests and documenting all results systematically. By analyzing this logged data, you can identify patterns in wrist strap performance, schedule preventive maintenance, and make informed decisions about replacements.
This proactive approach won't just help you comply with regulations – it'll also reduce your risk of costly ESD damage and improve your overall quality control measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Should an Anti-Static Wristband Typically Last Before Replacement?
You'll need to replace your anti-static wristband based on usage, but typically every 6-12 months. If you're using it daily, consider replacing it sooner, especially if you notice wear or damage.
Can Extreme Humidity Affect Wristband Test Results?
Yes, extreme humidity can greatly affect your wristband test results. You'll get false positives in high humidity and increased static risks in low humidity. That's why you should test in controlled environmental conditions.
What Causes False Positives During Anti-Static Wristband Testing?
You'll encounter false positives in anti-static wristband testing due to worn equipment, improper fitting, soil build-up, incorrect resistance levels, and electrical interference. Poor maintenance and inadequate training can also trigger false results.
Is Wristband Testing Necessary When Using Esd-Protective Gloves?
Yes, you'll still need to test your wristband even when wearing ESD-protective gloves. Gloves aren't a replacement for wristbands, and regular testing guarantees your primary static protection method works properly regardless of additional safeguards.
Should Operators Remove Watches or Jewelry During Wristband Performance Testing?
Yes, you must remove all watches and jewelry during wrist strap testing. They'll interfere with accurate readings and can compromise safety by creating unwanted conductive paths that bypass your wrist strap's protective features.
In Summary
You'll find that regular testing of your anti-static wristband is essential for maintaining ESD protection. Choose the testing method that best fits your workflow, from simple resistance measurements to advanced monitoring systems. Don't skip daily checks and keep detailed records of performance data. By following these seven testing approaches, you'll guarantee your wristband continues providing reliable static discharge protection.




Leave a Reply