For electronics storage, you'll want to choose between three main types of anti-static foam: pink anti-static foam (10^6-10^9 ohms), black conductive foam (below 10^5 ohms), or static-dissipative foam (10^5-10^9 ohms). Pink foam works well for general electronics, while black conductive foam offers superior protection for highly sensitive components by creating a Faraday cage effect. Your best choice depends on your specific needs – polyethylene (PE) foam provides better structural support for heavy items, while polyurethane (PU) foam suits lighter electronics. Storage conditions matter too – keep your foam between 10-27°C with 30-50% humidity for ideal protection. There's much more to take into account when protecting your valuable electronics.
Understanding Anti-Static Foam Properties
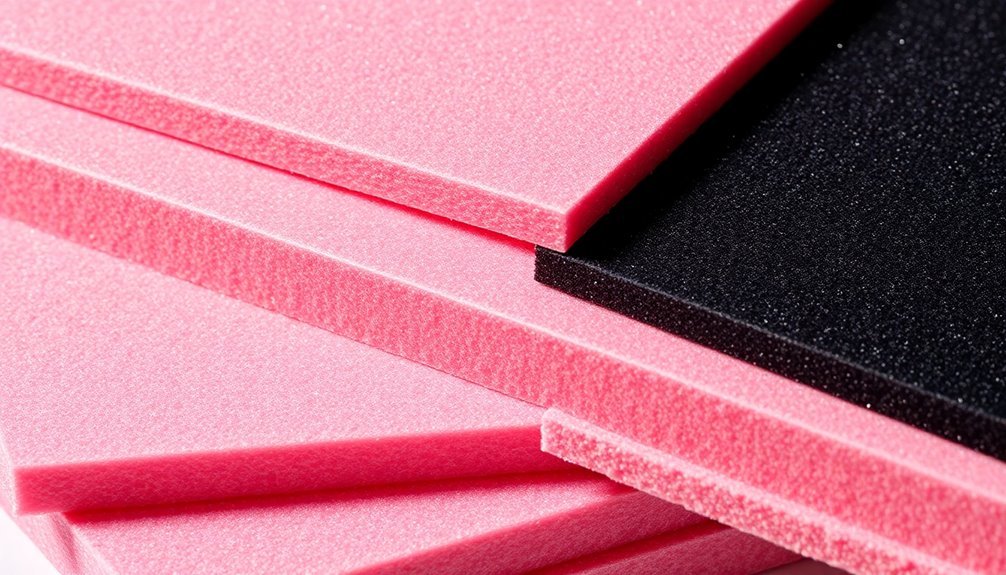

Many electronic components are highly sensitive to static electricity, making anti-static foam an essential storage solution. When you're looking to safeguard your electronics, understanding the key properties of anti-static foam will help you make informed decisions about storage solutions.
Anti-static foam's surface resistance ranges from 10^6 to 10^9 ohms, which provides effective protection against static discharge. It's made from polyurethane with conductive fillers and features an open cell structure that controls static electricity. Pink static dissipative foam offers an ideal balance of protection and cushioning for various electronic components.
You'll find that the foam's performance improves with increased humidity, and it includes additives like Glycerol Monostearate to enhance conductivity.
You should note that anti-static foam differs from conductive foam in several important ways. While conductive foam has a lower surface resistance (10^3 to 10^5 ohms) and allows faster charge transfer, anti-static foam provides moderate static control that's suitable for most electronics storage applications.
The foam's surface conductivity will decrease over time, so you'll need to think about replacement periodically.
When selecting anti-static foam, you can request custom sizes to guarantee your electronic components fit securely and receive the best protection.
Common Types of ESD Foam
Three primary types of ESD foam dominate the electronics storage market: anti-static, static dissipative, and conductive foam. Each type offers distinct levels of protection for your sensitive electronic components.
Anti-static foam, typically pink in color, features a surface resistance of 10^9 to 10^12 ohms. While it helps prevent static buildup through chemical treatments, you'll often need additional protection like silver conductive bags. Keep in mind that it's not designed for repeated use. This foam provides excellent cushioning protection for delicate electronic devices.
Static dissipative foam bridges the gap between anti-static and conductive materials. You'll find it in either black (carbon-impregnated) or pink (surface-treated) versions, with surface resistance ranging from 10^5 to 10^9 ohms.
It's particularly effective for transportation and storage, as it slowly dissipates charges to the ground.
Conductive foam, identifiable by its black color, provides the highest level of protection with surface resistance below 10^6 ohms. It creates a Faraday cage effect, effectively blocking electromagnetic fields.
While it's ideal for electronics protection, you'll need to insulate it from direct contact with batteries to prevent drainage.
When selecting ESD foam, verify it meets EIA-541 standards and matches your specific protection requirements.
PE Foam Vs EVA Foam
When choosing between PE and EVA foam for electronics storage, understanding their distinct properties helps determine the best fit for your needs.
PE foam offers excellent chemical resistance and static protection, making it particularly suitable for storing sensitive electronic components. You'll find it's especially effective at dampening vibrations during transportation, and its high load-bearing capacity supports heavier electronics. Its odorless properties make it ideal for enclosed storage spaces.
EVA foam stands out for its superior elasticity and shock absorption capabilities. You'll appreciate its water resistance and closed-cell structure when protecting electronics from moisture damage.
It's also highly flexible, allowing for custom-molded shapes to fit specific electronic components. While both materials provide thermal insulation, EVA foam adds excellent electrical insulation properties to prevent short circuits.
Your choice between the two should depend on your specific requirements. Choose PE foam if you're primarily concerned with static protection and need a cost-effective solution with good vibration dampening.
Opt for EVA foam if you're looking for superior shock absorption, flexibility for custom shapes, and enhanced protection against environmental factors like moisture and UV radiation. Both options deliver reliable protection, but their unique strengths serve different storage needs.
Surface Resistance and Protection Levels
Surface resistance levels typically determine the effectiveness of protective foam in safeguarding your electronic components. When you're selecting protective foam, you'll encounter three main types with distinct resistance levels: conductive, anti-static, and static-dissipative foam.
Conductive foam offers the highest level of protection with a surface resistance of 10^3-10^5 ohms. You'll find it's ideal for highly sensitive electronic components that require rapid static charge transfer. If you're storing critical electronic equipment, this is your best option. The foam's high carbon content makes it naturally more conductive than other types.
Anti-static foam provides moderate protection with a surface resistance of 10^6-10^9 ohms. It's suitable when you need general electronic packaging and storage solutions without requiring the highest level of conductivity. You'll find it effective for most standard electronic components.
Static-dissipative foam, with a resistance of 10^8-10^11 ohms, works differently by dissipating static charges. You'll want to take into account this option particularly in high-humidity environments where static dissipation is more important than conductivity.
Each foam type complies with industry standards for ESD protection, but you'll need to match the resistance level to your specific storage requirements.
Color Coding in ESD Foams
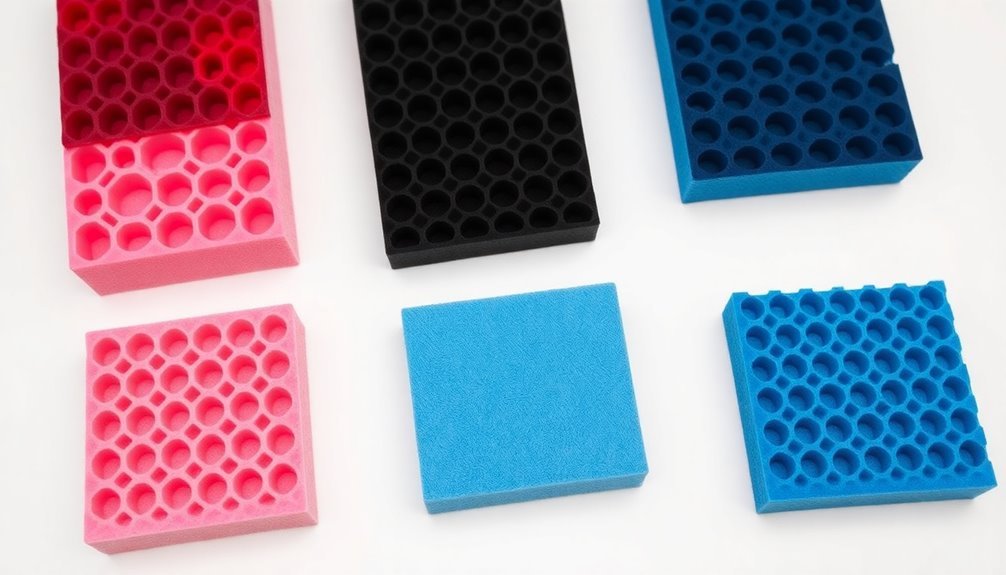

Color coding plays a vital role in identifying different types of ESD protective foams for electronics storage. When you're working with electronic components, you'll notice that pink foam is typically associated with anti-static properties. These pink foams have been chemically treated with anti-static agents, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic devices during storage and transport.
You'll find that black foams are generally conductive and provide Faraday cage-like protection, while blue containers offer anti-static properties that don't retain charges for extended periods. Regular surface resistance testing helps ensure these materials maintain their protective qualities. While color coding isn't a strict industry standard, it helps you quickly identify the appropriate foam for your needs.
When you're managing your electronics storage system, you should use color coding to streamline your inventory management and handling processes. However, don't rely solely on color identification – it's essential to verify that your chosen foam meets the required ESD protection standards.
You'll want to maintain consistency in your storage system and avoid mixing different types of foams, as this could compromise protection. Remember that some suppliers offer customized color options for specific applications, but maintaining a standardized color system in your facility will help prevent handling errors.
Materials and Manufacturing Methods
Through careful selection of materials, anti-static foam production combines specialized polymers with precise manufacturing techniques to create protective packaging for electronics.
You'll find four main materials used: polyurethane (PU) with its open-cell structure, polyethylene (PE), EVA, and EPE with their closed-cell designs. Each offers surface resistance ranging from 10^3 to 10^9, making them effective for static dissipation. The addition of pink dye coloring helps workers easily identify anti-static materials during handling.
The manufacturing process starts with the addition of conductive fillers and cross-linking to create antistatic pathways, particularly in PU foams.
When you're looking for custom shapes, manufacturers use die-cutting or waterjet cutting methods for precise dimensioning. For thicker protection, they'll employ lamination techniques, especially with PE foams that have a maximum single layer thickness of 6-7mm.
You can customize these foams extensively for your specific needs. Whether you need compartmentalized storage, eggcrate designs for enhanced cushioning, or precisely cut foam inserts, manufacturers can accommodate various specifications.
They'll consider factors like surface resistance requirements, antistatic duration, and environmental impact while maintaining high material quality standards for ideal electronics protection.
Choosing the Right Foam Type
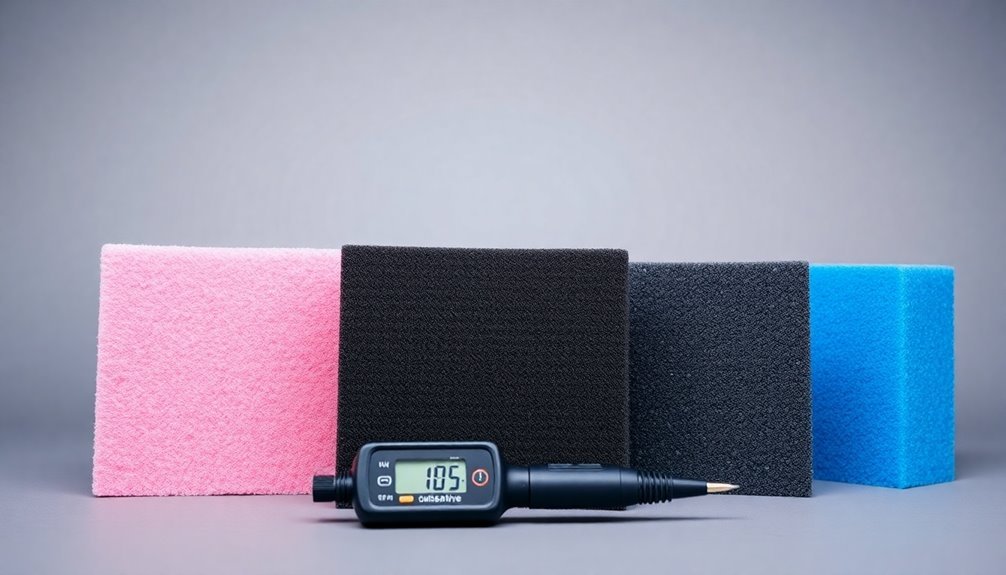

When selecting anti-static foam for electronics storage, you'll need to choose between three main types: anti-static, conductive, and static dissipative foams. Each type serves specific protection needs for your electronic components.
Anti-static foam, typically pink in color, dissipates electrostatic charges while allowing them to pass through. You'll find it's suitable for components that need basic static protection but don't require complete shielding. However, you might need to pair it with a static shielding bag for full protection. The foam's effectiveness is enhanced by humidity in the atmosphere.
If you're handling highly sensitive electronics, choose conductive foam. This black, carbon-filled material acts as a Faraday cage, blocking electromagnetic fields entirely.
Be careful when storing batteries in conductive foam, as it can drain them if their terminals make contact.
Static dissipative foam offers a middle-ground solution, allowing charges to flow gradually to the ground. Available in both black and pink varieties, it's perfect for work-in-progress situations where controlled discharge is essential.
Before making your choice, verify the foam meets EIA-541 standards for ESD-sensitive items.
Remember that anti-static foam isn't typically reusable, so plan accordingly for long-term storage needs.
Storage Requirements for Electronics
Proper storage requirements can make the difference between preserving your electronics and risking costly damage. You'll need to maintain specific environmental conditions, with temperatures between 10-27°C and humidity levels of 30-50%. Keep your devices away from direct sunlight and magnetic fields to prevent degradation and interference.
Before storing your electronics, back up all important data and clean them thoroughly using a microfiber cloth and compressed air for hard-to-reach areas. Don't use liquids directly on your devices.
When packing, fill empty spaces with appropriate materials and clearly label your boxes with handling instructions.
Position your electronics strategically in the storage unit. Don't stack heavy items on top of them, and keep them elevated off the floor using pallets or shelves. Place them away from the door to minimize exposure to temperature fluctuations and dust, but verify they're easily accessible if you need them frequently.
You'll want to use protective materials like anti-static foam and maintain adequate ventilation between items. For devices with lithium batteries, follow manufacturer guidelines carefully.
Monitor your storage environment regularly and verify proper security measures are in place to protect valuable equipment.
Foam Thickness and Protection
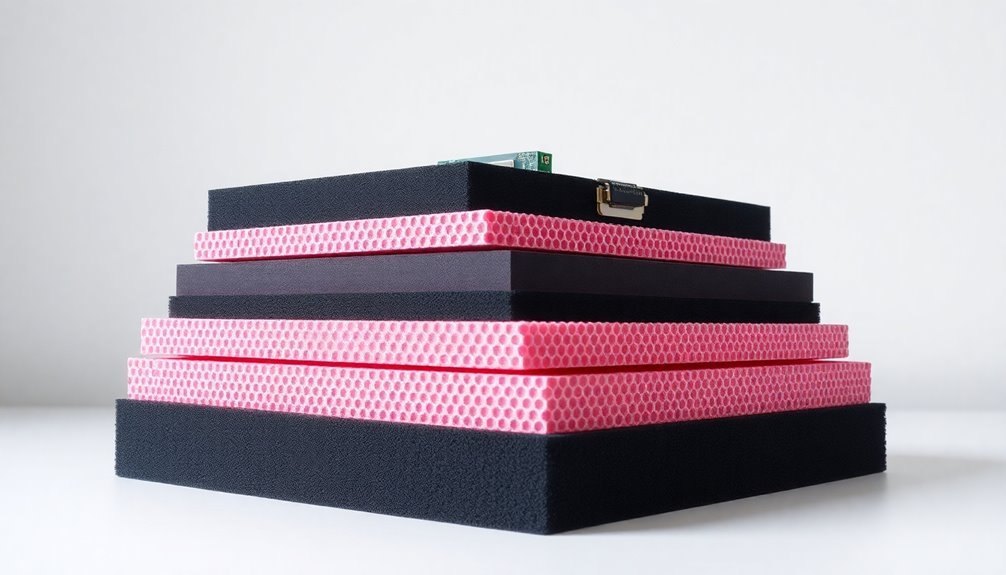

Selecting the right foam thickness is essential for protecting your electronic components from damage. You'll find anti-static foam sheets available in thicknesses ranging from 1/2" to 40 inches, giving you plenty of options for your specific needs.
When choosing thickness, consider that thicker polyethylene foams provide better structural support and protection for heavier electronics, while thinner options (1/4" to 1/2") work well for smaller items like circuit boards.
For the best protection of your electronic components, consider these key factors:
- Thicker foams offer enhanced shock absorption and vibration dampening, making them ideal for shipping larger equipment.
- Egg-crate foam designs provide additional cushioning and professional presentation for delicate devices.
- Closed-cell polyethylene foam resists punctures and tears, offering superior protection during transport.
- Anti-static properties prevent damaging electrostatic discharge while maintaining physical protection.
- Custom thickness options allow you to create precise fits for specific components.
Choose polyethylene foam when you need moisture resistance and durability, or opt for polyurethane foam if you're looking for a softer, more adaptable solution. Both materials can be treated with anti-static agents to meet EIA 541 standards for static decay, ensuring your electronics remain safe during storage and transport.
Static Control Performance Standards
Throughout the electronics industry, static control performance standards define the essential benchmarks for anti-static foam effectiveness. You'll need to guarantee your foam meets specific surface resistivity ranges for proper ESD protection. Conductive foams offer the highest protection at 10^3-10^5 ohms/square, while static dissipative foams provide moderate protection at 10^8-10^11 ohms/square.
| Foam Type | Resistivity Range | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Conductive | 10^3-10^5 Ω/sq | Highly sensitive components |
| Anti-Static | 10^6-10^9 Ω/sq | General electronics storage |
| Static Dissipative | 10^8-10^11 Ω/sq | Work-in-progress items |
To maintain compliance with industry standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20, you'll need regular testing and validation of your foam's performance. Check surface resistivity measurements periodically to confirm your foam maintains its protective properties. The effectiveness of anti-static foam isn't just about initial performance – you must consider long-term efficacy as well. Material selection plays a vital role, so choose specialized polymers or metalized films that meet your specific ESD protection requirements. Remember that different components may require different levels of protection, so match your foam type to your component sensitivity.
Custom Foam Solutions
When you're planning custom foam solutions for electronics storage, you'll need to evaluate design options like convoluted patterns, die-cut inserts, or layered configurations that best match your specific components.
Your material selection should align with your protection requirements, choosing between PU foam for lighter electronics, PE foam for heavier items, EVA foam for thermal management, or EPE foam for maximum cushioning.
These custom solutions can seamlessly integrate with your existing packaging systems through modular designs, standardized dimensions, and compatible closure mechanisms.
Design Process Options
The design process for custom foam solutions encompasses several critical stages that determine the effectiveness of electronic component protection. You'll need to carefully consider the specific requirements of your electronic components, including their size, weight, and sensitivity to static discharge.
By selecting the appropriate foam type and density, you're guaranteeing maximum protection against physical damage and electrostatic discharge.
When designing your custom foam solution, you'll work through these essential steps:
- Evaluating your components' protection needs and identifying the most suitable anti-static foam type (PE, EVA, EPE, or PU)
- Determining precise measurements and creating detailed component layouts for accurate die-cutting
- Selecting appropriate foam density based on your products' fragility and handling conditions
- Considering thermal management requirements and incorporating necessary features
- Finalizing design specifications for bonding and lamination processes if multiple layers are needed
The fabrication phase involves precision engineering techniques to create exact cuts and compartments. You can opt for die-cutting, custom shaping, or convoluted foam sets depending on your specific needs.
Professional foam fabricators will guarantee your design meets all protection requirements while maintaining cost-effectiveness and a professional appearance.
Integration With Packaging Systems
Integration of custom foam solutions with packaging systems requires careful alignment between protective materials and container specifications. You'll find that custom foam inserts can be seamlessly incorporated into various containers, including corrugated boxes and plastic cases, providing thorough protection for your electronics.
When you're selecting packaging components, you'll need to evaluate the compatibility between anti-static foam materials and your chosen container type. Materials like ETHAFOAM and EVAZOTE can be effectively integrated with ESD cardboard boxes and PP containers through processes such as die-cutting, injection molding, and bonding.
These techniques guarantee precise fits that maximize protection.
You'll achieve systematic protection by combining anti-static foam inserts with appropriate containers. The foam's ability to dissipate electrostatic charges safely works in tandem with ESD-protective containers to create a complete protective environment. This integration helps prevent both physical damage and static discharge during storage and transportation.
To optimize your storage system, you can utilize multilayer trays and convoluted foam designs that stabilize components while economizing space. This approach not only enhances protection but also improves storage efficiency for your electronic components.
Material Selection Guidelines
Selecting proper foam materials for your electronics storage requires a systematic approach based on multiple paramount factors. You'll need to carefully evaluate your specific requirements, considering both the physical characteristics of your electronics and the environmental conditions they'll face during storage or transport.
When choosing anti-static foam materials, you should focus on these vital guidelines:
- Consider the weight and rigidity of your components to determine whether you need soft or rigid foam solutions.
- Select between polyurethane and polyethylene based on your anti-static requirements and component sensitivity.
- Evaluate surface options – smooth surfaces work well for general protection, while eggcrate patterns offer enhanced cushioning for delicate items.
- Factor in the thickness requirements based on your electronic components' dimensions and fragility.
- Match your material choice with specific thermal management needs if temperature control is essential.
You'll want to guarantee your selected foam material includes appropriate chemical treatments for static dissipation while maintaining compatibility with your electronics.
For precision protection, consider working with custom die-cut solutions that perfectly match your components' shapes and sizes. This tailored approach will maximize protection while optimizing storage efficiency.
Long-Term Storage Considerations
Proper storage conditions play a vital role in maintaining the effectiveness of anti-static foam for electronics protection. When storing components long-term, you'll need to consider both the type of foam and the storage environment to guarantee maximum protection.
For sensitive electronics requiring complete protection, you should use conductive foam, which creates a Faraday cage effect. This black, carbon-filled foam offers superior shielding without needing additional static bags. However, don't use it with batteries, as it can drain their power through contact with conductive ends.
If you're working with components that need protection from static build-up but don't require full shielding, pink anti-static foam is suitable. Remember that you'll need to place these items in static shielding bags for complete protection, as this foam only prevents static build-up from friction.
Regular inspection of your storage foam is essential. While conductive foam can be reused after quality checks, anti-static foam typically isn't reusable due to quality degradation.
Keep in mind that anti-static foam has a surface resistance between 10^9 – 10^12 ohms, while conductive foam measures less than 10^6 ohms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Anti-Static Foam Lose Its Protective Properties if Exposed to Extreme Temperatures?
Yes, your anti-static foam can lose its protective properties when exposed to extreme temperatures. While EPE foam stays stable, other types will degrade above 80°C, potentially compromising their ability to prevent static buildup.
How Often Should Anti-Static Foam Packaging Be Replaced for Optimal Protection?
You'll need to replace your anti-static foam every 2-3 years under normal conditions. However, if you notice physical damage, discoloration, or frequent usage, you should replace it sooner to maintain maximum protection.
Is It Safe to Stack Multiple Layers of Different Anti-Static Foams?
You shouldn't stack different anti-static foams unless you've verified their compatibility. Mismatched foam types can cause static charge buildup and compromise protection. It's best to use uniform layers for safe electronics storage.
Can Anti-Static Foam Be Cleaned Without Compromising Its Protective Qualities?
Yes, you can safely clean anti-static foam using specialized anti-static foaming cleaners and microfiber cloths. Don't use harsh chemicals or abrasive methods, and always test on a small area first to maintain protection.
Do Vacuum-Sealed Anti-Static Foam Packages Provide Better Protection Than Regular Packaging?
Yes, you'll find vacuum-sealed anti-static foam packages offer superior protection compared to regular packaging. They'll prevent static discharge, reduce moisture exposure, eliminate dust contamination, and provide better physical protection for your components.
In Summary
Choose your anti-static foam carefully to protect your valuable electronics. You'll want to think about the foam's surface resistance, thickness, and compliance with ESD standards. Whether you select PE or EVA foam, make certain it meets your specific storage needs and protection requirements. Don't forget to check the foam's color coding and verify its long-term storage capabilities before making your final decision.





Leave a Reply