Friction buildup in data centers occurs primarily through connector wear, environmental stress, and contamination. You'll find that fretting corrosion, caused by micro-movements from vibration and thermal expansion, wears down protective metal plating on connectors. Airborne contaminants, including metal particles and chemical agents, can accumulate on surfaces and components, while black dust from iron oxide particles combines with airflow to create additional friction points. Temperature fluctuations and improper cooling management worsen these issues by promoting oxidation and component degradation. Understanding these friction sources will help you implement the right preventive measures to protect your data center equipment.
Connector Wear and Oxidation
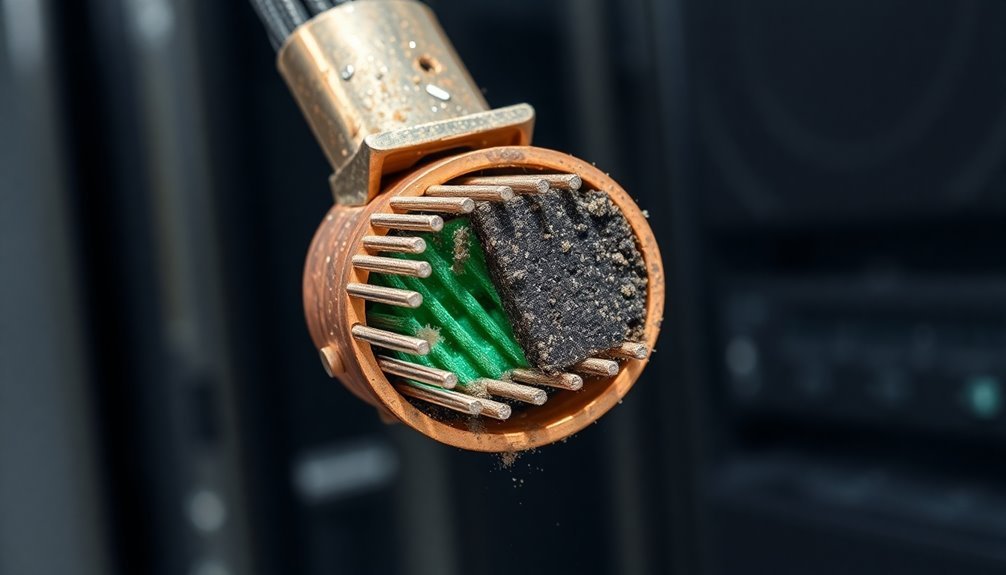

In modern data centers, connector wear and oxidation pose substantial reliability challenges. When you're dealing with constant vibrations and thermal cycles, your connectors become susceptible to fretting corrosion – a destructive process triggered by tiny movements between metal surfaces.
These micromovements wear through the protective metal plating, exposing the base material to oxidation. Elastic elements in design can help minimize these destructive movements.
You'll find this problem is particularly troublesome because the resulting oxide layer acts as an insulator, creating open circuits that lead to power failures and signal loss. The integrity of your connector's metal surface plays a vital role, as surface roughness and porosity can create pathways for moisture and contaminants to penetrate the protective coating.
To protect your connections, you'll need to focus on both material selection and preventive measures. Gold-plated or precious metal connectors offer better resistance to fretting corrosion, while clad metals provide superior protection compared to electroplated options.
You can markedly reduce the risk by applying connector grease during assembly, which minimizes metal-to-metal contact and prevents oxide buildup. Regular maintenance inspections help you identify potential issues before they escalate into serious problems.
Transportation Impact on Equipment
Transportation logistics frequently pose substantial challenges when moving data center equipment. When you're relocating servers and IT infrastructure, you'll face multiple risks that can impact equipment integrity and create friction points in your operations. Heavy components require specialized handling, and improper movement can lead to equipment damage and extended downtime.
State regulations often require special permits and police escorts for oversized loads. Your transportation strategy should focus on these critical aspects:
- Using motorized server rack tugs to reduce manual handling risks and labor hours by up to 80%
- Implementing white glove handling services for sensitive equipment movement
- Coordinating with experienced logistics providers who understand IT asset requirements
- Utilizing specialized trailers like RGN extendable units for safer transport
- Maintaining detailed inventory tracking systems to prevent loss and delays
You'll need to carefully plan your equipment moves to minimize potential damage. Proper design choices, such as reducing component dimensions, can cut transportation costs by 30-50%.
Don't overlook the importance of having the right infrastructure ready at your new location – this preparation will markedly reduce downtime during the relocation.
Remember that successful data center relocations depend heavily on coordinated project management and meticulous attention to handling procedures.
Environmental Stress Factors

Data centers are particularly vulnerable to airborne contaminants like metal particles and chemical agents that can wreak havoc on sensitive equipment.
Metal particles from friction and wear can accumulate over time, creating potential short circuits and compromising your system's reliability.
Chemical exposure from cleaning agents, industrial processes, and environmental pollutants can corrode components and degrade equipment performance, making proper air filtration systems essential for your data center's longevity. Static electricity discharges can damage sensitive IT components, making proper environmental monitoring crucial for preventing equipment failure.
Airborne Contaminants Impact Operations
Multiple airborne contaminants pose significant threats to data center operations, with outdoor air being the primary culprit. You'll find that urban locations are particularly vulnerable to sulfur corrosion, while air-side economizers can increase contamination risks even in areas with seemingly clean air. When diesel generators activate, they release harmful exhaust particles and nitrogen dioxide, further compromising air quality.
The impact of RoHS regulations has made electronic equipment more prone to corrosion in contaminated environments. The impact of these contaminants on your data center can be severe. They'll affect both your equipment and HVAC systems in several critical ways:
- Chemical pollutants corrode sensitive circuitry and damage electronic components
- Dust and particles clog server components, restricting airflow
- Overheated servers emit additional gaseous contaminants, creating a harmful cycle
- Poor air quality can trigger catastrophic equipment failures and fires
- HVAC components deteriorate faster, leading to cooling system breakdowns
You'll need to implement robust air quality management strategies to protect your facility. This includes installing chemical filtration systems, sealing all building penetrations, and using real-time atmospheric corrosion monitors. Maintaining proper air quality isn't optional – it's essential for preventing equipment damage and ensuring continuous operations.
Metal Particle Accumulation Risks
Beyond airborne pollutants, data centers face another significant threat: metal particle accumulation. Two particularly dangerous forms of metallic contamination you'll encounter are black dust and zinc whiskers, both of which can severely impact your facility's operations.
Black dust forms when iron oxide particles combine with airflow from handling units, often resulting from worn components and misaligned equipment. Regular preventative maintenance of air handling equipment is essential to minimize contamination risks. You'll find this conductive dust particularly troublesome as it adheres to magnetic and thermal components, potentially causing overheating and electrical shorts.
The consequences can be severe – over 200 data center fires in America, resulting in $12 million in damages, have been linked to black dust accumulation.
Zinc whiskers present another significant risk, especially in older facilities with raised floor HVAC systems. These microscopic filaments develop on electroplated steel surfaces due to molecular stress, growing from infrastructure components like floor tiles and pedestals.
To protect your facility, you'll need to implement specific prevention strategies: use non-zinc electroplated materials, install HEPA filters, and maintain proper floor tile sealing. Regular infrastructure inspections are vital for early detection and prevention of both black dust and zinc whisker formation.
Chemical Exposure Threatens Equipment
Data centers' most insidious threats often come from chemical exposure, particularly in the form of cleaning agents, construction materials, and fire suppression compounds. When these chemicals interact with your equipment, they can trigger environmental stress cracking (ESC), especially in plastic components, leading to premature failure and unexpected downtime.
You'll need to watch out for these common chemical exposure risks in your data center:
- Cleaning agents like isopropyl alcohol (IPA) that can accelerate stress cracking in plastic components
- Fire suppression gases, including halon, that may leave harmful residues on equipment
- Battery system chemicals that can leak and cause corrosion
- Construction materials releasing volatile compounds over time
- Chemical interactions between mechanical fasteners and adhesives that increase ESC risk
To protect your equipment, you'll want to implement strict chemical handling protocols and safeguard proper storage of all potentially harmful substances. Dry pipe systems using compressed air are essential to prevent water damage during fire suppression activities.
Regular inspections using copper and silver sensors can help you monitor corrosivity levels, while maintaining appropriate air cleaning systems will reduce chemical contamination.
Don't forget to provide thorough chemical safety training to your staff and enforce the use of proper PPE during maintenance activities.
Cooling System Maintenance Issues
Your regular filter inspection protocol must include checking for dust accumulation and debris that can substantially increase friction within the cooling system.
Neglecting these maintenance tasks can lead to severe energy inefficiencies in your cooling infrastructure.
When managing bearing maintenance schedules, you'll need to identify worn components before they create excessive mechanical resistance and strain.
These preventive measures directly impact your cooling system's efficiency, as clean filters and well-maintained bearings reduce unnecessary friction that can lead to increased power consumption and potential system failures.
Regular Filter Inspection Protocol
While maintaining a data center's cooling efficiency requires multiple components, proper filter inspection stands as one of the most critical protocols. You'll need to follow specific timelines, from daily checks to annual maintenance, to prevent friction-causing dust buildup and maintain ideal airflow.
ASHRAE recommends using MERV 11 or MERV 13 filters to achieve ISO class 8 cleanliness levels, though MERV 8 filters can work for continuous filtering. You'll find that neglecting these standards can lead to increased energy consumption and potential equipment damage. Trained cleaning staff must handle all filter maintenance to ensure proper safety protocols are followed.
Here's what you need to monitor in your filter inspection protocol:
- Daily visual checks for obvious dust accumulation and filter integrity
- Weekly examinations for clogs that could impair cooling efficiency
- Monthly filter replacements or thorough cleaning to prevent energy waste
- Quarterly detailed performance assessments of filter condition
- Bi-annual thorough maintenance to safeguard overall system efficiency
Remember that clogged filters strain your cooling systems, leading to increased PUE and higher energy costs. By implementing proper filter maintenance procedures and training your personnel accordingly, you'll prevent unnecessary friction buildup and maintain ideal cooling performance in your data center.
Clogged filters strain your cooling systems, leading to increased PUE and higher energy costs. By implementing proper filter maintenance procedures and training your personnel accordingly, you'll prevent unnecessary friction buildup and maintain ideal cooling performance in your data center.
Bearing Maintenance Schedules
Maintaining peak performance in cooling systems requires a thorough bearing maintenance schedule that addresses both preventive care and regular inspections. You'll need to implement regular checks for signs of wear, including seizures, cracks, and pitting that can lead to system inefficiencies and potential failures.
Your maintenance schedule should incorporate systematic inspections of bearing lubrication levels and quality. Don't skip cleaning the bearing environment, as contaminated lubricants can cause severe damage through corrosion and abrasion.
You'll want to monitor bearing temperatures consistently, as excessive heat often indicates developing problems that require immediate attention.
It's vital to have factory-trained technicians perform your maintenance tasks. They're equipped with specialized knowledge of precision cooling systems and can access manufacturer updates about engineering changes or recalls. You can't afford to rely on non-OEM service providers who might lack the expertise needed for these critical systems.
Neglected maintenance leads to increased friction, higher energy consumption, and costly system downtime. By following a structured maintenance schedule and addressing issues promptly, you'll extend your bearings' lifespan and maintain ideal cooling system performance.
Dust and Contamination Control
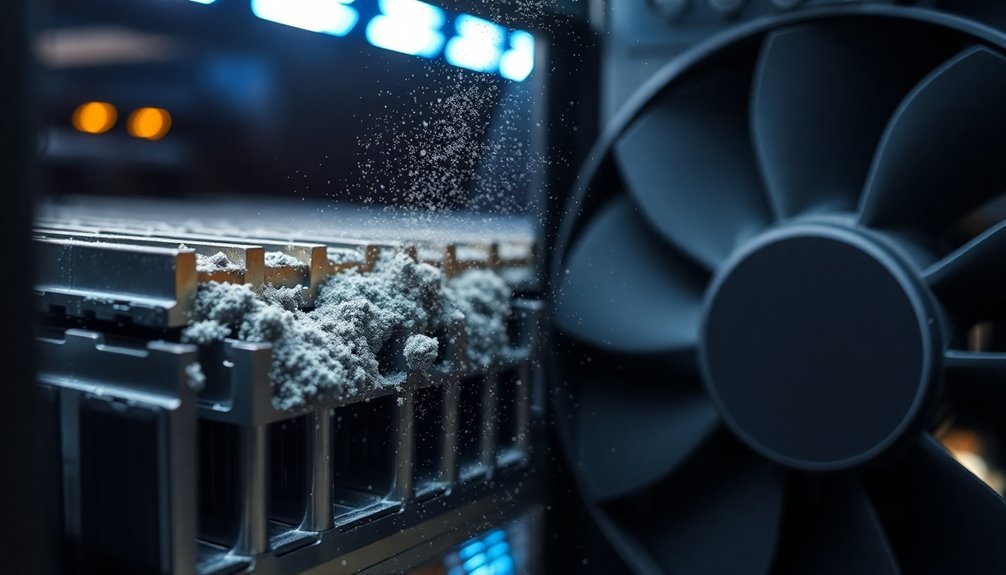
Effective dust and contamination control forms a critical foundation for data center operations. You'll need to combat both external and internal contamination sources that can lead to equipment damage and increased friction in your facility.
External sources include pollen, construction dust, and human-generated particles, while internal sources comprise particles from infrastructure and maintenance activities.
To maintain peak performance and reduce friction-related issues, implement these essential control measures:
- Install MERV-8 rated media filters and chemical filtration systems
- Use Dycem mats to reduce contamination from foot traffic by up to 99.9%
- Conduct regular cleaning with non-abrasive, non-static cleaning agents
- Monitor environmental conditions through sophisticated tracking systems
- Perform annual particle count and airflow tests
You'll want to establish a thorough cleaning schedule that includes vacuuming, mopping, and thorough equipment wipedowns. Remember to pay special attention to server racks, cooling systems, and overhead raceways.
Airflow Management Challenges
Proper airflow management stands as one of the most critical challenges you'll face in data center operations. You'll encounter issues like hot air recirculation, where exhaust air mixes with cold intake air, and bypass airflow that wastes your cooling resources. These problems can substantially impact your data center's efficiency and reliability.
Your equipment placement and maintenance practices directly affect airflow dynamics. When you don't properly maintain cooling systems or allow dust to accumulate, you're creating conditions that can lead to system strain and potential failures. You'll need to address both equipment-level and facility-wide challenges to maintain efficient airflow.
| Challenge Type | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Hot/Cold Containment | Temperature inconsistencies | Install containment barriers |
| Cable Management | Restricted airflow | Implement structured cabling |
| Rack Population | Cooling inefficiencies | Use appropriate blanking plates |
| System Monitoring | Delayed response to issues | Deploy environmental sensors |
Don't overlook the importance of proper monitoring systems and staff training. Without adequate CFD modeling and environmental monitoring, you won't be able to predict or respond to cooling failures effectively. Regular maintenance, proper documentation, and strategic equipment placement are essential for maintaining efficient airflow patterns.
Legacy Equipment Problems

While managing airflow challenges remains a constant priority, your data center's legacy equipment poses an equally pressing set of problems. Aging infrastructure can substantially impact your facility's operational efficiency, safety, and bottom line.
Your outdated equipment requires more power to operate, leading to increased energy costs and a larger carbon footprint. When your legacy systems deteriorate, you'll notice slower processing times and reduced storage capacity.
You'll face several critical issues with aging infrastructure:
- Your older equipment often operates below capacity while still drawing unnecessary power
- You're at higher risk of arc flash incidents due to deteriorating insulation
- Your outdated cooling systems struggle to handle dense, power-hungry IT equipment
- You'll experience more frequent unplanned outages and system downtime
- Your maintenance costs will continue to rise as equipment ages
To address these challenges, you'll need to implement regular inspections and consider modernizing your infrastructure. By upgrading your legacy systems, you can boost reliability, improve efficiency, and meet sustainability goals.
Incorporating Data Centre Infrastructure Management (DCIM) technology will help you predict and prevent electrical failures while optimizing your facility's performance.
Temperature Regulation Solutions
Temperature management demands a multi-pronged approach in modern data centers. You'll find that implementing the right cooling solution directly impacts your facility's friction management and overall efficiency.
Whether you're using traditional air cooling with CRAC units or advanced liquid cooling systems, your choice must align with your specific operational needs.
If you're running a smaller facility with legacy equipment, you'll want to think about air cooling solutions with hot and cold aisle configurations.
However, if you're dealing with high-density server racks, liquid cooling solutions offer superior heat removal capabilities. You can choose between immersion cooling or direct-to-chip systems, both of which effectively manage heat in high-power environments.
For facilities in appropriate climates, you'll find evaporative cooling provides an efficient alternative, though you'll need to monitor water quality closely.
To enhance your temperature regulation further, you should implement smart technology solutions. By incorporating AI-driven monitoring systems, you can reduce cooling energy usage by up to 40%, as demonstrated by Google's DeepMind implementation.
These smart systems continuously adjust cooling parameters based on real-time data, ensuring ideal temperature control while minimizing friction-related issues.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies

Implementing robust preventive maintenance strategies safeguards your data center against friction-related failures and performance issues. You'll need to focus on both environmental cleanliness and power system maintenance to minimize friction risks effectively.
Regular cleaning of air intakes, ducts, and filters maintains proper airflow while preventing dust accumulation that can cause mechanical wear.
Your preventive maintenance plan should include these essential activities:
- Monitor temperature and humidity levels continuously to detect potential friction-causing conditions
- Use anti-static cleaning tools and implement proper grounding measures to prevent static electricity buildup
- Conduct regular inspections of power cables, connections, and circuit breakers for signs of wear
- Test backup systems and UPS units to confirm they're ready during critical situations
- Document all maintenance activities and create a thorough schedule for routine checks
Don't forget to leverage IoT sensors and monitoring software to track performance metrics in real-time. This data-driven approach helps you identify potential friction issues before they escalate.
Train your staff to recognize warning signs and report concerns promptly. By maintaining detailed records of all maintenance activities, you'll establish a reliable history of system performance and maintenance effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Humidity Affect Friction Buildup in Data Center Components?
When humidity's too low in your data center, you'll see increased static electricity and friction between components. When it's too high, you'll get moisture buildup that causes corrosion and additional friction issues.
Can Electromagnetic Interference Contribute to Accelerated Connector Wear in Data Centers?
Yes, EMI can accelerate your connector wear by causing micro-vibrations and unwanted electrical currents. You'll notice increased friction and degradation where connectors meet, especially in high-frequency environments within your data center.
What Role Does Static Electricity Play in Friction-Related Issues?
Static electricity intensifies friction by creating electrostatic charges that attract dust and particles to your equipment. You'll notice it can cause surface wear, component damage, and increased resistance between connecting materials.
How Do Different Metal Compositions Affect Friction Rates in Data Centers?
You'll find that metal composition directly impacts friction rates through resistivity levels. Higher-resistance metals like stainless steel and aluminum create less friction, while dissimilar metal combinations can accelerate wear through galvanic action.
Does Altitude Impact Friction Buildup in Data Center Equipment?
Yes, altitude affects friction in your data center equipment. You'll notice increased friction due to reduced cooling efficiency at higher altitudes, which leads to higher operating temperatures and greater wear on moving components.
In Summary
You'll find that friction buildup in data centers stems from multiple interconnected factors. By addressing connector degradation, transportation damage, environmental stress, and cooling system inefficiencies, you can minimize operational friction. Don't overlook the impact of dust accumulation and poor airflow management. Regular maintenance checks, proper temperature control, and updating legacy systems are your best defenses against friction-related problems in your data center.





Leave a Reply