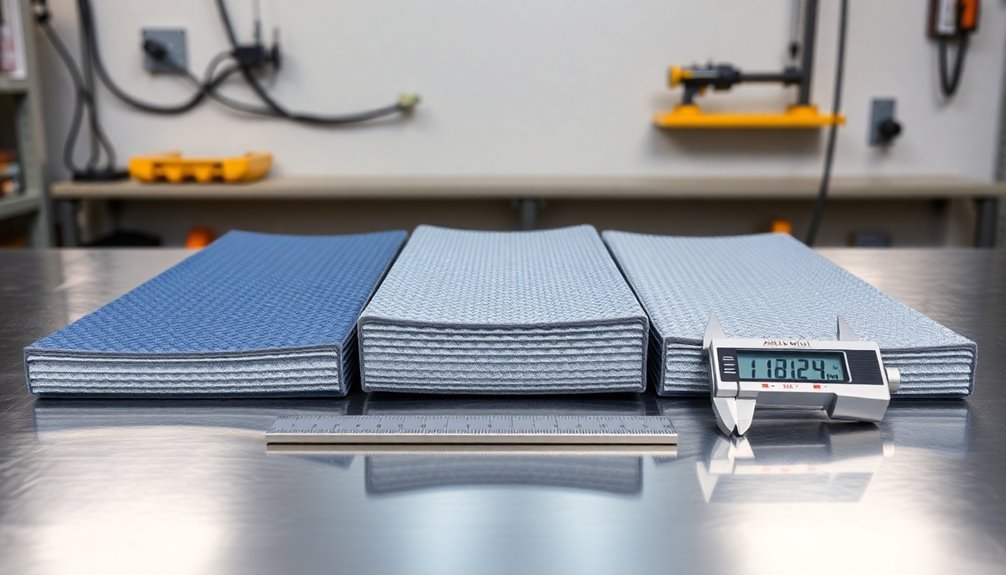
When choosing an ESD mat thickness, you'll want to first match it to your application – use 1-2mm for electronics assembly and up to 3mm for high-traffic areas with heavy equipment. Next, consider your mat material, as rubber mats maintain properties better in varied conditions while vinyl mats may require careful thickness selection due to form changes over time. Finally, verify your chosen thickness meets resistance testing requirements, with readings between 10^6 and 10^12 ohms for RTT testing and 10^6 to 10^9 ohms for RTG testing. Understanding these key factors will help you make a more informed decision for your specific needs.
Understanding Application-Based Thickness Requirements

Three key considerations drive the selection of ESD mat thickness: application requirements, regulatory compliance, and practical usability. When choosing your ESD mat thickness, you'll need to carefully evaluate your specific application needs to guarantee peak performance and protection.
For electronics manufacturing and assembly workstations, you'll want to select thinner mats between 1mm and 2mm. These provide sufficient protection while maintaining a low profile that won't interfere with your work. The mats feature embedded carbon layers that effectively dissipate static charges. The standard 2mm thickness offers optimal performance for most electronics applications.
If you're setting up an area that experiences heavy foot traffic or requires supporting substantial equipment, opt for thicker mats up to 3mm for enhanced durability.
You don't need to worry about ESD mat thickness for high-voltage applications, as these mats are specifically designed for handling sensitive electronic components.
If you're in specialized industries like pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturing, you'll need to verify that your chosen thickness meets any additional regulatory requirements beyond standard ESD specifications.
Remember that thickness isn't the only factor determining effectiveness – your mat must meet ANSI/ESD S4.1 and ANSI/ESD S20.20 resistance standards regardless of its thickness.
Focus on selecting a thickness that balances protection requirements with practical workspace considerations.
Material Type Affects Thickness Selection
Material selection plays an essential role in determining the ideal thickness of your ESD mat. When choosing between vinyl and rubber materials, you'll need to take into account their distinct properties and how they influence the required thickness of your mat.
Rubber mats maintain consistent ESD properties regardless of environmental conditions and offer superior heat resistance. You'll find that rubber mats work well in thicker formats, especially for applications involving heat-generating equipment or high-traffic areas. Their durability makes them ideal for floor applications where thicknesses of 3mm are common. The high chemical resistance of rubber mats makes them particularly suitable for industrial settings.
Vinyl mats, while easier to cut and more cushioned, require careful thickness consideration due to their tendency to change form under different conditions. You'll find that thinner profiles (around 1-2mm) are ideal for tabletop applications, as vinyl mats can become harder over time. These mats should be connected to proper grounding accessories for optimal static control.
When examining material composition, reflect on whether you need a single-layer, two-layer, or three-layer mat. Two-layer mats, combining conductive and dissipative layers, often require additional thickness to maintain proper electrical properties while meeting the standard resistance requirements of less than 10^9 ohms/square.
Performance Testing Different Thicknesses

When testing ESD mat thickness performance, you'll need to conduct both Resistance-Top-To-Top (RTT) and Resistance-To-Groundable Point (RTG) measurements to verify compliance with ANSI/ESD S4.1 standards.
For RTT testing, place two 5-pound electrodes 10 inches apart and at least 2 inches from any edge. Your readings should fall between 10^6 and 10^12 ohms to confirm proper surface conductance across different thicknesses. Surface resistance measurement procedures should be performed without cleaning the mat surface first.
For RTG testing, you'll want to position one 5-pound electrode at the mat's furthest convenient point while connecting the other lead to ground. Your measurements should register between 10^6 and 10^9 ohms. Use a specialized instrument with 100VDC open circuit voltage for accurate readings. Thinner mats between 1.5 to 2mm typically provide better component stability and prevent bouncing during handling.
Remember that thickness can affect how your mat performs within these ranges. Regardless of thickness, your mat must maintain dissipative properties, falling between 10^5 and 10^11 ohms/square.
If your readings show conductive properties (less than 10^5 ohms/square), the mat won't provide adequate ESD protection. Regular testing is essential since the mat's electrical properties can change over time, potentially affecting its ESD protection capabilities across different thicknesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can ESD Mats Be Stacked to Achieve Better Static Protection?
No, you shouldn't stack ESD mats. It won't improve static protection and could actually compromise your grounding system's effectiveness. Each mat is designed to work independently with specific electrical properties for proper static control.
How Often Should ESD Mats Be Replaced Under Normal Working Conditions?
Under normal working conditions, you'll need to replace your ESD mat every 1-2 years. However, you should monitor it regularly and replace it sooner if you notice physical wear or it fails resistance testing.
Do Temperature Fluctuations Affect the Thickness of ESD Mats Over Time?
Yes, temperature fluctuations will affect your ESD mat's thickness over time. You'll notice more changes in vinyl mats, which can soften and deform, while rubber mats maintain their thickness better in varying temperatures.
Will Cleaning Solutions Cause ESD Mats to Deteriorate or Lose Thickness?
Yes, harsh or incompatible cleaning solutions can cause your ESD mat to deteriorate and lose thickness over time. You'll need to use manufacturer-approved cleaners and follow proper maintenance guidelines to prevent damage.
Are Thicker ESD Mats More Resistant to Punctures From Sharp Components?
Yes, you'll find that thicker ESD mats offer better resistance to punctures from sharp components. They provide more material depth to prevent penetration, especially when you're working with pointed tools or parts.
In Summary
When you're selecting an ESD mat thickness, you'll need to weigh your specific application requirements, material composition, and performance testing results. Don't just opt for the thickest or thinnest option available. Instead, consider your workspace conditions, the type of components you'll be handling, and conduct thorough resistance testing. Making an informed choice will guarantee ideal static protection for your sensitive electronics.




Leave a Reply