Grounded tool kits are essential for protecting your electronic components from electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. When you work with sensitive electronics, static electricity can build up on your body or tools, potentially causing immediate or long-term damage to components. Using grounded tools provides a safe path for electrical currents to flow into the ground instead of through your devices. You'll prevent voltage fluctuations, reduce shock risks, and maintain stable working conditions for precision tasks. Quality grounded tools also improve work accuracy and help guarantee continuous operation of your equipment. Understanding proper ESD protection can make the difference between success and costly repairs.
Understanding ESD Safety Fundamentals
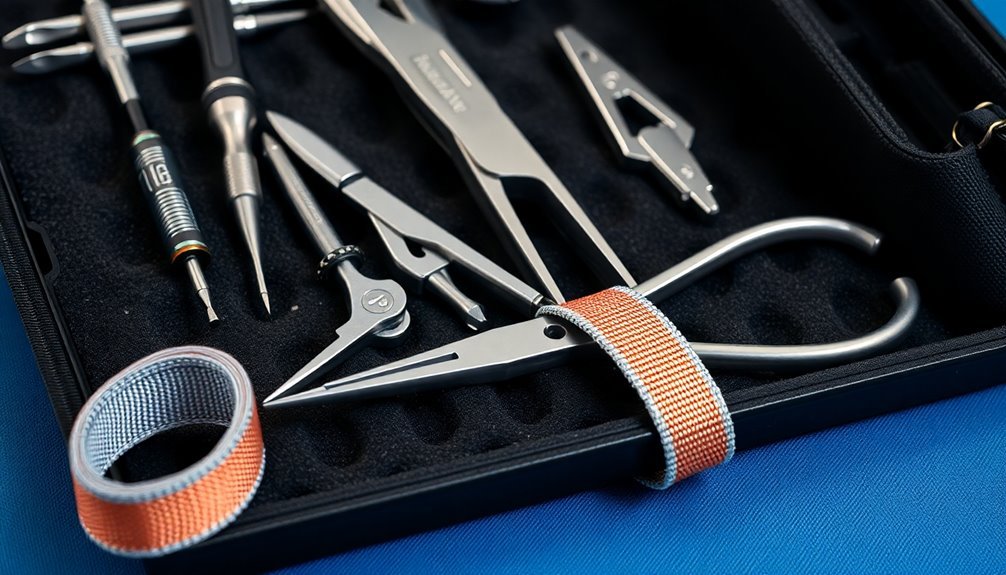
Static electricity poses a significant threat to electronic components, making ESD safety measures essential for anyone working with sensitive equipment.
When you handle electronic devices without proper protection, you risk causing costly damage through electrostatic discharge, which can instantly destroy sensitive components or create latent defects that emerge later.
You'll need to understand that ESD safety revolves around three core principles: grounding, bonding, and controlling your work environment. By using grounded tools and wearing antistatic clothing, you're actively preventing static charge buildup that could harm your electronics. Regular testing of grounding accessories ensures their continued effectiveness in protecting your equipment.
Your movement, synthetic materials, and uncontrolled static sources in your workspace all contribute to ESD risks.
To protect your electronic components effectively, you must implement thorough ESD control measures. This means you'll need to use grounded tools, maintain proper bonding between conductive surfaces, and shield sensitive components from external charges.
You should also consider the role of environmental factors – controlling temperature and humidity levels helps reduce static electricity generation.
Benefits of Grounded Tool Protection
Safety lies at the heart of grounded tool protection, offering multiple layers of defense for both you and your electronic equipment.
When you're working with sensitive electronics, grounded tools create a reliable path for potentially dangerous electrical currents to flow safely into the ground instead of through you or your devices. This protection isn't just about preventing immediate damage – it's about guaranteeing long-term reliability and safety in your electronic work. Static electricity discharge risks are significantly minimized in hazardous work environments.
Protect Your Investment
Grounded tools prevent voltage fluctuations and electrical noise that can damage sensitive components, helping you avoid costly repairs and replacements while maintaining system stability.
Enhance Your Safety
You'll substantially reduce the risk of electrical shock, as grounded tools direct surplus electricity away from your hands and body during operation.
Improve Work Quality
By eliminating electrical interference and maintaining stable voltage levels, you'll achieve more precise and reliable results in your electronic work, especially when dealing with sensitive components.
Proper grounding guarantees continuous operation and protects against data loss, making it essential for any serious electronics work.
When you invest in grounded tools, you're not just following safety protocols – you're protecting yourself and your equipment while improving the quality of your work.
Common Grounded Tool Applications
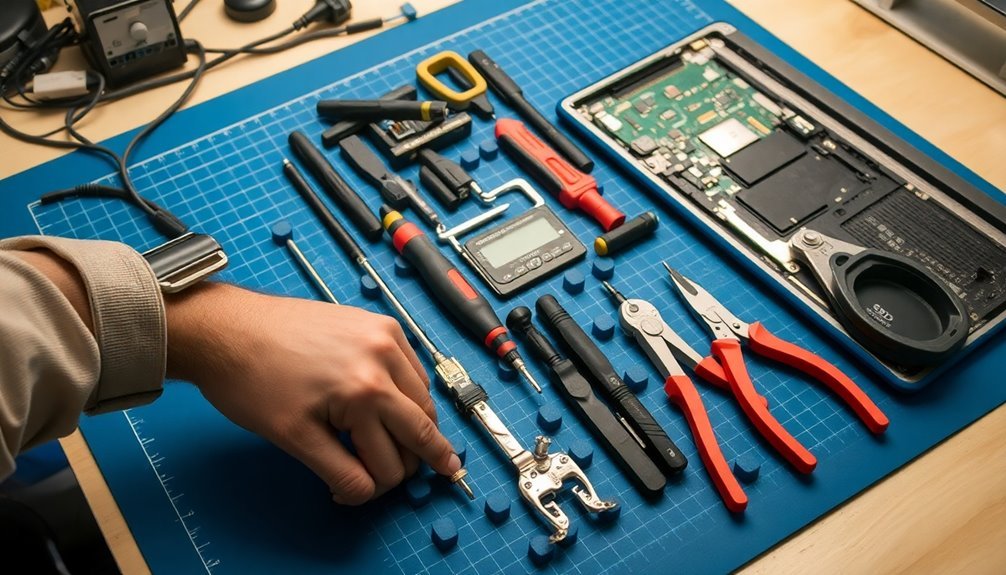

When you're working with circuit testing equipment, grounded tools guarantee accurate measurements while protecting sensitive components from electrostatic discharge.
Anti-static wrist straps are essential when handling computer components to prevent accidental static electricity damage.
You'll need properly grounded multimeters, oscilloscopes, and logic analyzers to perform reliable diagnostics on electronic circuits.
For precision surface mount work, you'll require specialized grounded tools like anti-static tweezers, fine-tipped soldering irons, and ESD-safe microscopes to safely handle and install tiny components.
Circuit Testing Equipment
The essential role of circuit testing equipment extends across numerous applications where grounded tools guarantee both safety and accuracy. When you're working with electronic circuits, you'll need properly grounded testing equipment to perform various specialized tasks while protecting yourself and your components from electrical hazards. Modern test systems can perform massively parallel testing of up to 20 boards simultaneously to maximize efficiency.
- You'll rely on In-Circuit Testing (ICT) to examine individual components and circuits on PCBs, ensuring each element functions correctly within the broader system.
- For digital components, you'll use Boundary Scan Testing to analyze test patterns and responses, helping you identify potential issues in complex circuits.
- When dealing with power systems, you'll need High-Current Testing equipment to verify circuit breakers and current relays, ensuring they operate within specified parameters.
Your testing arsenal should include essential tools like oscilloscopes for signal visualization, signal generators for calibration, and LCR meters for component measurement.
Don't forget to maintain proper grounding connections through secure cables and verified outlet grounds. By using a master ground plate, you'll establish consistent grounding across all your test equipment, which is vital for accurate readings and compliance with safety standards.
Precision Surface Mount Work
Successfully executing precision surface mount work demands specialized grounded tools that protect sensitive components from static discharge while guaranteeing accurate placement. You'll need high-quality metric nut drivers and precision screwdrivers with rotating tops, particularly when dealing with components secured with Loctite. These tools aren't just for convenience – they're essential for preventing static electricity damage that can destroy sensitive electronics.
When you're working with surface mount technology (SMT), you'll find that proper grounding isn't optional. Your tools must maintain consistent ground connection to prevent static buildup, which can instantly damage components. The process allows for extreme miniaturization capabilities compared to traditional through-hole technology. Using grounded equipment also protects you from electrical shocks while improving the overall reliability of your work.
For professional-grade SMT assembly, you'll need to complement your hand tools with precision placement machines. These systems use advanced vision technology and robotic arms to guarantee exact component positioning.
Don't forget to maintain proper grounding throughout your workspace – implementing star grounding techniques helps eliminate ground loops and reduces signal interference. Regular tool calibration and alignment checks will help maintain the accuracy and reliability of your SMT work.
Selecting Quality ESD Tool Kits
When you're choosing an ESD tool kit, start by examining the anti-static properties of each component through their surface resistivity ratings and material specifications.
You'll need to verify that the tools provide adequate discharge protection by checking their static dissipative ranges, which should typically fall between 1×10^6 and 1×10^9 ohms. Proper ESD protection is crucial since sensitive electronic components can be damaged by static discharge events as low as 100 volts.
Testing the ground connection points and measuring the discharge rates using an ESD field meter will confirm your kit's effectiveness in preventing potentially damaging static buildup.
Evaluating Anti-Static Components
Properly evaluating anti-static components and ESD tool kits requires understanding both material properties and industry standards. When you're selecting anti-static tools and materials, you'll need to take into account both volume and surface resistivity measurements, though surface resistivity often provides more reliable indicators of ESD protection performance. Regular testing helps maintain proper discharge capability over time.
Material composition plays a vital role, with options ranging from conductive carbon-loaded plastics to specialized dissipative polymers.
- You'll want to check that tools meet surface resistivity requirements of 10^6 to 10^9 ohms for ESD safe grips, while ensuring they're made from materials resistant to chemicals and solvents for long-term durability.
- Don't forget to evaluate the physical form and surface characteristics, as surface roughness can substantially impact anti-static properties and overall performance.
- Make sure your selected components comply with industry standards like ANSI/ESD.S20.20 and DOD-HDBK-263, as these set the baseline for reliable ESD protection.
Pay attention to moisture content in materials, as it affects static discharge capabilities. When evaluating complete tool kits, verify that they incorporate both conductive and dissipative materials to create an extensive ESD protection system.
Measuring Discharge Protection Levels
Building on the foundation of anti-static component evaluation, measuring discharge protection levels requires a systematic approach to selecting quality ESD tool kits. You'll need tools that can accurately measure static fields, ground impedance, and surface resistance to guarantee compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20 and BS EN 61340-5-1 standards.
| Test Type | Measurement Range | Required Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Static Field | 0-20kV/inch | Field Meter |
| Ground Impedance | 0-1000MΩ | Resistance Tester |
| Surface Resistance | 103-1012Ω | Surface Meter |
When measuring discharge protection, you must verify that your tools can detect and count ESD events that could damage sensitive electronics. Your testing equipment should facilitate both contact and air-gap discharge tests according to IEC 61000-4-2 specifications. Regular calibration of these instruments is vital for maintaining accuracy. You'll want to focus on tools that can measure the effectiveness of your TVS diodes and other protection circuits, guaranteeing they provide appropriate clamping voltages and discharge paths. Remember to document all measurements as part of your compliance verification plan, and maintain records of regular testing to demonstrate ongoing adherence to industry standards.
Proper Maintenance of Grounded Tools

The maintenance of grounded tools demands consistent attention to guarantee both safety and peak performance. You'll need to establish a regular cleaning routine, proper storage practices, and consistent inspection procedures to keep your tools in optimum condition.
For electronics work, you'll want to focus on these critical maintenance aspects:
- Clean your tools after each use with a dry rag, and perform deep cleaning periodically using damp cloths and lightly oiled cotton swabs. Don't forget to use compressed air to clear vents and crevices of debris.
- Store your tools in their original cases or climate-controlled drawers, keeping them away from moisture and extreme temperatures. Your garage or basement can work well if the environment isn't too humid.
- Inspect power cords regularly for fraying or damage, and check prongs for proper alignment. Don't attempt to repair damaged cords yourself – always seek professional help.
You'll also need to maintain moving parts with machine oil and keep battery contacts clean. For battery-operated tools, implement a regular charge-discharge cycle every couple of weeks, and store batteries in a cool, dry place to extend their lifespan.
For battery-operated tools, implementing a regular charge-discharge cycle every couple of weeks is crucial. This helps in preventing battery degradation and ensures the tools remain functional over time.
Additionally, storing batteries in a cool, dry place is essential to extend their lifespan. This environment prevents excessive wear and tear, keeping the batteries in good condition for a longer period.
Workplace Safety and Compliance Standards
Within today's electronics workplace, safety standards and compliance requirements form the backbone of protecting both workers and sensitive equipment. You'll need to comply with IEC 61508 series standards and OSHA regulations, particularly when working with electrical and electronic systems. These standards emphasize the critical importance of using properly grounded tools and following lockout/tagout procedures.
You're required to implement thorough safety measures, including proper PPE selection and ESD protection protocols. When you're handling sensitive electronics, you must use antistatic wrist straps and mats to prevent costly damage from static electricity.
Regular inspection of your grounded tools and equipment isn't just recommended – it's essential for maintaining compliance and preventing workplace accidents.
Remember that you're legally obligated to guarantee your workplace meets OSHA requirements. Failing to comply with these standards, especially lockout/tagout procedures, can result in severe penalties.
You'll need to maintain proper documentation of your safety protocols and implement regular training programs. By using properly grounded tool kits and following established safety procedures, you're protecting your workers from electrical hazards while safeguarding sensitive electronic components from ESD damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Grounded Tools Be Safely Used in Wet Environments?
While grounded tools provide better safety, you shouldn't use any electrical tools in wet environments. If you must work in damp conditions, make certain you're using GFCI protection and proper protective gear.
How Often Should Grounding Resistance in Tool Kits Be Tested?
You should test your tool kit's grounding resistance every 5-9 months, following standard testing intervals. Don't wait longer, as seasonal changes can affect resistance values and compromise your equipment's safety performance.
What's the Average Lifespan of Esd-Safe Coating on Grounded Tools?
You'll typically get 1-2 years from ESD-safe coatings on your grounded tools, but this varies based on your usage environment. Regular cleaning, proper storage, and avoiding harsh solvents will maximize the coating's lifespan.
Do Grounded Tools Require Special Storage Conditions Between Uses?
Yes, you'll need to store grounded tools in dry, non-conductive containers and maintain their grounding connections. Keep them away from moisture, extreme temperatures, and electrical circuits to protect their functionality between uses.
Can Regular Tools Be Converted to Esd-Safe Tools Through Modifications?
You can't reliably convert regular tools to ESD-safe tools. Material replacement is essential, as standard tools lack proper conductive properties. It's safer and more effective to purchase purpose-built ESD-safe tools instead.
In Summary
You can't underestimate the importance of grounded tool kits in electronics work. They're your first line of defense against costly ESD damage and help guarantee both your safety and the integrity of sensitive components. By investing in quality grounded tools and maintaining them properly, you'll meet workplace safety standards while protecting valuable equipment. Make grounded tool kits an essential part of your electronics toolkit – they're worth every penny.





Leave a Reply