Regular testing of your anti-static floor mat is essential to protect against costly electronic damage and equipment failures. ESD-related losses cost industries billions annually, with component failures accounting for up to 33% of total failures. Your mat's effectiveness can deteriorate over time due to wear, contamination, or environmental factors like humidity changes. By conducting routine resistance-to-ground (RTG) tests, you'll guarantee proper static dissipation and catch potential issues before they lead to expensive damage. A properly maintained anti-static mat delivers an impressive 900-2300% return on investment, making it a critical part of your ESD protection strategy. The full impact of ESD protection extends far beyond what meets the eye.
The Cost of ESD Damage

In the electronics industry, ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) damage inflicts staggering financial losses ranging from $0.5 to $5 billion annually.
You'll find that component failures due to ESD can account for up to 33% of total failures, with replacement costs varying from mere cents for simple diodes to hundreds of dollars for complex hybrid components.
When you factor in repair, rework, shipping, labor, and overhead costs, the total impact becomes even more significant. Businesses that experience ESD-related data loss events often struggle to recover their critical information.
What's particularly challenging is that ESD damage often goes undetected, making it difficult to justify prevention budgets.
You're looking at static losses that vary dramatically across the supply chain: component manufacturers face losses of 16-22%, subcontractors 9-15%, contractors 8-14%, and end-users experience the highest at 27-33%.
What's worse, ESD damage can create latent defects that aren't immediately apparent but lead to device failure over time.
You'll find these hidden costs in customer returns and field service expenses, which often exceed your in-house scrap and rework costs. Major companies like Western Electric have demonstrated 900-2300% return on their ESD prevention investments.
Industry experts have found that implementing ESD prevention programs can deliver an impressive ROI of 3:1 to 11:1, making regular testing and maintenance essential for protecting your bottom line.
Understanding Static Buildup Risks
You'll find that static buildup can severely damage electronic components through both visible and invisible electrostatic discharges (ESD).
Regular resistance-to-ground testing is essential to ensure your anti-static floor mats are functioning properly.
Your sensitive equipment might suffer from undetected ESD events that gradually weaken components, leading to premature failures or intermittent malfunctions.
What's particularly concerning is that many ESD-related damages occur without any noticeable sparks or immediate signs of destruction, making it essential to implement proper preventive measures. These incidents contribute to billions in losses across industries annually due to damaged electronic components.
Static Damage to Electronics
Static electricity poses a significant threat to modern electronics, with damages running up into billions of dollars annually across industries. When you handle electronic components without proper protection, you're risking severe damage that isn't always immediately visible. The effects can range from instant component failure to latent defects that shorten your device's lifespan.
Your electronic components are particularly vulnerable to electrostatic discharge (ESD) in several ways:
- Metal melt and junction breakdown can occur in sensitive components like microprocessors and memory chips.
- Magnetic storage devices can suffer data corruption or complete data loss.
- Integrated circuits may experience oxide failure, leading to immediate or delayed malfunction.
You'll find that static buildup happens in everyday situations you mightn't expect. Simply walking across a carpeted floor, pulling tape from a dispenser, or handling plastic component bags can generate enough static to damage sensitive electronics. Low humidity environments significantly increase the risk of static electricity buildup and discharge. The sudden release of current between charged objects can occur through simple friction or material separation.
The ESD Association's estimates show these damages can cost up to $5 billion annually, affecting both manufacturing yields and product quality. That's why proper ESD prevention measures aren't just helpful—they're essential for protecting your valuable electronic investments.
Hidden ESD Event Threats
Many hidden ESD threats lurk in everyday activities that you wouldn't suspect of causing damage to electronic components. Simply walking across carpet, removing your jacket, or getting up from your chair can generate thousands of volts of static electricity. Specialized ESD control flooring provides a critical conductive pathway to safely discharge static buildup.
While older electronic components had gate protection devices to shield against ESD strikes, modern electronics often lack these safeguards.
What's particularly concerning is that sensitive electronics can be damaged by discharges under 25 volts – far below what you'd feel or notice.
These invisible threats become even more dangerous in dry environments where static charges build up more easily. You mightn't realize that synthetic materials in your workspace, including packaging materials and furniture, are constantly generating static potential.
The real danger lies in the fact that ESD damage isn't always immediately apparent. Your components might appear to function normally at first, only to fail later during critical operations.
The financial impact of these hidden threats is staggering, costing industries billions annually. As electronic devices become increasingly complex with smaller circuits, they're more vulnerable to ESD damage.
That's why you'll need to maintain consistent testing of your anti-static equipment, including floor mats, to guarantee they're effectively dissipating these hidden charges before they can cause harm.
Testing Equipment and Tools
To test your anti-static floor mat effectively, you'll need an ESD resistance meter that can measure both RTG (Resistance to Ground) and RTT (Resistance Top-to-Top) values.
Your testing kit should include grounding cables that create a dedicated path between the mat and an electrical ground point, typically through conductive snaps installed on the mat's surface.
For accurate measurements, you'll want to guarantee your grounding cables are properly connected and that your resistance meter is calibrated according to ANSI/ESD standards.
Essential Testing Meters
For accurate testing of anti-static floor mats, several important meters and testing equipment are necessary to maintain proper ESD protection standards. The most significant device you'll need is a static resistance meter, like the Metriso 3000 test kit, which measures both top-to-ground (RTG) and top-to-top (RTT) resistance.
Your meter should comply with ESD Association Standard Test Method 4.1-2017 and be capable of detecting resistance levels up to 1.0 x 10^9 ohms for RTG tests.
You'll want to verify your testing equipment includes these key components:
- Continuous monitors for real-time ESD integrity checks
- Resistance test kits for measuring electrical resistance
- Grounding testers to verify cable connections
When using these meters, you'll need to take into account various testing parameters, including humidity levels and temperature conditions.
It's important to maintain regular calibration of your testing equipment to guarantee accurate measurements. Remember to test at both standard (50%) and low (12%) humidity levels to assess static dissipation effectiveness.
Your testing voltage should be appropriate to measure resistance without causing damage to the mat or compromising its conductive properties.
Grounding Cable Requirements
When testing anti-static floor mats, proper grounding cable connections serve as your first line of defense against static buildup.
You'll need to ascertain your grounding cables maintain a resistance of less than 1 x 10^9 ohms to effectively dissipate static charges and protect your sensitive equipment.
For mats that aren't directly connected to a conductive work surface, you must use grounding cables to prevent static accumulation.
These cables connect to electrical outlets, creating a reliable path for static discharge. You'll find conductive snaps on the corners of your mat where you can attach these essential grounding cables.
To verify your grounding system's effectiveness, you'll need to conduct regular tests using an ESD resistance meter or a Metriso 3000 test kit.
Following the ANSI/ESD S7.1 testing method, you'll measure both surface-to-ground and surface-to-surface resistance at various humidity levels.
These measurements confirm whether your grounding cables are functioning within acceptable parameters.
Maintaining ESD Safety Standards
Safety standards in ESD protection aren't just guidelines – they're essential requirements that protect both equipment and personnel. When you maintain proper ESD safety standards, you're ensuring compliance with significant regulations like ANSI/ESD S6.1 and STM 4.1-2017. Your commitment to regular testing plays an important role in upholding these standards and protecting your workplace.
To maintain ESD safety standards effectively, you'll need to focus on consistent testing and monitoring of your anti-static floor mats. This includes performing both top-to-top (RTT) and top-to-ground (RTG) resistance measurements using proper ESD meters. You should also consider environmental factors like humidity levels, as they can affect your mat's performance.
Key aspects of maintaining ESD safety standards include:
- Implementing a regular testing schedule based on your facility's risk level
- Training your personnel on proper testing procedures and documentation
- Using continuous monitoring systems in high-risk areas
Remember that failing to maintain these standards can result in costly equipment damage, workplace hazards, and compliance violations.
Common Testing Methods Explained

You'll need to understand three key testing methods to properly evaluate your anti-static floor mats: RTG (Resistance-to-Ground) testing with a 5-pound electrode, mat-to-mat resistance checks for connected surfaces, and proper use of specialized ESD test meters.
Testing between mats guarantees continuous protection across your workspace, while RTG measurements verify proper grounding connections.
Your ESD test meter must be capable of measuring high resistance values between 10^6 and 10^9 ohms for accurate results.
RTG Testing Fundamentals
Resistance-to-Ground (RTG) testing serves as the cornerstone method for verifying anti-static floor mat functionality. When you perform RTG testing, you're measuring the electrical resistance from a specific point on your mat's surface to its ground connection point. This fundamental test guarantees your mat maintains proper grounding, which is vital for ESD protection in your workspace.
You'll need to conduct RTG testing regularly, even if you have constant monitoring systems in place. The process requires a 5 lb electrode connected to your resistance meter's positive terminal, while the negative lead connects to an electrical ground point, typically through a properly wired AC outlet's third wire ground.
Key aspects of RTG testing include:
- Setting appropriate test voltage (10V or 100V) based on expected resistance levels
- Testing multiple locations, especially heavily used areas
- Performing measurements at least quarterly for compliance verification
Remember to maintain clean surfaces and check all connections if your measurements exceed specified limits.
While RTG testing doesn't evaluate the worksurface's performance directly, it's essential for verifying the ground connection that keeps your ESD protection system functioning effectively.
Mat-to-Mat Resistance Checks
While RTG testing forms the foundation of mat verification, mat-to-mat resistance checks provide a broader picture of your ESD protection system's effectiveness. You'll need to conduct both Surface-to-Surface (STS) and Resistance-to-Ground (RTG) tests using specialized ESD resistance meters to guarantee extensive protection for your sensitive equipment.
| Test Type | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Catches worn spots that could compromise your equipment's safety |
| Surface-to-Surface | Confirms uniform static dissipation across your work area |
| Resistance-to-Ground | Verifies your mat's proper grounding connection |
| Environmental Testing | Guarantees protection in varying humidity conditions |
When performing these checks, you'll want to test your mats under different environmental conditions, as humidity levels can greatly impact their performance. Make sure you're documenting all test results to maintain compliance with ESD Association standards, particularly STM 4.1-2017 and ANSI/ESD S7.1. Your resistance values should fall below 1 x 10^9 ohms for RTG tests to meet industry standards. Remember to use proper testing equipment, including calibrated ESD meters and appropriate grounding cables, to guarantee accurate measurements and maintain your certification requirements.
Using ESD Test Meters
Proper testing of anti-static floor mats requires specialized ESD meters and a thorough understanding of testing protocols. You'll need to use surface resistance meters that can test at both 10V and 100V settings to guarantee accurate readings within the required resistance range of < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms for electronics manufacturing environments.
When using your ESD test meter, you'll want to follow the ANSI/ESD STM 7.1 procedures carefully. Place one electrode on the floor mat and measure the resistance to ground. Don't forget that environmental factors like temperature and humidity can affect your readings, so maintain consistent testing conditions.
- Use a megohmmeter or multimeter to conduct regular resistance testing, guaranteeing readings stay within your facility's specified range.
- Combine resistance testing with walking body voltage tests using a charge plate meter to verify real-world performance.
- Document all test results and compare them over time to track any degradation in anti-static properties.
Your testing program should include regular checks with properly calibrated instruments. If you're working in electronics manufacturing, aim for resistance measurements below 1.0 x 10E9 ohms, while end-user environments can accept readings between 1.0 x 10E6 and 1.0 x 10E9 ohms.
Signs of Mat Deterioration
Monitoring your anti-static floor mat's condition helps prevent equipment damage and workplace accidents. You'll need to watch for physical signs of wear and changes in performance that indicate your mat requires replacement.
| Warning Sign | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Surface Damage | Cracks, tears, or visible wear mean compromised protection |
| Material Changes | Hardening or softening indicates chemical breakdown |
| Static Events | Sparks or failed grounding show loss of effectiveness |
| Layer Separation | Delamination exposes internal components to damage |
You should regularly inspect your mat's surface for discoloration, fading, or tears that could compromise its effectiveness. Pay attention to how the mat feels under your feet – if it's becoming too hard, too soft, or showing decreased thickness, it's losing its protective qualities. Environmental factors like heavy foot traffic, chemical exposure, and temperature fluctuations can accelerate deterioration.
Don't ignore performance indicators such as increased static discharge incidents or failed resistance readings. When your mat stops dissipating static electricity effectively, you'll notice more frequent static events or sparking when handling sensitive equipment. These signs indicate it's time to replace your mat before costly damage occurs.
Essential Testing Schedule

A robust testing schedule forms the backbone of effective anti-static floor mat maintenance.
You'll need to adjust your testing frequency based on your environment's risk level and the critical nature of your operations. In high-risk settings like clean rooms and electronics manufacturing, you should conduct daily tests to guarantee consistent grounding and safety compliance.
For standard environments, monthly testing is typically sufficient. Use an ESD Resistance Meter to perform both top-to-top and top-to-ground resistance tests, confirming readings remain below 1 x 10e9 ohms for manufacturing activities.
Don't forget to maintain detailed logs of your test results to track mat performance over time.
- Daily testing for critical areas with continuous monitoring for high-value products
- Monthly checks including resistance measurements and thorough cleaning
- Annual extensive inspections with equipment calibration and protocol reviews
Your annual testing should be particularly thorough, encompassing all ESD equipment and mats.
This thorough check allows you to spot wear patterns that mightn't be visible during routine testing.
It's also the perfect time to recalibrate your testing equipment and update your ESD safety protocols as needed.
Proper Grounding Techniques
Effectively grounding your anti-static floor mats requires careful attention to established safety protocols.
You'll need to choose between several proven grounding methods, including connecting your mat to a conductive work surface or using grounding cables linked to an electrical outlet. If you're working with insulative floors, you'll want to use specialized mats with built-in snaps for direct cable connections.
To maintain proper grounding, you should implement continuous monitoring systems that alert you when your mat loses its ground connection.
You'll also need to conduct regular resistance-to-ground (RTG) tests to verify your mat's grounding effectiveness. Don't forget to comply with ANSI/ESD S6.1 and S4.1-2006 standards throughout this process.
For complete protection, combine your grounded mat with complementary equipment like ESD-safe wrist straps and anti-static shoes.
You'll achieve the best results by installing your mat correctly and training your team on proper grounding procedures.
Remember that effective grounding isn't just about equipment protection – it's vital for workplace safety too.
Resistance Measurement Guidelines
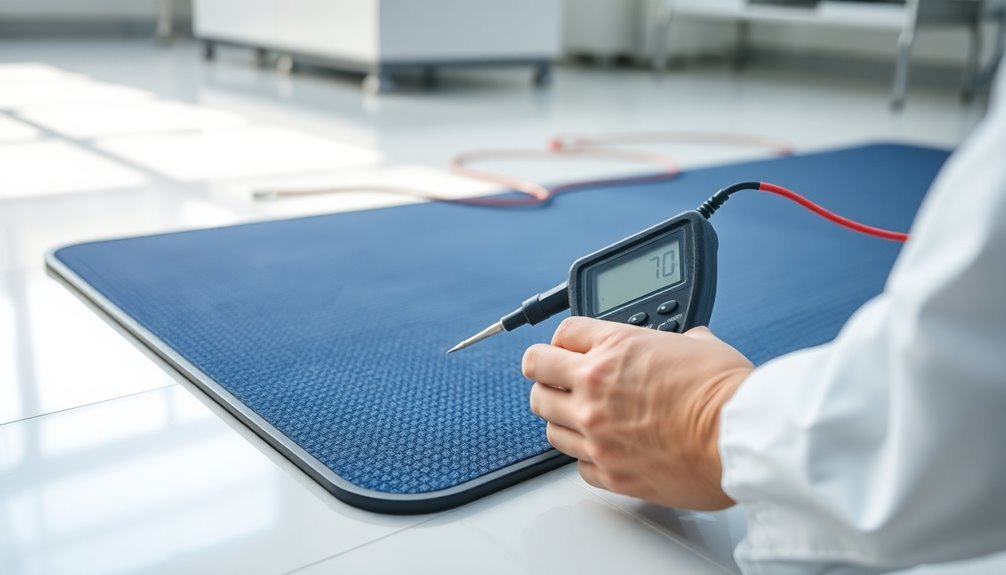

Proper resistance measurement stands at the core of verifying your anti-static floor mat's performance. You'll need to follow ANSI/ESD S7.1 standards, which specify using an ohmmeter with two 5-pound probes positioned 3 feet apart.
When testing, apply 10 volts of electricity and measure the resistance between these points to guarantee your mat falls within acceptable ranges.
For effective ESD protection, your floor mat should measure between 1 x 10^6 and 1 x 10^9 ohms for static dissipative properties. If readings fall below 1 x 10^6 ohms, your mat is considered conductive, while readings above 1 x 10^9 ohms indicate it's not suitable for ESD control.
- Use a resistance meter, megohmmeter, or multimeter to conduct regular tests
- Confirm your testing equipment is properly calibrated and maintained
- Document all measurements for compliance and tracking purposes
Remember to interpret your results based on your specific industry requirements. Your path-to-ground resistance shouldn't exceed 3.5 x 10^7 ohms when combined with personnel.
If you're unsure about your measurements, consider scheduling a professional ESD audit for a thorough assessment of your mat's performance.
Environmental Factors Affecting Performance
Throughout the year, environmental conditions play an essential role in your anti-static floor mat's performance.
You'll notice significant variations in static control effectiveness as humidity levels change, with low humidity increasing static buildup and high humidity reducing it. Even with higher humidity, you'll still need your anti-static mat for consistent protection.
Temperature fluctuations can affect your mat's conductivity, while extreme temperatures may degrade its performance over time.
You'll need to pay attention to your workplace environment, as heating and air conditioning systems can alter indoor humidity levels and impact your mat's effectiveness.
Environmental contaminants pose another challenge to your mat's performance.
Dust, dirt, and chemical spills can compromise its conductive properties, while regular foot traffic causes wear that reduces efficiency.
The materials beneath your mat, such as carpet or painted floors, can also interfere with proper grounding.
Your mat's aging process naturally decreases its conductivity, and physical damage or UV exposure can accelerate this deterioration.
When you're working in environments with synthetic fibers or plastics, you may need enhanced protection.
Regular testing becomes essential to guarantee your mat maintains its protective properties across these varying conditions.
Testing Documentation Best Practices

Professional documentation forms the backbone of any reliable anti-static mat testing program. When you're testing your anti-static floor mats, you'll need to maintain detailed records that include test dates, environmental conditions, and specific measurements. Your documentation should follow ANSI/ESD standards and provide a clear audit trail for compliance purposes.
To guarantee your documentation meets industry standards, you'll want to focus on these essential elements:
- Record all test parameters, including relative humidity levels, temperature, and equipment calibration status
- Document both initial and follow-up test results using standardized forms that capture resistance measurements at multiple points
- Maintain a log of any corrective actions taken when tests fall outside acceptable ranges
Remember to keep your testing equipment calibration certificates on file and regularly update your documentation procedures to reflect any changes in testing protocols.
You'll need to train your personnel on proper documentation methods and guarantee they understand the importance of accurate record-keeping. If you're using third-party verification services, maintain copies of their test reports alongside your internal documentation.
This thorough approach to documentation won't just satisfy compliance requirements – it'll help you track your mat's performance over time and predict when replacement might be necessary.
Troubleshooting Failed Test Results
Failed test results can signal serious issues with your anti-static floor mats that require immediate attention. When your resistance to ground (RTG) readings exceed 1.0 x 10^9 ohms, you'll need to investigate several common causes, including insufficient grounding, improper installation, or material degradation.
To resolve failed tests, start by checking your mat's grounding connections. Verify that all snaps and cables are securely fastened and that there aren't any insulating materials, like carpet or paint, between your mat and the ground path.
If you've placed the mat on an insulating surface, you'll need to establish a proper conductive path to ground.
You can prevent future failures by implementing regular maintenance routines. Clean your mats frequently to remove contaminants that affect static dissipation, and schedule regular RTG tests following ESD Association Standard Test Method 4.1-2017.
If your mat shows signs of deterioration or consistently fails tests despite proper maintenance, you'll need to replace it with a new one that meets ESD standards.
Remember to document all your tests and maintenance activities to maintain compliance with ANSI/ESD S6.1 requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Anti-Static Mats Be Cleaned With Regular Household Cleaning Products?
No, you shouldn't use regular household cleaners on anti-static mats. They'll damage the mat's static-dissipative properties. Instead, you should use mild soap, water, or specialized ESD cleaning products designed for these mats.
How Long Does a Typical Anti-Static Floor Mat Last Before Replacement?
You'll need to replace your anti-static floor mat every 3-6 months in high-traffic areas, though it can last years with light use. Regular cleaning and proper maintenance will help extend its lifespan.
Do Anti-Static Mats Work Effectively in High-Humidity Environments?
Yes, your anti-static mats will work effectively in high-humidity environments. They're designed and tested at various humidity levels, including 50% and 12%, to guarantee they consistently dissipate static electricity to ground.
Can Multiple Workstations Share the Same Anti-Static Floor Mat Safely?
You can share an anti-static floor mat across workstations if you've confirmed proper RTG readings and sized it correctly. However, make certain there's no overlapping, as this could create inconsistent static dissipation between stations.
Are Anti-Static Floor Mats Safe for Employees Wearing Medical Devices Like Pacemakers?
Yes, you'll find anti-static floor mats are safe and beneficial for employees with pacemakers. They protect medical devices by dissipating static electricity safely to ground, reducing risks of harmful electrostatic discharge in your workspace.
In Summary
Testing your anti-static floor mat regularly isn't just about compliance – it's about protecting your valuable equipment and maintaining a safe work environment. You'll catch potential issues before they cause costly damage, guarantee consistent static dissipation, and keep your workspace ESD-safe. Don't wait for equipment failure to check your mats. Make testing part of your routine maintenance schedule to avoid unnecessary risks and expenses.





Leave a Reply