You'll find five effective foam solutions to protect your valuable electronics: conductive foam with carbon particles for complete static shielding, anti-static foam that prevents friction-based buildup, static dissipative foam for controlled discharge, custom-fit foam inserts designed for precise component dimensions, and thermal management foam that regulates temperature while providing impact protection. Each type offers specific benefits, from the Faraday cage effect of conductive foam to the cushioning properties of static dissipative options. Your choice depends on your component's sensitivity level, and understanding the unique properties of each solution will help you make the best selection for your needs.
Static Protection Foam Types
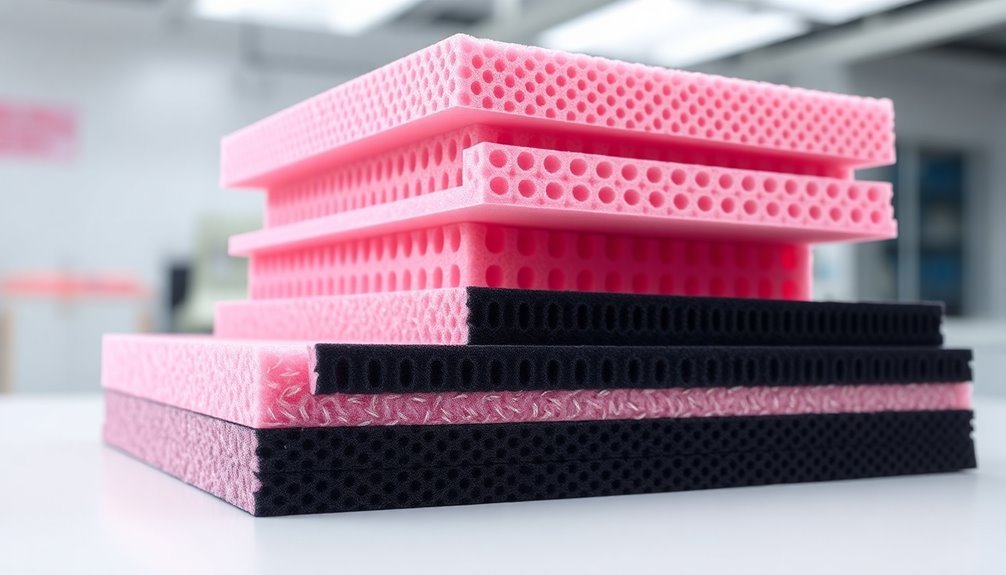

When it comes to protecting sensitive electronics from static damage, three main types of protective foam stand out: conductive, anti-static, and static dissipative.
Conductive foam contains carbon particles and creates a Faraday cage around your electronics, offering complete static shielding with a surface resistance below 10^6 ohms. While it's highly effective, you'll need to be careful as it can drain batteries that come in direct contact with it. It provides rapid static dissipation and requires no additional shielding from external charges.
You'll find anti-static foam, often pink in color, has a surface resistance between 10^9 and 10^12 ohms. It's designed to prevent static buildup through friction, but you should know it won't provide full shielding and its protective properties diminish over time.
Static dissipative foam bridges the gap between the other two types, with a surface resistance of 10^5 to 10^9 ohms. You can use it when you need controlled, gradual static discharge. It's available in both black and pink variations, depending on its treatment method.
Each foam type serves specific protection needs: conductive for full shielding, anti-static for basic static prevention, and dissipative for controlled discharge. You'll need to take into account your specific application when selecting the right foam solution.
Anti-Static Foam Applications
In electronics manufacturing and storage, anti-static foam serves as a critical protective solution across multiple applications. You'll find this versatile material being used extensively in custom-fit packaging, where it creates secure compartments that shield electronic components from both physical and electrostatic damage during transit and storage.
When you're working in manufacturing environments, you can rely on anti-static foam as an effective work surface. It'll help prevent static buildup while you're handling sensitive components like integrated circuits and computer chips. Cleanroom facilities commonly incorporate this foam into their construction to maintain controlled environments.
The foam's surface resistivity, ranging from 10^6 to 10^12 ohms/cm, guarantees consistent protection across different atmospheric conditions.
You can customize anti-static foam to fit your specific needs, whether you're storing individual components or entire electronic assemblies. The material's adaptability allows you to create precise cutouts and compartments that match your components' exact dimensions.
When you're selecting anti-static foam for your application, you'll want to think about factors like surface resistivity requirements and environmental conditions. Choose from various densities (18, 24, or 28) and colors (pink or gray) to match your specific protection needs while guaranteeing compliance with industry standards.
Reusable Foam Storage Solutions
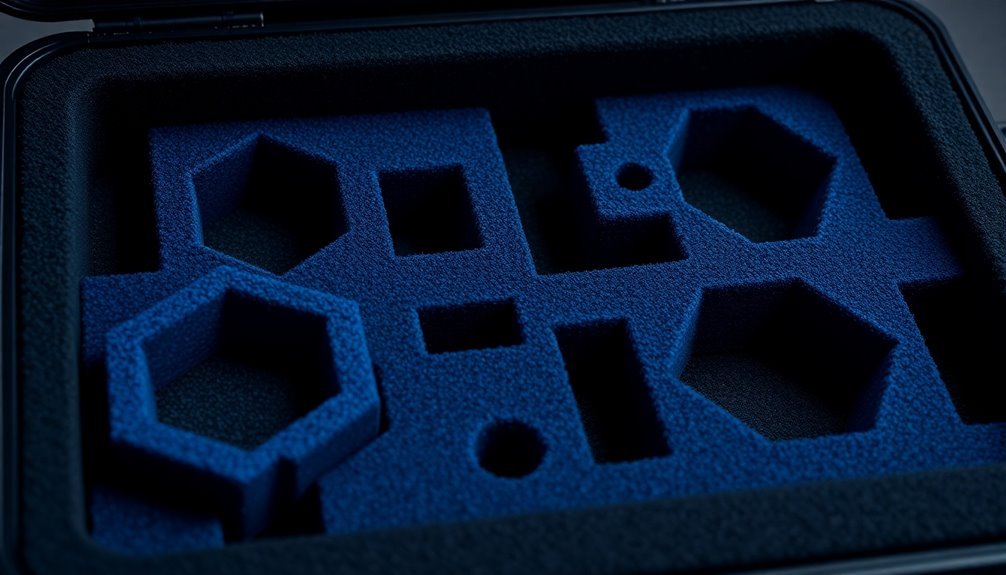

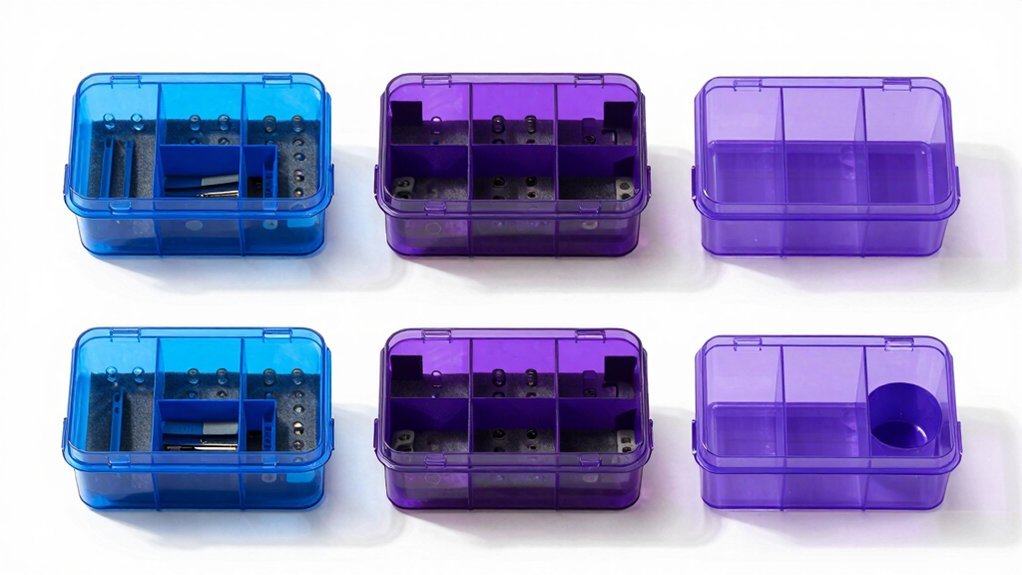
Through innovative design and durable materials, reusable foam storage solutions offer you a sustainable approach to protecting electronic components and devices. You'll find significant cost savings by eliminating the need for disposable padding materials while contributing to environmentally friendly practices in your operations.
When you're working with electronics, you can customize these foam solutions using materials like polyurethane, polyethylene, or EVA foam to create perfect-fit storage spaces. The 130 interlocking pieces allow for endless configuration possibilities to match your exact needs.
The closed-cell foam structures provide excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties, ensuring your sensitive components remain secure during storage and transportation.
You can maximize your storage efficiency by implementing tessellating patterns and interlocking pieces that allow you to craft precise cavity shapes. The modular design means you'll be able to reconfigure your storage setup as your needs change.
Whether you're organizing a shadow board for tools or creating protective packaging for shipping electronic devices, these foam solutions adapt to your requirements.
The versatility of reusable foam storage extends across various applications, from component storage to transportation protection. You'll benefit from the durability of these solutions, as they maintain their protective properties through multiple uses while keeping your electronic items safely organized.
Custom ESD Packaging Designs
Custom ESD packaging designs serve as your first line of defense against static electricity damage in electronic components. When you're handling sensitive electronics, you'll need packaging solutions that offer precise protection against both static discharge and physical impacts.
These custom designs guarantee your components fit snugly, minimizing movement and reducing the risk of damage during shipping and storage. Effective layouts incorporate multi-layer protection systems to maximize component safety.
You'll find various ESD materials available for your specific needs, including anti-static, conductive, and dissipative foams. Whether you're working with polyurethane, polyethylene, or specialty foams, you can select materials that match your exact requirements.
The design process involves careful consideration of your component's dimensions, vibration assessments, and cushioning calculations to create the best protective environment.
Before committing to full production, you can take advantage of prototyping services to test and evaluate your customized ESD solutions. This collaborative approach allows you to fine-tune the design while adhering to industry standards.
Through custom ESD packaging, you'll not only protect your valuable electronic components but also enhance your brand's professional image and boost customer confidence in your products.
Electronic Component Foam Selection
Building on your ESD packaging needs, selecting the right foam material for electronic component protection requires careful consideration of both static protection levels and physical cushioning properties.
You'll need to match your component's sensitivity with the appropriate foam type: conductive foam for highly sensitive parts, static dissipative for moderate protection, or anti-static foam for basic static prevention.
Conductive foam, typically black and carbon-filled, offers the highest level of protection with resistivity under 10^4 ohms/sq, creating a Faraday cage effect around your components. Custom-designed foam inserts and trays provide precise component fitting for enhanced protection during transport. For moderate protection, consider blue static dissipative foam, which provides controlled discharge with resistance values between 10^8-10^11 ohms. Pink anti-static foam works well for components requiring basic static prevention.
When choosing your foam's base material, you'll find polyurethane (PU) and polyethylene (PE) are the primary options. PU foam delivers excellent shock absorption and cushioning, while PE foam offers superior flexibility and compression resistance.
Don't forget to factor in your operating environment – temperature ranges and humidity levels should influence your selection to guarantee long-term protection for your electronic components.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Static Protection Foam Typically Last Before Needing Replacement?
You'll need to replace standard static protection foam after about one year, though high-quality antistatic foams can last over three years. Regular testing is essential to confirm it's still providing reliable protection.
Can Static Protection Foam Be Safely Cleaned Without Compromising Its Protective Properties?
You can safely clean static protection foam using gentle methods like a damp lint-free cloth and mild cleaner. However, you'll need to test a small area first and verify it's completely dry afterward.
What Temperature Ranges Can Electronic Protection Foams Safely Operate Within?
You'll find most electronic protection foams work safely from -40°C to 107°C, but if you need extreme temperature protection, specialized polyimide foams can handle -150°C to 204°C, and Solimide foams reach 300°C.
Are There Specific Humidity Requirements for Storing Items in Static Protection Foam?
You'll need to maintain 30-70% relative humidity when storing items in static protection foam, with 40-60% being ideal. Lower humidity compromises the foam's dissipative properties, while higher levels improve static protection.
How Can You Test if Static Protection Foam Is Still Providing Adequate Protection?
You'll need to conduct resistance testing using a surface resistivity meter, check for physical wear, and perform static decay tests. Regular inspections help guarantee your foam maintains proper resistance values within 10^3-10^11 ohms.
In Summary
You'll find these five foam solutions offer reliable protection for your sensitive electronic components. Whether you're choosing anti-static foam for shipping, reusable storage options, or custom ESD designs, selecting the right foam type is essential for preventing damage. Consider your specific needs for static protection, cushioning requirements, and component sizes when implementing these foam solutions in your electronics handling process.





Leave a Reply