To protect your electronic components from ESD damage, you'll need several essential pieces of safety equipment. Start with an anti-static wrist strap connected to a proper ground point, and wear ESD-safe gloves that meet ANSI standards. Set up your workstation with an ESD mat, ionizer, and static-dissipative surface, keeping the area free from static-generating materials like plastic bottles. Store components in ESD-safe containers and maintain proper humidity levels in your workspace. Don't forget testing equipment like voltmeters to verify your protection measures. The right combination of these tools can make the difference between component failure and long-term reliability.
Understanding ESD Protection Basics
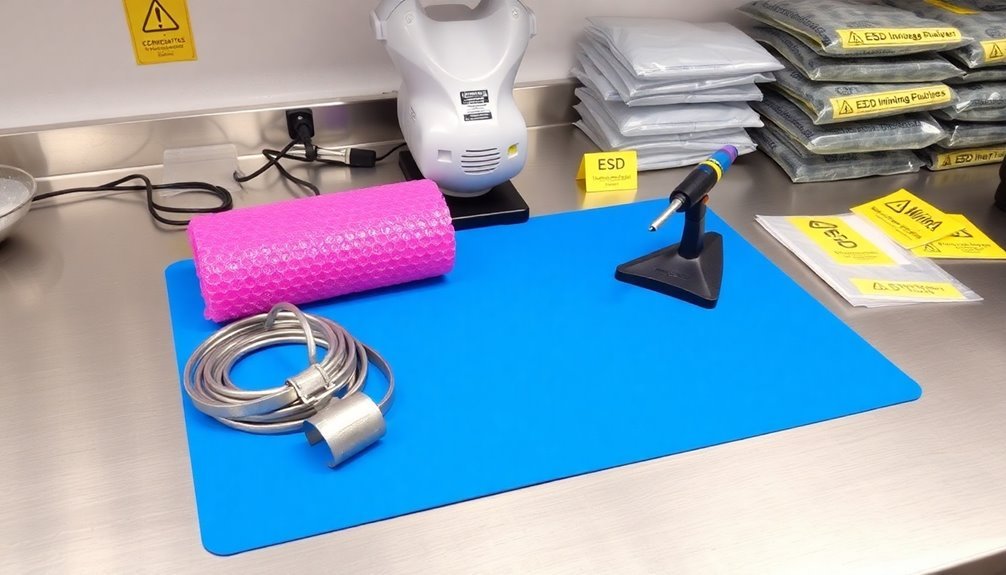

Electronics professionals rely on four fundamental methods to protect sensitive components from electrostatic discharge (ESD). These methods include diversion, which channels dangerous voltage pulses away from sensitive components to ground; absorption, where components are designed to withstand ESD events; shielding, which provides protective barriers around vulnerable parts; and grounding, which establishes safe paths for static discharge.
Using proper ESD control products helps prevent reliability issues and system failures. You'll need to implement these protection methods through various components and strategies. ESD suppressors, like protection diodes and varistors, act as your first line of defense by managing potentially damaging voltage spikes. TVS diodes are particularly effective for protecting power, ground, and data lines through reverse breakdown mechanisms.
When you're designing systems, you'll want to select components that include built-in ESD protection and incorporate appropriate shielding measures into your board layout.
To guarantee effective protection, you must regularly test and evaluate your ESD safety measures. You can use specialized ESD test equipment to identify vulnerabilities in your setup and verify that your protection systems are working properly.
It's essential to comply with industry standards and conduct regular audits of your ESD protection measures, as these guidelines help maintain consistent safety levels and protect your sensitive electronic components from damage.
Anti-Static Wrist Straps
For reliable ESD protection, anti-static wrist straps serve as your essential first line of defense when handling sensitive electronic components.
These devices continuously discharge static electricity through their low-resistance design, featuring a hand ring resistance of 103 ohms and a wrist strap impedance factor under 50 ohms. You'll benefit from their rapid discharge time of 0.1 seconds, ensuring immediate protection against ESD threats. The wireless design provides enhanced mobility while eliminating the risks associated with tethered straps. Multiple options including hypo-allergenic fabric versions are available for those with sensitive skin.
When you're working with electronics, you'll appreciate the strap's built-in safety features, including a 1MΩ resistance that protects you while effectively grounding static electricity.
The straps come in various materials like stainless steel, nylon, and elastic nylon fiber, offering both durability and comfort during extended use.
You'll find these straps particularly valuable in electronics assembly, repair work, and any environment where static electricity poses a risk to sensitive components.
They're designed to meet ANSI/ESD 6.1 standards and can be customized with different cord lengths to suit your workspace.
For thorough protection, you can pair them with ESD heel straps, ensuring complete static control while maintaining mobility in your work area.
Proper Grounding Systems
A well-designed grounding system forms the backbone of any effective ESD protection strategy. You'll need to establish a reliable grounding method, with the equipment ground (green-wire ground) being the preferred choice for connecting all conductive surfaces. The grounding requirements must be tailored to your specific facility type and size.
For ideal protection, you should implement a common point ground system that guarantees all grounding conductors share the same electrical potential. A current limiting resistor should be incorporated into ground cords for operator safety.
You can use several grounding methods, including dedicated earth grounds with conductive rods sunk at least 3 feet into the ground, or alternative grounds like water pipes and metal support stanchions.
When setting up your system, use proper grounding cables and ESD mats to connect your work surfaces to the common point ground. Don't forget to incorporate appropriate flooring and footwear systems for thorough protection.
To maintain safety and effectiveness, you'll need to regularly test your grounding system using ground resistance testers.
Make sure all installations comply with standards like ANSI/ESD S6.1 and the National Electrical Code. Remember, preventing potential differences between equipment and separate ESD grounds is vital to avoid electrical overstress hazards.
Always have your grounding system certified by a qualified electrician to guarantee operator safety.
ESD Safe Workstations
Building on proper grounding principles, your ESD safe workstation serves as the primary defense against static damage during electronics handling.
You'll need to equip your station with essential components like antistatic bench matting, ESD-safe tools, and conductive component boxes to create a protective environment for sensitive electronics. Plastic bottles and aluminum cans should be strictly prohibited in the workspace.
Regular safety evaluations must be performed to maintain ESD control effectiveness.
Start by installing ESD floor mats and table mats to establish reliable paths to ground.
Add an ionizer to neutralize static in your workspace, and incorporate ESD monitors to regularly test your wrist straps and heel straps.
Your workstation should feature static-dissipative tops with common grounding points, and it's vital to position it within a designated Electrostatic Protected Area (EPA).
Don't forget essential accessories like earth bonding points and plugs for secure grounding connections.
Use conductive waste bins and ESD refuse sacks for safe disposal of sensitive materials.
Keep your components organized in ESD-safe containers and use conductive brushes for cleaning PCBs.
Remember to use an EPA-approved chair that dissipates static buildup.
This thorough setup guarantees maximum protection for your electronic components during handling and assembly.
Personal Protective Equipment
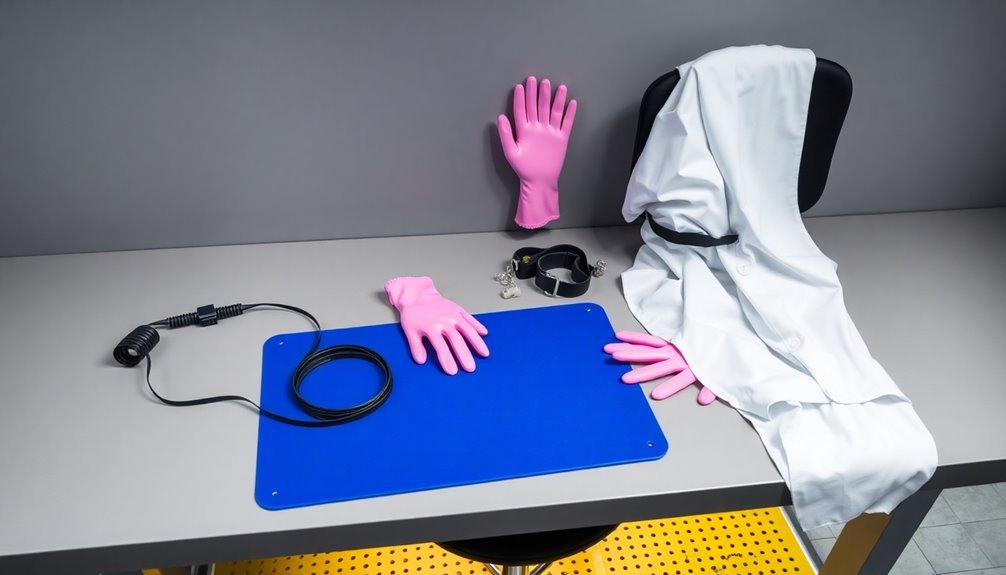

Proper protection starts with your personal ESD safety gear, forming a critical line of defense against static damage to sensitive electronics. You'll need to wear ESD aprons made of conductive fabric that safely dissipates static electricity while providing comfort through adjustable straps.
When handling sensitive components, you'll want to use specialized ESD gloves that meet strict standards like ANSI/ESD SP15.1-2011. These gloves come with polyurethane-coated fingertips for better grip and are available in various materials from nitrile to conductive carbon/nylon yarn.
| PPE Type | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aprons | Conductive fabric, adjustable straps | Manufacturing, assembly |
| Gloves | PU-coated tips, multiple materials | Electronics handling |
| Footwear | Conductive materials, cleanroom-safe | All ESD areas |
| Headgear | Secure fit, static dissipative | Cleanrooms, assembly |
| Testing Tools | Resistance meters, decay testers | Quality control |
Don't forget your ESD footwear and headgear – they're essential components of your protective ensemble. Your shoes should provide proper grounding, while caps prevent static buildup near your head. Remember, all PPE must meet specific resistance requirements, typically below 1.0 x 10^11 ohms, to guarantee effective static control.
Static Dissipative Floor Solutions
When selecting ESD floor mat materials, you'll need to take into account both carbon-based options and polymer flooring solutions that match your facility's resistance requirements of 1-1000 Mohms for static dissipative surfaces.
Your grounding system installation must include proper connection points, verified electrical continuity, and compatibility with workplace footwear to guarantee effective static charge dissipation.
To maintain your ESD floor protection, you'll want to implement regular resistance testing, keep the surface clean of debris, and monitor environmental humidity levels, as these factors directly impact the floor's static control performance.
Choosing Floor Mat Materials
Selecting the right static dissipative floor mat material requires careful evaluation of both technical specifications and practical needs. You'll want to focus on materials that maintain resistance levels between 1 x 10^6 to 1 x 10^9 ohms while meeting your facility's specific requirements.
| Material Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Labs & Clean Rooms | Easy maintenance, no waxing needed |
| Rubber | Heavy Traffic Areas | Durable, supports heavy equipment |
| Carpet Style | Office Spaces | Comfortable, noise reduction |
| Anti-fatigue | Standing Workstations | Ergonomic, reduces worker fatigue |
When choosing your floor mat material, you'll need to weigh factors beyond just static dissipation. Reflect on whether you'll need slip resistance for safety, durability for heavy equipment areas, or comfort for standing workers. Don't forget to check if the material you're assessing is compatible with your existing ESD footwear program.
Remember that different areas of your facility may require different mat materials. For example, you might want rubber mats in your equipment rooms but carpet-style mats in office areas where aesthetics matter. Always verify that your chosen material meets relevant industry standards and manufacturer specifications for your specific application.
Grounding System Installation Steps
Successfully installing a grounding system for static dissipative floors requires careful attention to specific steps and safety protocols. You'll need to install copper grounding straps for every 1,000 square feet of ESD flooring, guaranteeing at least one strap per room connects to a verified electrical ground.
When grounding to an AC electrical outlet, start by removing the center and grounding screws. Punch a hole in your copper strap, then secure it to the outlet before running it down the wall to the subfloor.
If you're using building steel as your ground point, you'll need to remove any paint or coatings from the I-beams before attaching the straps.
For floors installed on or below grade, you can drive a copper rod into the ground and connect it to your grounding strap using a wire nut.
Don't forget to use conductive adhesive to link your ESD flooring to the ground – it's an effective alternative to expensive copper grids.
After installation, you must test the system using a volt ohm meter to verify proper grounding. Your resistance to ground should measure less than 1.0 x 10^9 ohms to guarantee adequate ESD protection.
Maintaining ESD Floor Protection
Proper maintenance of ESD flooring extends far beyond initial installation and keeps your static protection system working effectively. You'll need to implement regular cleaning protocols and conduct resistance testing to guarantee your floor's static dissipative properties remain intact. For volume conductive flooring, you won't need to worry about recoating, which greatly reduces maintenance downtime.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean with ESD-approved cleaners | Weekly |
| Test electrical resistance | Monthly |
| Inspect for physical damage | Quarterly |
| Verify footwear compatibility | Semi-annually |
| Document maintenance records | Ongoing |
To maintain ideal ESD floor protection, you should use only manufacturer-recommended cleaning solutions and avoid harsh chemicals that could compromise the floor's conductivity. If you're using dissipative or conductive flooring with special coatings, you'll need to follow specific maintenance schedules for reapplication. Don't forget to regularly check your floor's compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards through resistance testing. When you notice any signs of wear or decreased effectiveness, consult with your flooring manufacturer immediately. Remember that proper maintenance not only extends your floor's lifespan but also guarantees continuous protection for your sensitive electronic equipment.
Component Storage and Handling
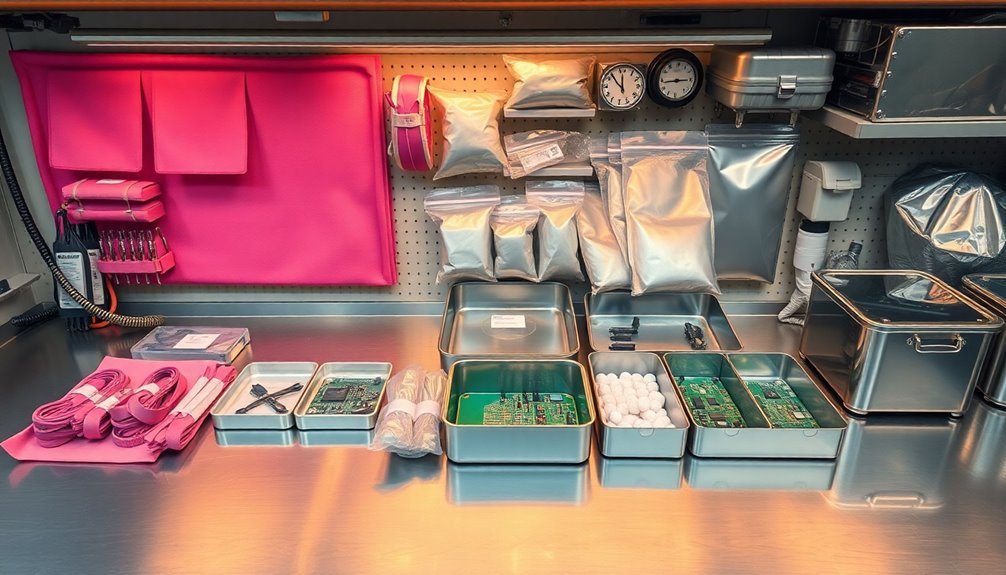

In today's electronic manufacturing environment, safe component storage and handling practices are essential for protecting sensitive devices from electrostatic discharge.
You'll need to store components in ESD-safe containers and maintain a controlled environment with proper temperature and humidity levels.
Don't use traditional packaging materials like plastic bags or bubble wrap, as they can generate harmful static electricity.
When handling components, you must wear dissipative gloves and use a wrist strap to stay properly grounded.
Always use anti-static tools and avoid direct contact with the components.
You'll need to store items in ESD-safe bins and on grounded shelving covered with conductive materials.
For transportation, you'll want to use grounded carts equipped with ESD-safe covers.
It's important to designate specific pathways for moving components and limit unnecessary human movement in sensitive areas.
Before transporting any items, inspect them carefully for damage or contamination.
Remember to use anti-static bags that meet industry standards for component storage, and incorporate desiccants to maintain low humidity levels.
Proper labeling of ESD-sensitive components will help alert handlers to exercise appropriate caution during handling and storage.
Testing Equipment Requirements
You'll need reliable testing equipment to verify your ESD safety measures are working effectively, including continuous monitoring systems that track personnel grounding and environmental conditions in real-time.
Your essential toolkit should include surface resistance meters to check workstations, floor mats, and other ESD-safe surfaces for proper conductivity levels.
Personnel testing stations, including wrist strap and footwear testers, will help you confirm that operators maintain proper grounding throughout their shifts.
ESD Monitoring System Basics
Testing equipment fundamentals form the backbone of any reliable ESD monitoring system. You'll need both single-wire and dual-wire continuous monitors to effectively test the electrical connections between your ground points, cords, wristbands, and personnel.
Dual-wire systems provide thorough monitoring, while resistive continuous monitors measure impedance changes to reduce false alarms.
To maintain compliance with standards like IEC 61000-4-2, you'll want to use ESD testing simulators that verify voltage levels and current waveforms. You'll also need specific ESD targets and adapters to capture these waveforms accurately.
Your testing arsenal should include voltmeters and voltage dividers to verify voltage levels across your system.
Don't forget that regular calibration is vital – you should calibrate your monitoring equipment annually to guarantee operational integrity. Your oscilloscopes and attenuators must be properly maintained as part of your calibration process.
Remember that continuous monitoring isn't just about equipment – it's an essential component of your overall ESD control program, helping you prevent costly damage to sensitive electronics by constantly verifying the functionality of your wrist straps and other protective measures.
Surface Resistance Measurement Tools
Surface resistance measurement tools range from basic handheld meters to sophisticated lab-grade equipment, each designed to verify the electrical properties of ESD-protective surfaces.
You'll find that these meters come with varying measurement ranges, from basic models like the Fraser 740 SRM measuring up to 10¹² Ohms/Square to advanced units like the Hioki SM7110 capable of measuring up to 2 x 10¹⁹ Ω.
For general workplace testing, you can rely on handheld devices like the Botron Digital SRM or Fraser 740 SRM, which offer portability and quick measurements.
If you need extensive testing capabilities, lab-grade equipment like the METRISO 3000 provides additional features such as temperature and humidity monitoring, plus software for data handling.
When selecting a meter, you'll want to evaluate accuracy levels – most offer ±10% accuracy – and compliance with relevant standards.
The METRISO 3000 and Hioki SM7110 comply with key ESD standards like IEC61340-2-3.
You'll also need to check the included accessories; most professional models come with specialized probes, electrodes, and carrying cases for complete measurement capabilities in various industrial applications.
Personnel Testing Equipment
Beyond measuring surfaces, protecting personnel requires specific equipment to verify the effectiveness of ESD safety gear. You'll need three main types of testing equipment to guarantee your ESD protection remains reliable: wrist strap testers, footwear testers, and clothing testers.
Wrist strap testers verify the electrical path between you and ground, displaying either pass or fail results. For footwear, you'll use test stations with floor plates that check your ESD shoes or heel straps while standing on them. Both systems must meet strict resistance and conductivity requirements to maintain safety standards.
| Testing Type | Test Frequency | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Wrist Straps | Daily | 1M-10M ohms |
| Footwear | Daily | <35M ohms |
| ESD Clothing | Monthly | <1012 ohms |
You'll need to implement regular testing schedules and maintain detailed records of all test results. Don't forget to train your employees on proper testing procedures – they should understand how to use each piece of equipment correctly. Remember that compliance with industry standards isn't optional; it's vital for protecting sensitive electronic components from static damage.
Environmental Control Measures

Creating a safe environment for electronics handling requires multiple control measures to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. You'll need to focus on four key areas: flooring and grounding, temperature and humidity control, lighting and ionization, and proper storage solutions.
Start with proper ESD-protective flooring and guarantee all surfaces are connected to a common ground using mats and straps. You'll need to test these connections regularly to maintain their effectiveness. Clear marking of ESD-safe zones will help separate them from non-protected areas.
You must maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels, as high humidity helps minimize static charges while low humidity increases ESD risks. Install humidifiers or dehumidifiers as needed, and guarantee good air circulation throughout your workspace.
Don't overlook proper lighting to reduce shadows, and install ionizers in critical areas like assembly lines. These devices generate balanced positive and negative ions to neutralize static charges in the air and on surfaces.
For component storage, you'll need ESD-safe containers and static shielding metalized packaging for highly sensitive items. Choose all packaging materials based on their ESD safety properties to prevent damage during storage and handling.
Maintenance of ESD Equipment
Regular maintenance protocols play an essential role in keeping your ESD protection system effective. You'll need to conduct routine audits of all ESD equipment and implement a testing schedule to guarantee everything's functioning correctly.
Start by checking your grounding systems daily, including wrist straps and mats, verifying they're properly connected and maintaining resistance levels between 1 x 10^4 and 1 x 10^9 ohms. Use surface resistance testers to verify the integrity of your ESD worksurfaces.
When cleaning these surfaces, only use approved ESD cleaners, as regular cleaners containing silicone can compromise their effectiveness.
Inspect your grounding connections regularly, ensuring they're secure and using appropriate connecting devices like metallic crimps and banana plugs. Don't rely on alligator clips, as they can provide unreliable contact.
Set up continuous monitoring systems to alert you if wrist straps or ground connections fail.
Maintain proper calibration of your testing equipment according to industry standards S20.20 and ESD TR53. Train your staff regularly on correct equipment usage and establish clear SOPs for maintenance procedures.
Remember to use only ESD-safe tools when performing any repairs or maintenance tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do Esd-Safe Gloves Typically Last Before Needing Replacement?
You'll need to replace your ESD-safe gloves every 3-6 months with regular use, but they can last longer with proper care. Watch for signs of wear, reduced performance, or chemical exposure to determine replacement timing.
Can Regular Cleaning Products Be Safely Used on Esd-Protected Surfaces?
No, you shouldn't use regular cleaning products on ESD-protected surfaces. They'll leave harmful residues and can damage the surface's ESD properties. Always use specifically designed ESD-safe cleaning products for proper maintenance.
What Happens if an Ionizer Malfunctions During Sensitive Component Handling?
If your ionizer malfunctions, you'll risk static buildup that can cause instant ESD damage to components. You won't always see the damage right away, but it can destroy sensitive electronics and create spark hazards.
Do ESD Protection Measures Interfere With Wireless Communication Devices?
Yes, ESD protection can interfere with your wireless devices if not properly designed. You'll notice that high-capacitance protection measures can detune RF pathways, but using low-capacitance TVS diodes will minimize these communication issues.
How Does Extreme Weather Affect the Performance of ESD Protective Equipment?
You'll notice your ESD equipment's performance varies with weather extremes. High humidity can reduce effectiveness through corrosion, while low humidity increases static risks. Temperature swings and air movement also impact protective capabilities.
In Summary
You'll need to consistently maintain and properly use all your ESD safety equipment to protect sensitive electronic components. Don't skip regular testing of wrist straps, grounding systems, and workstation surfaces. Remember, it's far cheaper to invest in quality ESD protection than to replace damaged components. Keep your storage solutions, testing equipment, and environmental controls up to date, and you'll minimize costly ESD-related failures.





Leave a Reply