When handling electronic components, you'll need to follow five essential workstation compliance standards. First, verify your workspace meets IEC 61340-5-1 requirements for electrostatic protective areas (EPA) with proper grounding and ESD-safe materials. Second, implement JEDEC JESD625B protocols for semiconductor handling and protection. Third, maintain ISO 9001 quality management systems for consistent production standards. Fourth, follow proper grounding system testing according to IEEE 81 standards. Fifth, establish documentation procedures for audits and traceability. Understanding these foundational standards will open the door to mastering safe electronics handling practices.
ESD Workstation Design Requirements
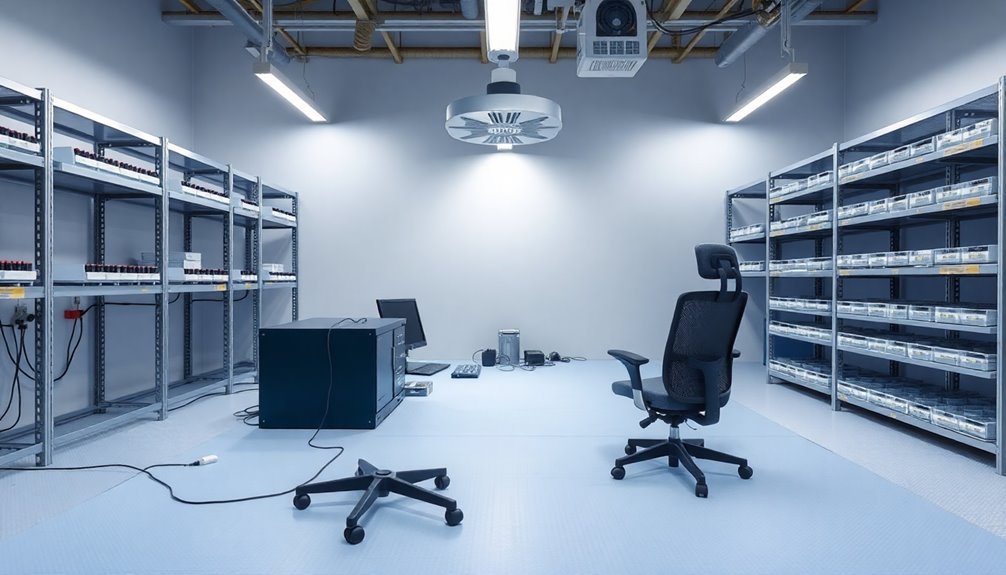

When designing an ESD workstation, you'll need to incorporate several critical components to protect sensitive electronic equipment from static discharge damage.
Start with a static-dissipative work surface made from rubber, vinyl, or laminate materials, and make certain it's connected to a common point ground with less than 1 x 10E6 ohms resistance. Install a 10mm grounding snap in each work surface mat for proper grounding connection.
You'll need to equip your workstation with a wrist strap and coil cord set to ground personnel, along with ESD floor mats for mobile workers who'll use heel grounders.
Install multiple grounding points, all connected to the same electrical ground, and include ESD equipment testers to verify that your wrist straps and heel grounders are functioning correctly.
Choose workbenches made from metal and wood while avoiding insulative plastics that can generate static charges.
You'll want to set up your station within a designated EPA zone and design it for single-user operation to minimize ESD risks.
Don't forget to include ESD-safe tools and consider adding air ionizers to neutralize static buildup on insulators that can't be grounded.
Keep ESD-sensitive components in a clearly marked, separate area from non-ESD-sensitive activities.
Grounding System Testing Standards
Proper grounding system testing stands as the foundation for any effective ESD workstation setup. You'll need to follow IEEE 81 for systems with resistance above 1 ohm, while IEEE 81.2 is your go-to standard for larger grids requiring less than 1 ohm resistance. The Three Point Fall-of-Potential procedure remains the most widely used testing method for verifying ground system integrity. Testing is critical since ESD-related failures can account for up to 30% of electronic device failures.
| Testing Type | Application | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Point-to-Point | Equipment Grounding | Monthly |
| Visual Inspection | Fixed Installations | Quarterly |
| Resistance Testing | Total Ground System | Annually |
When you're testing your workstation's grounding system, you'll need to guarantee all components connect to a common ground point. This includes your ESD mats, floor matting, and personnel grounding devices. You must bond your auxiliary grounds to the equipment grounding conductor and verify that your grounding cords have secure connections. For mine power systems, MSHA regulations require annual testing of ground systems. Remember to maintain proper documentation of all resistance measurements, as they're vital for compliance and safety verification. Regular evaluation of these grounding systems helps prevent ESD-related damage and guarantees workplace safety.
Material Resistivity Measurement Protocols
Accurate material resistivity measurements form the cornerstone of electronics handling safety protocols. You'll need to employ specific measurement techniques, with the four-point collinear probe method and van der Pauw method being the most reliable approaches for different sample types. These methods eliminate common measurement errors from probe resistance and contact resistance. Temperature fluctuations must be carefully monitored and controlled during measurements due to semiconductors' high temperature coefficients.
To guarantee precise measurements, you'll calculate volume resistivity using the formula ρ = (V/I) * (π * t / ln(2)), while applying the necessary Resistivity Correction Factor (RCF) to account for variations in electric energy distribution.
You must use high impedance voltmeters to minimize current draw and maintain measurement accuracy.
When conducting measurements, you'll want to use equipment like the 4200A-SCS Parameter Analyzer with four SMU instruments for van der Pauw measurements. Each terminal requires connection to an SMU instrument, and you'll need to perform four distinct tests to calculate resistivity accurately.
For high resistance samples, you must use specialized equipment with high input impedance. Remember to follow IPC standards and industry-specific protocols to guarantee compliance with electronics manufacturing requirements and safety regulations.
Environmental Control Specifications
Within electronics handling facilities, strict environmental control specifications govern four critical areas: temperature, electromagnetic interference, mechanical conditions, and hazardous substances.
You'll need to maintain specific temperature ranges for your electronic equipment, guaranteeing that operating temperatures don't exceed recommended limits. Your equipment shouldn't generate excessive heat, keeping temperature differences within 10°C during normal operation. The workstation should maintain CE mark compliance for safety and environmental protection requirements.
For electromagnetic compatibility, you must test your equipment for both conducted and radiated emissions, preventing interference with other devices and radio communications.
Your workstation must protect equipment from mechanical shock and vibration. You'll need to conduct drop tests, topple tests, and vibration assessments to guarantee your equipment remains functional under operational conditions. The mounting and enclosures you use should minimize these mechanical impacts.
For hazardous substance control, you'll need to comply with RoHS directives and conduct testing for restricted materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium using XRF spectroscopy. You must also follow ecodesign regulations that address energy efficiency and sustainable electronics practices. Stay current with international environmental standards like IEC 62430 to guarantee your workstation meets all compliance requirements.
Documentation and Audit Procedures

Beyond environmental controls, maintaining thorough documentation represents a fundamental aspect of electronics handling compliance.
You'll need to verify your design documentation includes detailed circuit diagrams, wiring schematics, and component lists with standardized formats. Each document must carry preparation dates and modification records to maintain traceability.
For production and testing, you'll want to maintain detailed assembly instructions and parts lists. Your test procedures should include detailed tables and results, while installation guides must outline setup procedures step-by-step.
Don't forget to document maintenance schedules and procedures for regular upkeep. Quality documentation helps reduce support costs by minimizing the need for extensive training and rework.
When it comes to audits, you're required to document clear objectives and maintain detailed plans. You'll need to record quality standards, regulations, and previous audit findings. Keep track of any non-conformities and document your corrective actions promptly.
Your record management system should organize electronic documents systematically. Include narrative descriptions and technical characteristics in your technical documentation.
Make sure you're maintaining system design records, implementation details, and migration documentation. Remember to standardize all documentation formats and make them easily accessible to authorized personnel.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Employees Undergo Compliance Training for Electronics Handling Certification?
You'll need to complete electrical safety training every 1-3 years, with annual inspections. For certification renewal, you must obtain 24 continuing education units every 24 months and maintain proper documentation of your training.
What Personal Protective Equipment Is Mandatory for Visitors to Electronics Workstations?
You'll need safety glasses with side shields, long pants, and closed-toe shoes when visiting electronics workstations. Additional PPE may be required based on specific hazards in the area you're accessing.
Can Employees Use Personal Devices While Working at Compliant Electronics Stations?
You can't use personal devices at compliant electronics stations unless specifically authorized by IT. You'll need to follow strict BYOD policies, including MDM software installation and security protocols for work-related activities.
What Emergency Procedures Should Be Followed if Hazardous Materials Contact Skin?
You'll need to immediately flush the affected area with water, remove contaminated clothing, and wash with soap. Don't delay seeking medical attention if symptoms persist after washing the exposed skin.
How Frequently Should Workstation Compliance Certification Be Renewed for Different Standards?
You'll need to renew OSHA certification every 5 years, HAZWOPER every 3 years, CCB every 2 years with 40 CEUs, and Cyber Essentials annually. ISO certifications require yearly audits but renewal periods vary.
In Summary
You'll maintain a safer and more reliable electronics handling environment by consistently following these five workstation compliance standards. Regular testing of grounding systems, proper material resistivity checks, and stringent environmental controls protect sensitive components from ESD damage. Keep your documentation updated and conduct routine audits to guarantee ongoing compliance. These practices aren't just guidelines – they're essential safeguards for your facility's success.





Leave a Reply