Keep your ESD wrist strap in top condition by testing it daily with a dedicated station, checking for resistance between 750K ohms and 35 megohms. Clean the strap with mild detergent, avoiding bleach and high temperatures that can damage silver fibers. Guarantee a snug but comfortable fit against your skin and verify proper grounding connection before each use. Don't daisy chain straps – connect each one independently to the ground bus. Store your strap in a protective case when not in use, and replace it every 6-12 months or if you spot damage. Following these essential tips will help you maintain peak static protection.
Daily Testing for Optimal Performance
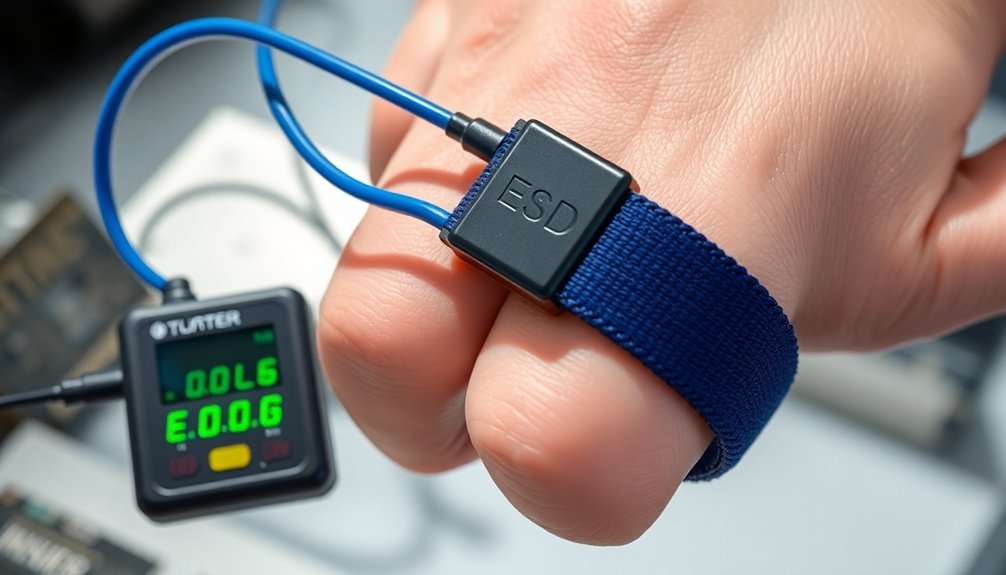

Anyone working with sensitive electronic components knows that daily testing of ESD wrist straps isn't optional – it's crucial for maintaining proper protection.
You'll need to test your wrist strap at designated test stations or use a continuous monitor at your workbench to verify its functionality. The portable ED698 model is ideal for workshop supervisors conducting spot checks.
To test your wrist strap, put it on, plug it into the tester, and press the hand contact plate. The tester will measure the resistance through your skin, cuff, resistor, and ground cord. A current limiting resistor of 1 megohm is built into the ground cord as a safety feature.
You'll see a green light for a pass or red light for a fail. Make sure you record your test results to maintain compliance with standards like EN 61340-5-1.
If you're not using continuous monitoring, you must test your wrist strap daily before starting work. Your testing frequency should align with your risk exposure and the volume of products you handle.
Consider switching to continuous monitoring if you're working with products that demand constant, reliable grounding.
Don't forget about your tester's calibration requirements. You'll need annual calibration to guarantee accurate measurements, though tools like the ED311 can help you complete on-site calibration in just 10 minutes.
Proper Cleaning and Maintenance
The proper cleaning and maintenance of your ESD wrist strap is essential for its continued effectiveness. When cleaning your wristband, use mild, non-ionic detergents and avoid harsh chemicals like bleach. Proper cleaning protocols help maintain health and safety standards in ESD-protected environments. Regular maintenance is essential for IEC compliance and workplace safety standards.
If you have a metallic expansion wristband, make sure it's thoroughly dried to prevent corrosion. For elastic wristbands, wash them in cool or warm water and either tumble dry on low heat or hang to dry.
You'll want to use liquid detergents rather than dry ones to prevent caking and reduce wear from friction. When wiping down surfaces, opt for soft microfiber cloths and avoid abrasive cleaning tools.
While isopropyl alcohol can be used occasionally, it's not recommended for regular cleaning – instead, choose ESD-specific cleaners to maintain your strap's performance.
Don't forget to inspect your wrist strap regularly for signs of wear. When you notice deterioration, replace the wristband materials promptly – you can order replacement strips directly from manufacturers like DESCO.
After any cleaning or maintenance, always test your wrist strap system to verify proper electrical resistance and skin contact. Remember to follow the manufacturer's specific cleaning instructions to maintain your strap's effectiveness.
Secure Grounding Connection Methods
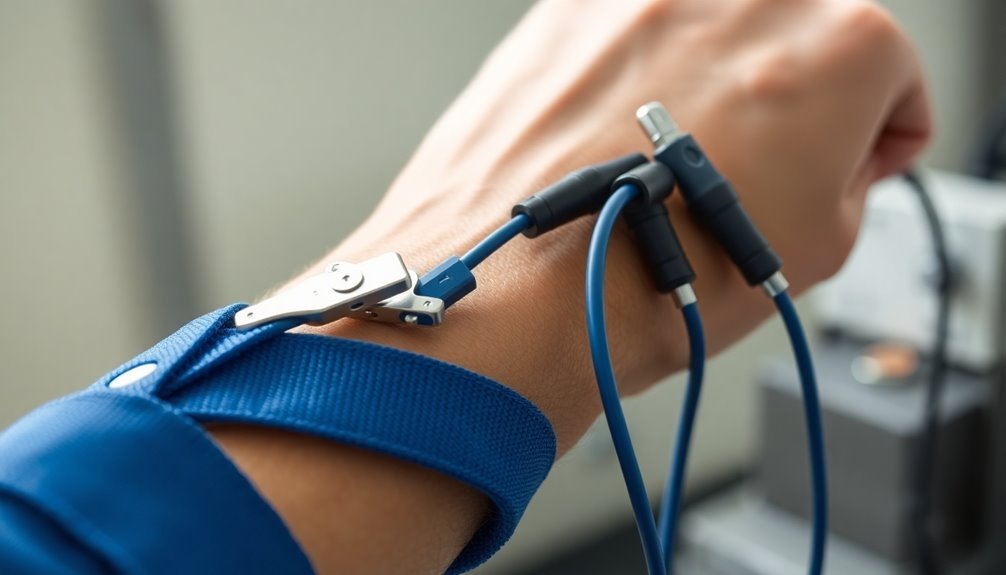
You'll need to connect your ESD wrist strap to a direct ground bus system to guarantee reliable static discharge protection.
To establish this connection, insert the banana plug firmly into the designated ground port until you hear or feel it lock into place.
Make sure you've tested the connection using an ESD wrist strap tester before beginning your work to confirm proper grounding.
Proper skin contact is critical for the wrist strap to effectively conduct static electricity away from your body.
Direct Ground Bus Connection
Establishing a secure ground bus connection serves as the foundation for effective ESD protection in your workspace. You'll need to connect your wrist strap's coil cord directly to a grounding point using either a banana plug or an eyelet that screws into an electrical outlet. Don't daisy chain multiple wrist straps together; instead, guarantee each strap connects independently to the ground bus or equipment ground. The integrated 1 megohm resistor helps control the static discharge rate for optimal safety. The blue anti-static strap provides reliable protection while working on sensitive electronic components.
| Essential Action | Critical Details |
|---|---|
| Pre-use Testing | Test ground with AC Outlet Analyzer before initial setup |
| Connection Type | Use banana plugs or eyelets for secure attachment |
| Maintenance Check | Inspect grounds every six months |
| Safety Protocol | Never exceed 250 VAC when working with equipment |
Before you start using your grounding system, test the intended ground with an AC Outlet Analyzer and Wrist Strap Tester. This verification guarantees proper wiring and protection. You'll want to implement a common point ground when working with multiple wrist straps, as this provides the most reliable grounding solution. Remember to conduct regular maintenance checks of all ESD grounds at least every six months to maintain ideal protection and comply with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
Banana Plug Installation Steps
Properly installing banana plugs requires careful attention to detail and the right tools for a secure ESD grounding connection. Start by gathering your wire stripper, cutting pliers, ruler, and flat head screwdriver. You'll need to strip 1-2 cm of insulation from your wire to expose the copper strands.
Once you've exposed the wire, twist the copper strands together to form a single, tight strand. Loosen the screw on your banana plug and insert the twisted wire into the bottom opening. Make sure you've identified the correct terminals for compatibility with your ground connection point.
Tighten the screw firmly to secure the wire, then slide the protective casing over the connection. Before finalizing the installation, check for any stray wire strands that could cause shorts, and verify the polarity matches your connection points. Speakon and XLR connectors are better suited for professional audio applications.
You'll want to test the connection to confirm it's working properly. If you're working in tight spaces, consider using angled banana plugs, while stackable plugs work well for complex setups. For high-voltage applications, opt for shrouded banana plugs to prevent accidental contact.
Don't forget to regularly check and tighten connections to maintain reliable ESD protection.
Adjusting for Comfort and Safety
To guarantee your ESD wrist strap provides reliable protection, you'll need to adjust the band for a snug but comfortable fit against your skin.
Insert the links into the slotted opening at a downward angle, sliding them in or out of the backplate until you've achieved the right size, then lock them into place by pulling down on the band.
Check your wrist strap's fit daily, making sure it maintains consistent skin contact without being too tight or too loose.
Proper Band Sizing
A well-fitted ESD wrist strap forms the foundation of effective static discharge protection.
You'll need to verify your wristband fits snugly while maintaining comfort to achieve proper skin contact. Don't overtighten the band, as this can restrict movement and compromise effectiveness.
For elastic adjustable wristbands, you'll want to work with the clasp mechanism. Pull upward on the "tail" material extending from the clasp to open it, then adjust the elastic until you achieve the ideal fit.
Once you've marked the proper size, trim any excess material about 1/4" from your mark to prevent fraying.
Regular maintenance of your wrist strap is essential. You should test the system frequently to confirm proper electrical resistance and skin contact.
When cleaning your wristband, use non-ionic softeners and detergents, avoiding temperatures above 120°F. Make it a habit to inspect your wrist strap daily for signs of wear or damage.
To maintain peak protection, you'll need to verify the fit periodically throughout your workday. If you notice any loosening or discomfort, readjust the band immediately to guarantee continuous static protection while you work.
Lock and Link Adjustments
Different wrist strap styles require specific adjustment methods for ideal protection. For elastic adjustable bands, you'll need to place the band on your wrist, pull up on the tail material to open the clasp, and adjust until you achieve a snug but comfortable fit. When working with metal wristbands, insert the link end into the slotted cap opening at a downward angle, then slide links in or out of the backplate to achieve proper sizing.
| Adjustment Type | Steps | Safety Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic Band | 1. Open clasp 2. Adjust material 3. Close clasp 4. Leave tail extended |
Test electrical resistance |
| Metal Links | 1. Insert into slot 2. Slide links 3. Cut excess 4. Lock in place |
Verify skin contact |
| Daily Checks | 1. Check for wear 2. Monitor elasticity 3. Test resistance 4. Verify ground |
Use wrist strap tester |
| Maintenance | 1. Clean regularly 2. Avoid heat exposure 3. Use proper detergents 4. Check grounding |
Test with continuous monitor |
Remember to avoid placing the strap over clothing cuffs and regularly test your wrist strap's electrical resistance. Don't use worn-out or stretched bands, as they won't provide adequate protection. Keep skin contact consistent, and guarantee proper grounding at your workstation.
Daily Fit Checks
Performing daily fit checks on your ESD wrist strap helps maintain both comfort and protection throughout your work shift. You'll need to confirm your wrist strap fits snugly without being too tight, as proper skin contact is essential for reliable grounding. Check the band's position and adjust it whenever you notice any looseness or discomfort.
During your daily inspection, examine the wristband material for signs of wear, fraying, or damage. Pay special attention to the metal components and confirm they're making proper contact with your skin. If you're using an elastic band, verify that it hasn't lost its elasticity.
For metal bands, check that the adjustment mechanisms are working correctly and aren't corroded.
Don't forget to test all components of your wrist strap system using an ESD test station. This includes verifying the resistance levels of the wristband, ground cord, and skin interface. If you notice any irregularities during testing, replace the affected components immediately.
Keep records of your daily checks to maintain compliance with ESD control protocols and confirm consistent protection against static discharge.
Storage and Protection Guidelines

Regular maintenance is essential.
Clean your wrist straps with mild detergents, and conduct routine inspections for signs of wear.
Make certain you're testing the straps regularly for proper electrical resistance and keeping detailed maintenance records to guarantee compliance with safety standards.
Resistance Testing Best Practices
Accuracy in resistance testing forms the cornerstone of ESD wrist strap safety. You'll need to guarantee your wrist strap maintains a resistance between 750K ohms and 35 megohms to meet ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
Test your wrist strap daily at designated stations or use continuous monitors in high-risk environments.
When you're testing, watch for both high and low resistance failures. If you get a high fail reading (above 35 megohms), check for common issues like dry skin, a dirty wristband, or a broken coil cord. You can resolve skin resistance problems by applying electronics-approved lotion.
For low fail readings (below 750K ohms), inspect your coil cord for shorts and guarantee you don't have any unintended ground connections.
Keep detailed records of your compliance verification tests, and don't skip regular maintenance. Clean your wrist strap with mild detergent and dry it thoroughly to prevent corrosion.
If you're using a continuous monitoring system, make sure it's properly isolated from other devices to avoid interference. Remember to verify the breakaway force requirement using a strain gauge – it should be greater than one pound to prevent accidental disconnects.
Avoiding Common Wear Issues
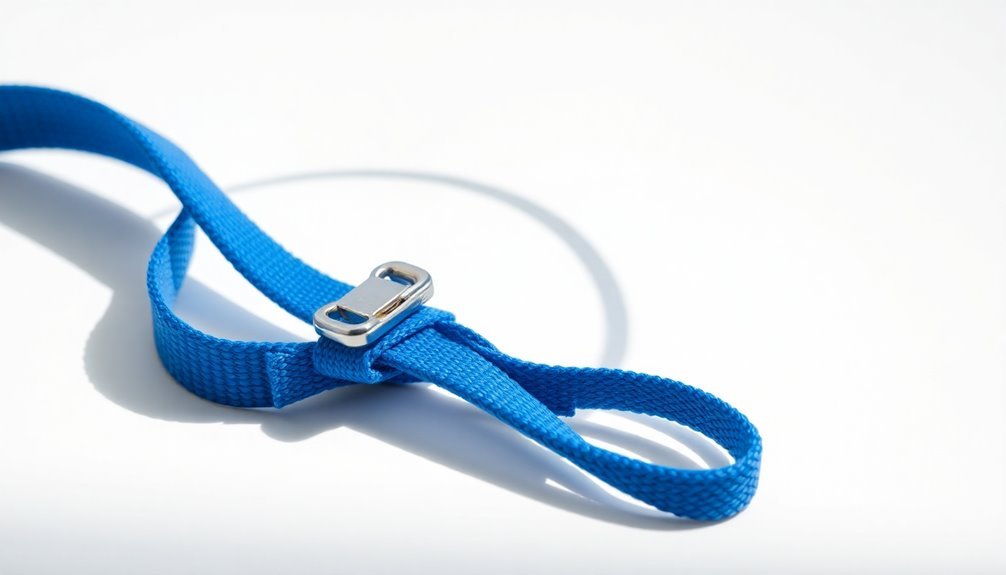

Worn spots and frayed edges on your ESD wrist strap can compromise its effectiveness and put sensitive electronics at risk. To prevent these common wear issues, you'll need to implement proper handling and storage practices while being mindful of material limitations.
Start by storing your wrist strap in a protective case or pouch when it's not in use. Don't fold or bend the strap excessively, as this creates weak points that can lead to premature failure. Keep your strap away from sharp objects that could puncture or scratch the material, and use a strap holder during work sessions to prevent unnecessary strain.
You should inspect your strap regularly for signs of damage or wear. Clean it using only mild soap and water, avoiding harsh chemicals that could degrade the material. After cleaning, make sure you dry the strap thoroughly to prevent moisture-related deterioration.
Store it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, which can weaken the material over time. Remember to replace your strap every 6-12 months, or sooner if you notice any visible damage. Don't try to extend the life of a worn strap – it's not worth risking damage to sensitive components.
Safe Use Around Equipment
Proper care of your ESD wrist strap goes hand-in-hand with using it safely around equipment. When working with static-sensitive components, you'll need to verify your wrist strap connects to a proper grounding point or grounded metal surface.
Before each use, inspect your strap for signs of wear or damage, and always use models that include a 1-megohm resistor for protection against electrical shock.
Keep safety at the forefront by following established guidelines for your specific work environment. You'll want to maintain distance from high-voltage equipment and moving machinery parts. Additionally, make sure you're using ESD-safe tools and materials when handling sensitive components, and verify that all workstations are properly grounded.
- Always check that your wrist strap meets relevant industry standards like ANSI/ESD S1.1 before use
- Never work in high-humidity environments, as moisture can compromise the strap's effectiveness
- Use only certified straps with built-in current limiting devices when working with sensitive equipment
For maximum protection, verify you've received proper training on ESD safety procedures and regularly review manufacturer guidelines for your specific wrist strap model.
Stay vigilant about keeping your equipment grounded and maintaining safe working practices.
Material Care and Laundering

Maintaining your ESD wrist strap's material integrity requires specific cleaning and care methods. You'll need to use mild detergents when cleaning your wristbands, and if you're using fabric ones, wash them in cool or warm water. For those with hypoallergenic needs, choose wristbands made from nylon material and hypoallergenic stainless steel.
When laundering your wristbands, use your standard home washing machine on a gentle cycle or industrial "Pony" machines with loads under 200 pounds. Opt for liquid detergents instead of dry ones to prevent caking and wear. You shouldn't expose your wrist straps to bleach or temperatures above 120°F, as the silver fibers are heat-sensitive.
After washing, either tumble dry on low heat or hang-dry to preserve the material's integrity. Keep your metallic expansion bands completely dry to avoid corrosion. While you can use non-bleach sanitizers, be aware they might affect performance over time.
Don't dry clean your wristbands, as this can degrade their properties. Regular cleaning with products like Woolite will help maintain ESD performance, but remember to replace your wristbands once they've reached the end of their useful life.
Regular Inspection Procedures
Before using your ESD wrist strap, you'll need to perform a quick visual inspection for any obvious damage or wear to the band and cord.
Set up your testing equipment, such as a commercial wrist strap tester, to verify proper functionality and grounding capabilities.
You must guarantee resistance measurements fall between 800k ohms and 10 megohms, testing daily for regularly used straps and adjusting frequency based on your product's value and reliability requirements.
Visual Checks Before Use
Safety-conscious technicians must perform visual inspections of their ESD wrist straps before each use to prevent potential damage to sensitive electronic components.
You'll need to check for any visible signs of wear, including cuts, frays, or damaged parts that could compromise the strap's effectiveness. It's essential to verify that your ground cord connections are secure and that the wrist band makes direct contact with your skin, unobstructed by clothing.
Before handling ESD-sensitive items, confirm your wrist strap system meets the required resistance range of 500 kΩ to 10 MΩ by testing it at an ESD test station.
You should keep detailed records of these tests, including any issues found and corrective actions taken, for at least one year to maintain compliance standards.
- Always inspect the coiled cord's strain relief points and stud connections, as these are common failure points that can break the grounding path.
- Clean the interior of the wrist band regularly, but avoid silicone-based cleaners that can create an insulative barrier.
- Test the entire system while worn to verify proper grounding, and consider using continuous monitors for real-time verification of functionality.
Testing Equipment Setup
For ideal performance, you'll want to maintain your testing station properly.
Replace batteries when the low battery indicator stays on, and verify annual calibration using NIST traceable standards.
If your tester fails calibration and doesn't have adjustable components, you'll need to send it back to the manufacturer for recalibration.
Resistance Measurement Guidelines
Regular resistance measurements stand at the heart of ESD wrist strap maintenance.
You'll need to verify your readings fall between 750 kilohms and 35 megohms to meet industry standards, with 10 megohms being a common upper limit in many facilities. When measuring, connect your wrist strap to a calibrated tester and touch the metal plate to get an accurate reading.
Pay close attention to factors that can affect your measurements. Dry skin often leads to high resistance readings, while accidentally touching grounded surfaces during testing can create false low readings.
If you're getting consistent high fails, check for loose wrist bands or damaged cords. For low fails, inspect for shorted resistors or unwanted ground paths.
- Test your wrist strap daily before starting work, and consider continuous monitoring for sensitive applications
- Maintain proper skin contact by keeping the band snug but not tight, and address dry skin issues promptly
- Connect only to designated Earth Bonding Points (EBP), avoiding temporary connections to dissipative mats
Remember to calibrate your testing equipment regularly and document your measurements to maintain compliance with ESD protection standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can ESD Wrist Straps Cause Allergic Reactions in Sensitive Individuals?
Yes, you can experience allergic reactions from ESD wrist straps if you're sensitive to materials like rubber or nickel. That's why it's important to choose hypoallergenic options made with stainless steel or special nylon filaments.
How Often Should the Grounding Cord Be Replaced?
You should replace your grounding cord based on regular inspections, typically every 6-12 months with heavy use. However, if you're testing daily and find no damage, your cord may last longer with proper care.
Is It Safe to Wear ESD Wrist Straps With Medical Devices?
You shouldn't wear ESD wrist straps with medical devices unless specifically approved. They can interfere with device operations and pose safety risks. Always consult your healthcare provider or device manufacturer for guidance.
What's the Maximum Length Allowed for an ESD Wrist Strap Cord?
You shouldn't use ESD wrist strap cords longer than 12 feet, as this is the industry-standard maximum length. Longer cords could reduce effectiveness and create safety hazards in your workspace.
Can Multiple Wrist Straps Share the Same Grounding Point?
Yes, you can connect multiple wrist straps to a single grounding point if your grounding device supports multiple connections. Just make sure it's properly connected to a safe facility ground for everyone's protection.
In Summary
Your ESD wrist strap's longevity depends on your consistent care and attention to detail. Test it daily, clean it regularly, and store it properly to maintain its effectiveness. Don't skip inspections or ignore wear and tear – your sensitive electronics rely on this crucial protection. By following these maintenance tips, you'll extend your strap's lifespan and guarantee reliable static discharge protection for years to come.





Leave a Reply