You'll need to test your ESD wrist straps daily in high-traffic areas where ESD protection is critical. For moderate-use environments, weekly testing is acceptable, while monthly checks suffice for low-use settings. Always test immediately after any physical damage or alterations to the strap. Use either a portable tester or continuous monitoring system to verify resistance readings fall between 800 kΩ and 9 MΩ, following ANSI/ESD S1.1-2021 standards. Document your test results with date, time, and measurements to maintain compliance. Understanding the full scope of ESD testing requirements can help you establish a robust protection program.
Daily Testing Requirements
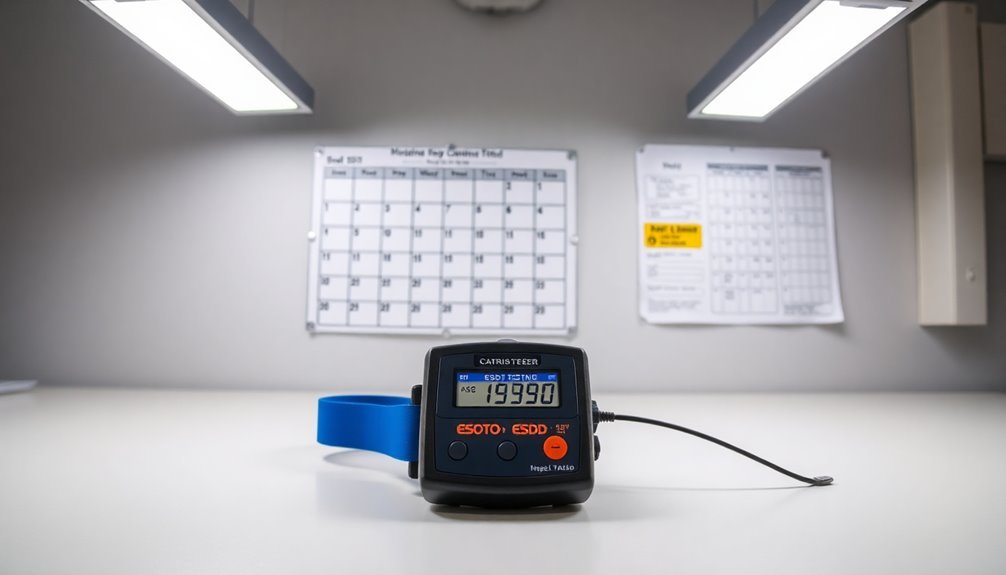

In accordance with industry standards, you must test your ESD wrist straps daily to confirm proper grounding protection. This daily testing requirement isn't just a suggestion – it's a critical practice that guarantees your wrist straps remain reliable and effectively protect ESD-sensitive components from damage. Risk assessment factors should guide any modifications to the testing schedule.
You'll need to follow specific industry standards, including ANSI/ESD S1.1-2021 and ESD TR20.20, which mandate regular testing procedures. A successful test requires resistance readings between 800 kΩ and 9 MΩ to ensure proper grounding performance. When you perform your daily test, you'll wear the wrist strap and connect it to a specialized tester that indicates pass or fail status through green and red lights.
If you're working in an environment that requires constant, reliable grounding, you can opt for continuous monitoring systems instead of daily testing.
Don't forget to maintain detailed records of your daily tests for quality control and compliance verification. If your wrist strap fails testing, you'll need to separately test both the wrist band and cord to identify which component needs replacement.
Remember that your testing equipment must be regularly calibrated to confirm accurate measurements and maintain compliance with industry standards.
Risk Assessment Guidelines
A thorough risk evaluation forms the foundation for determining how often you should test your ESD wrist straps.
You'll need to evaluate several key factors that directly impact your testing requirements and schedule.
Start by evaluating your product's value and sensitivity. If you're handling expensive or highly sensitive components, you'll want to implement more frequent testing protocols.
Consider your work environment's conditions, including humidity levels and exposure to cleaning chemicals, as these can affect your wrist straps' performance and longevity.
Examine your usage patterns carefully. If you're using wrist straps daily in critical operations, you'll need to align with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards that recommend daily testing.
For less critical applications, you might opt for semi-annual testing, but always document your reasoning based on risk exposure.
Don't forget to review your historical test data. If you've noticed patterns of failure or degradation, you'll need to adjust your testing frequency accordingly.
Your risk evaluation should also factor in the physical condition of your wrist straps, as visible wear and tear can indicate the need for more frequent testing or replacement.
Continuous Monitoring Systems
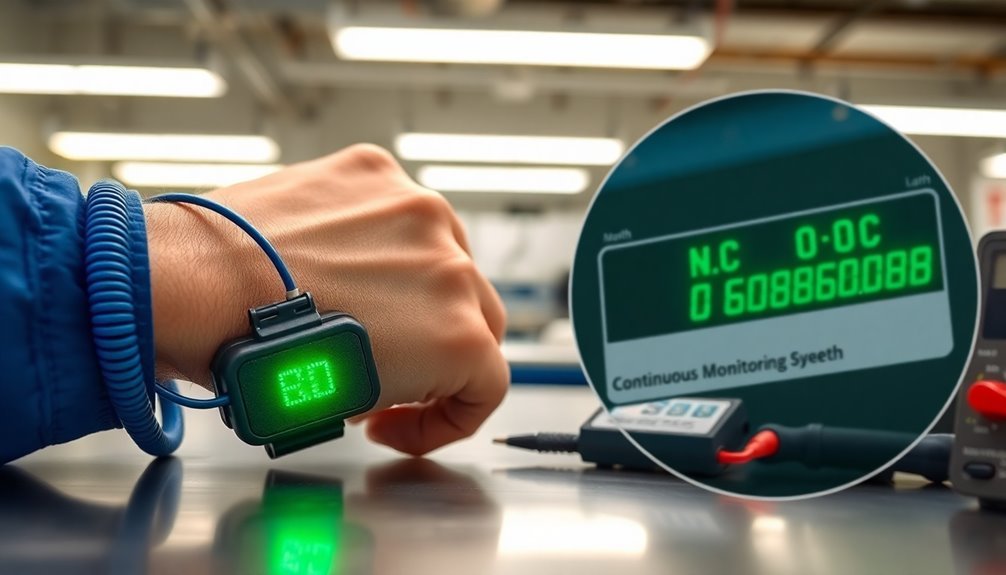

Continuous monitoring systems revolutionize ESD wrist strap testing by providing automated, real-time verification of your grounding protection. These systems eliminate the need for daily manual testing while offering immediate alerts if your wrist strap's resistance exceeds acceptable ranges. High-value manufacturing often requires this level of constant monitoring. Visual inspections are not sufficient for detecting failures in grounding equipment.
You'll experience minimal workplace interruptions and benefit from consistent, reliable grounding protection throughout your shift.
When you're implementing a continuous monitoring system, you'll need to ascertain it integrates properly with your workbench setup and meets industry standards like ANSI/ESD S1.1 and ESD TR20.20. While these systems require a higher upfront investment than periodic testing equipment, they'll reduce your long-term testing costs and provide more robust compliance verification.
You should be aware of potential challenges when using continuous monitoring systems. Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to maintain accuracy, and you'll need to watch for interference from other electrical components.
Proper training is vital to avoid user errors that could lead to false readings. Despite these considerations, continuous monitoring systems offer superior protection through automated testing, real-time feedback, and thorough record-keeping capabilities that streamline your ESD protection program.
ESD Testing Equipment Options
When choosing ESD testing equipment, you'll find two main options: portable testers for periodic spot checks and continuous monitors for real-time protection.
Portable testers offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness for daily testing requirements, while continuous monitoring systems provide automated, uninterrupted verification of your wrist strap's functionality.
These automated systems can log test results and alert you immediately if your wrist strap fails, offering enhanced protection for sensitive components.
Portable Vs Continuous Monitors
Testing your ESD wrist strap requires choosing between two main equipment options: portable testers and continuous monitors. Your choice depends on your specific needs and application requirements.
| Feature | Portable Testers | Continuous Monitors |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront cost |
| Operation | Battery-powered, handheld | Workbench-mounted, constant |
| Testing Method | Spot checks and daily tests | Real-time monitoring |
| Reliability | Good for basic needs | Superior for critical operations |
| Best Use Case | Small workshops, supervision | High-value production lines |
If you're running a small workshop or need occasional testing capability, portable testers like the ED698 will serve you well. They're cost-effective and provide quick pass/fail indicators for daily testing requirements.
However, if you're handling high-value components or need constant assurance of proper grounding, you'll want to invest in continuous monitors. They'll eliminate the need for daily testing while providing real-time feedback on your wrist strap's performance. You won't have to worry about missing potential failures between scheduled tests, as these monitors instantly alert you to any breaks in the ground path.
Remember to maintain regular calibration schedules regardless of which option you choose.
Automated Testing Features
Modern automated testing equipment takes ESD wrist strap monitoring to the next level beyond basic portable and continuous monitors. You'll find sophisticated features that streamline your testing process while ensuring compliance with standards like ANSI/ESD S1.1-2021 and IEC 61340-5-1.
These systems provide immediate pass/fail indicators and automatically log critical data, including operator identity, test results, and timestamps.
Today's automated testers offer extensive solutions that can handle multiple testing needs in one device. You won't need separate equipment for different ESD items, as many systems can test wrist straps, footwear, and garments.
The built-in data management capabilities eliminate manual record-keeping and reduce human error in your testing procedures.
- Combination testers perform simultaneous wrist strap and footwear testing
- Automated calibration tools allow for quick on-site verification without disassembly
- Digital logging systems maintain detailed records for audit compliance
- Real-time monitoring alerts notify you of any compliance issues immediately
- Integrated testing stations streamline employee check-in procedures
When selecting an automated tester, you'll want to evaluate features that match your facility's specific needs while ensuring compliance with relevant industry standards.
The right system will balance efficiency with reliable performance monitoring.
Maintenance Best Practices

Proper maintenance of ESD wrist straps goes beyond simple testing and requires a thorough approach to secure reliable static protection.
You'll need to guarantee regular calibration of your test equipment to maintain measurement accuracy, and tools like the ED311 can help you perform on-site calibration without sending equipment to a laboratory.
Keep your wrist straps clean by using mild detergents regularly to prevent corrosion and maintain proper conductivity.
Don't wear your wrist straps too tightly, and avoid daisy chaining them together, as these practices can lead to premature wear and damage.
When you're not using your wrist straps, store them in a clean, dry environment to preserve their effectiveness.
If you encounter any issues during testing, troubleshoot by checking each component individually – the wrist band, ground cord, and skin interface.
Replace any faulty parts immediately before resuming work.
Remember to maintain detailed records of your maintenance activities for quality control purposes.
Documentation and Record Keeping
While maintaining your ESD wrist straps helps guarantee physical integrity, documenting their test results creates an essential trail of accountability.
You'll need to keep daily test records that include the date, time, and results of each assessment to confirm compliance with industry standards. These records serve as evidence of conformity to technical requirements and can help you identify potential issues before they become problems.
You should store your test documentation either digitally using personnel grounding testers connected to a computer or in traditional log books.
Remember to review your records regularly and maintain them for the period specified in your company's ESD control plan. This documentation will prove invaluable during audits and help you track trends in wrist strap performance.
- Document all failed tests and corrective actions taken
- Include the frequency and sampling percentage of tests in your ESD control plan
- Store records in an easily accessible format for audit purposes
- Review documentation regularly to identify patterns or recurring issues
- Adjust testing frequency based on the vital nature of ESD-sensitive items handled
Make certain you're using test results to refine your ESD control procedures and maintain peak protection for your sensitive components.
Calibration Schedules
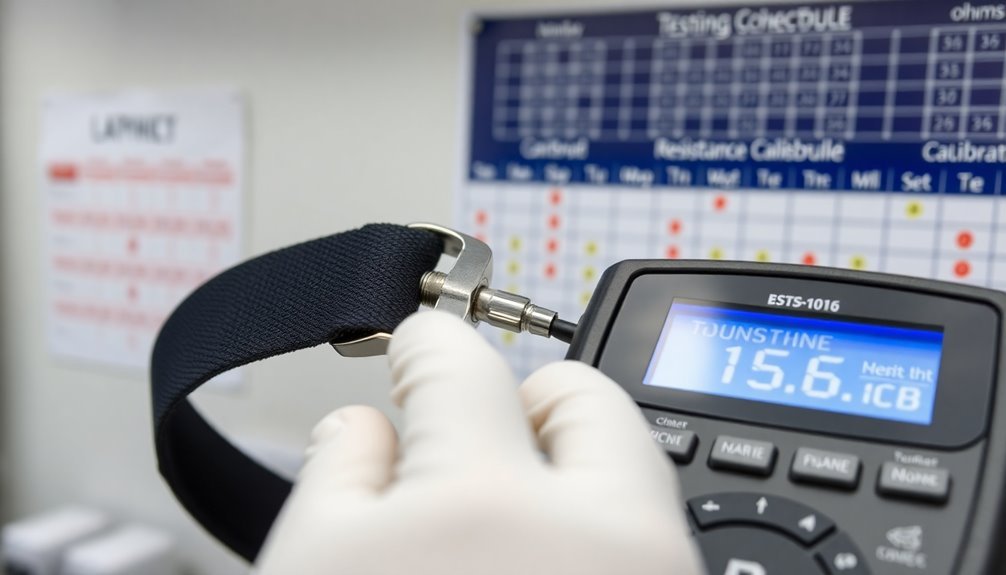
Regular calibration of your ESD wrist strap testers serves as the foundation for maintaining accurate measurements and reliable protection.
You'll need to calibrate your testers annually to guarantee they're functioning within the specified parameters of 750 kilohms to 35 megohms. Annual certification must be completed and documented for all ESD stations.
The calibration process is straightforward and typically takes about 10 minutes using tools like a resistance decade box or verification testers such as the ED311 Periodic Calibration Tool.
You can perform these calibrations on-site while following manufacturer guidelines and industry standards like ANSI/ESD S1.1 and EN 61340-5-1.
Your calibration frequency may need adjustment based on how vital your ESD-sensitive items are and the potential risk of ESD protective equipment failure.
During calibration, you'll verify the tester's operation by using specific resistance values and checking the output against acceptable limits.
It's important to maintain proper documentation of all calibration procedures to demonstrate compliance with industry standards.
Remember that calibration isn't just about meeting requirements – it's imperative for preventing false readings that could compromise your entire ESD control program and potentially damage sensitive components.
Industry Standards and Compliance
You'll need to follow key industry standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20 and EN 61340-5-1 when establishing your ESD wrist strap testing program.
Your testing documentation must include detailed records of daily wrist strap checks, resistance measurements, and any failures or replacements that occur. Visual inspections and functional testing should be completed before handling sensitive components.
Maintaining proper compliance records isn't just about meeting requirements—it's critical for demonstrating your ESD control program's effectiveness and protecting sensitive electronics from damage.
Daily testing is recommended unless you have implemented continuous monitoring systems for your wrist straps.
Industry Standards For Testing
Industry leaders have established clear guidelines for testing ESD wrist straps to guarantee workplace safety and protect sensitive electronics. According to ESD-S1.1 standards, you'll need to test your wrist straps daily if you're using them on a regular basis. This requirement stems from the fact that wrist straps have a finite lifespan and can fail unexpectedly, potentially compromising your ESD protection system.
For more stringent compliance, you'll need to follow these standardized testing protocols:
- ANSI/ESD S20.20 outlines minimum technical requirements for ESD control programs, including specific testing frequencies.
- EN 61340-5-1 mandates proper grounding or equipotential bonding when handling ESD-sensitive items.
- ESD-S1.1, paragraph 6.1.3 specifically requires daily testing of wrist strap systems.
- TR 20.20 guidelines emphasize regular testing due to the limited lifespan of wrist straps.
- Quarterly and semi-annual testing protocols must include thorough checks of both worksurfaces and wrist straps.
If you're working with highly sensitive components or in critical applications, you should consider implementing continuous monitoring systems. These systems provide immediate feedback on wrist strap failures and can replace traditional periodic testing while ensuring consistent protection against ESD damage.
Key Compliance Documentation Needs
Along with proper testing procedures, maintaining thorough documentation of your ESD wrist strap testing is essential for compliance and quality control.
You'll need to record key information including operator identification, test results, resistance measurements, and the time of testing. Your documentation should align with standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340-5-1.
Your records must include daily test logs that demonstrate conformity to industry standards and help you quickly identify potential issues.
You'll want to maintain detailed testing procedures in your ESD control plan, specifying the frequency and sampling percentage of your tests. This guarantees consistency and reliability across all testing activities.
Don't forget to document your test equipment's calibration and verification procedures.
You should regularly calibrate your testing equipment and maintain records of these calibrations to guarantee accuracy.
Your documentation should prove that your personnel grounding testers are functioning correctly and meeting technical requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can ESD Wrist Straps Be Shared Between Multiple Operators?
No, you shouldn't share ESD wrist straps between operators. It's unsafe, compromises personal hygiene, affects grounding reliability, and violates safety protocols. Each operator needs their own dedicated strap for proper ESD protection.
What Happens if I Forget to Test My Wrist Strap One Day?
If you've missed a day of testing, you'll need to test your wrist strap immediately before use. Don't risk damaging sensitive components – perform the test right away and document the oversight.
Do Wireless ESD Wrist Straps Provide the Same Level of Protection?
Yes, wireless ESD wrist straps provide equivalent protection when properly maintained. You'll get similar grounding performance, but you'll need to monitor battery life and signal integrity to guarantee they're working correctly.
Should ESD Wrist Straps Be Worn Over or Under Long Sleeves?
You should always wear your ESD wrist strap under long sleeves with direct skin contact. Don't place it over clothing, as sleeves can interfere with grounding and compromise your protection against static discharge.
Can ESD Wrist Straps Cause Skin Irritation or Allergic Reactions?
Yes, you can experience skin irritation or allergic reactions from ESD wrist straps due to their materials like silver fibers, elastic bands, or metal snaps. If you notice any discomfort, try alternative materials or consult a doctor.
In Summary
You'll need to test your ESD wrist straps daily before starting work to guarantee proper grounding and protection of sensitive electronic components. Don't skip your testing routine, even if you're using continuous monitoring systems. Keep detailed records of all tests, maintain your equipment according to manufacturer guidelines, and follow industry standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20. Regular testing and maintenance will protect your work and investments.




Leave a Reply