When packaging computer components, you'll need to follow several essential foam protection methods. Always use anti-static foam to prevent damaging electrical charges, and create custom-fitted cavities for each part to prevent movement. Layer components strategically, placing heavier items at the bottom with denser foam support. Maintain temperature control by using EPS foam for sensitive parts, and implement double boxing with at least 3 inches of cushioning on all sides. Don't forget to wrap individual components in anti-static material first, and secure graphics cards separately. These foundational tips will help safeguard your valuable hardware during transit, but there's much more to think about for ideal protection.
Choosing Anti-Static Foam Protection
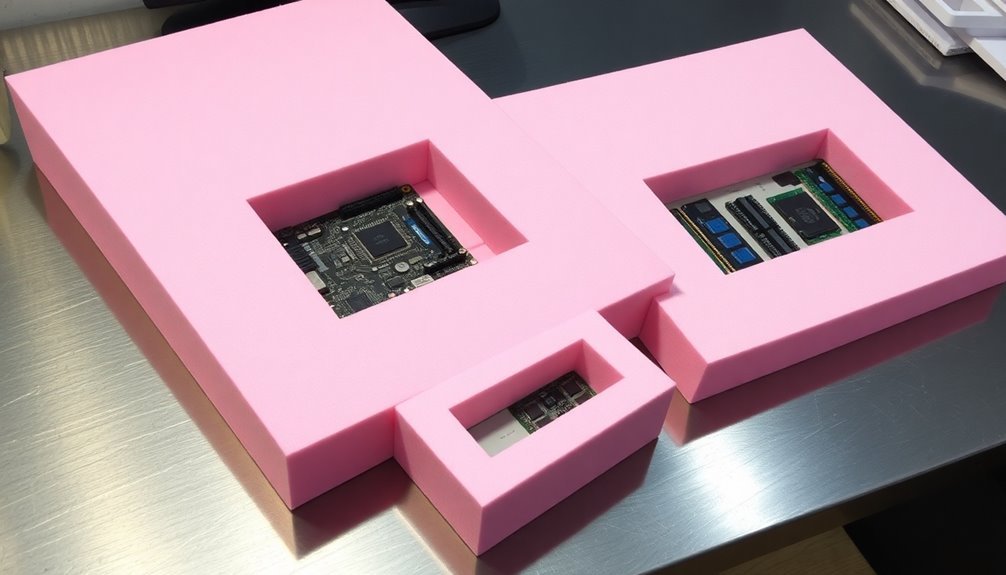

For protecting sensitive computer components, selecting the right anti-static foam is crucial. You'll find several types available, each serving specific protection needs.
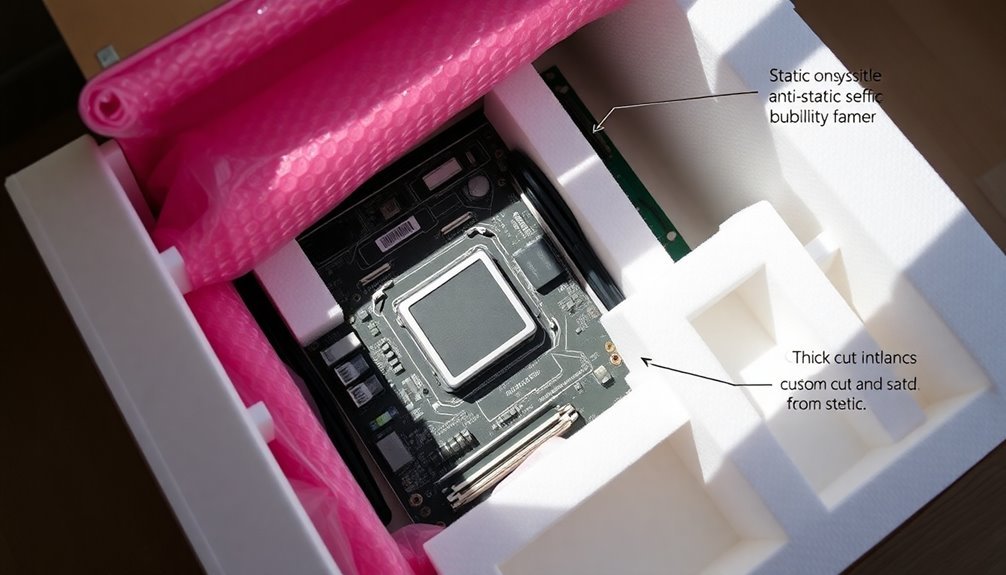
The pink color identification helps easily distinguish anti-static foam from regular packaging materials.
Conductive foam provides the highest level of protection by creating a Faraday cage around your components, while standard anti-static foam prevents static buildup without full shielding.
When packaging delicate computer parts, you'll want to think about the foam's material properties. Polyurethane anti-static foam features an open-cell structure with conductive fillers, making it ideal for cushioning circuit boards and chips.
If you're looking for more rigid protection, high-density conductive polyethylene foam works well for securing component leads.
You can tailor your foam protection based on your specific needs. Die-cut pads fit perfectly in ESD boxes, while foam sheets can be sized to wrap around larger components.
For particularly fragile or expensive parts, think about conductive memory foam, which offers superior cushioning properties.
If you're working with multiple components, you'll benefit from compartmentalized foam solutions that keep parts separated and secure.
Remember to match the foam's protective properties with your components' sensitivity levels to safeguard adequate ESD protection.
Proper Component Cushioning Methods
When packing computer components, you'll need to layer them strategically with enough space between each part to prevent contact during transit.
You should select cushioning materials with the right density based on your components' weight and fragility, typically requiring 2-3 inches of foam for ideal protection.
Remember to secure each component with multiple layers of cushioning material while maintaining proper load distribution across the foam's surface area. Consider using protective foam structures like expanded polystyrene or polyethylene that specifically absorb shock and vibration during shipping.
Layer Components Strategically
Inside any computer component shipping box, proper layering serves as your primary defense against transit damage. You'll need to take into account both the weight and sensitivity of each component when determining your foam layering strategy.
For delicate electronic parts, start with anti-static foam as your base layer, then add convoluted foam inserts for precision cushioning. The pink coloring of the foam helps easily identify anti-static properties when organizing your packaging materials.
When layering multiple components, follow these critical steps:
- Position heavier items at the bottom using denser foam like cross-linked polyethylene, ensuring they're placed on their largest, flattest surface to distribute weight evenly.
- Create custom-fitted foam cavities for each component, maintaining proper spacing to prevent contact during transit.
- Secure components with additional foam layers on top, using ties or tape when necessary to prevent shifting.
Don't forget to fill any void spaces with supplementary foam pieces to prevent unwanted movement.
If you're packaging sensitive electronics, incorporate conductive foam layers to shield against electromagnetic interference.
For unusually shaped components, custom-cut foam inserts will provide the most secure fit and protection throughout the shipping process.
Cushioning Density Selection
The right cushioning density makes all the difference in protecting your computer components during transit. You'll need to calculate the static loading (psi) by dividing your component's weight by the surface area that contacts the foam. This calculation helps you select the best foam density and thickness for maximum protection. The best practice is to examine cushioning performance curves to validate your foam selection decisions.
| Component Type | Recommended Foam | Density Range |
|---|---|---|
| Graphics Cards | Edge Armor | Medium-High |
| Motherboards | Polyethylene | Medium |
| Hard Drives | Polyurethane | Low-Medium |
| CPUs/RAM | Urethane | Low |
For delicate components like processors and RAM, you'll want to use low-density urethane foams that won't put excessive pressure on the parts. Graphics cards, with their vulnerable edges, benefit from dual-density Edge Armor foam. Motherboards require medium-density polyethylene foam to support their weight while protecting sensitive areas.
Don't make the mistake of choosing overly dense foam – it can actually reduce protection and increase costs. Instead, match your foam selection to your component's fragility level and g-limit. Consider the expected drop heights during shipping when determining your final foam thickness requirements.
Temperature And Moisture Control
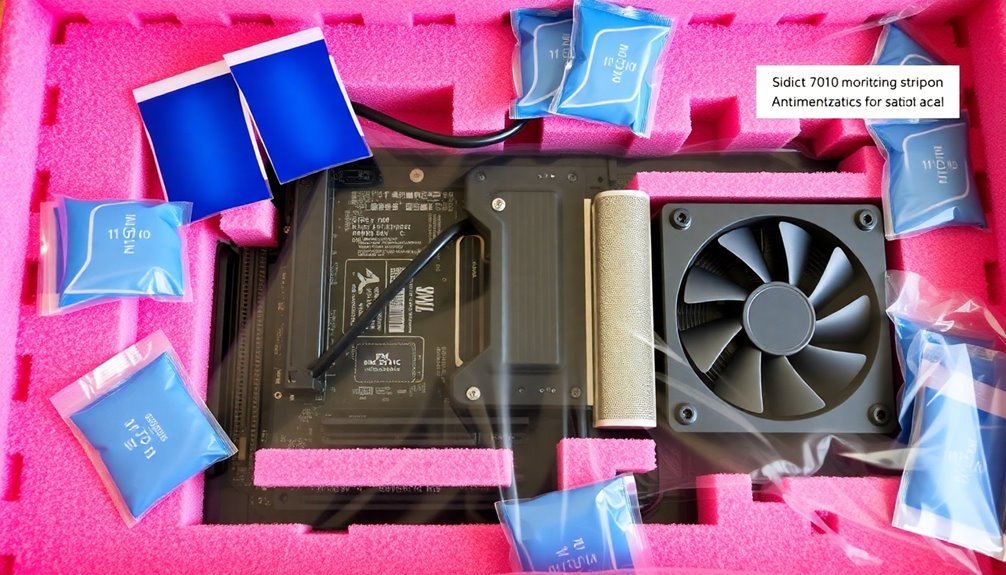

Throughout the shipping process, temperature and moisture control play critical roles in protecting computer components from damage. You'll need to carefully select foam packaging materials that provide both thermal protection and moisture resistance to safeguard your components arrive safely at their destination.
EPS foam is particularly effective for temperature-sensitive components, offering excellent insulation properties that protect against thermal fluctuations. The unique nature of EPS means it provides superior insulating qualities even in extreme shipping conditions.
When you're dealing with moisture concerns, anti-static and ESD foams provide essential protection against moisture-induced static electricity that could damage your computer parts.
For the best protection of your computer components, follow these key steps:
- Select the appropriate foam type (EPS, PU, or PE) based on your specific temperature requirements and the environmental conditions during shipping.
- Incorporate anti-static or conductive foam materials to prevent moisture-related static electricity damage.
- Design custom foam inserts that provide a snug fit while maintaining proper airflow around sensitive components.
Remember to think about both open-cell and closed-cell foam options, as they offer different levels of moisture protection.
You'll also want to guarantee compliance with industry standards like EIA-541 when selecting your packaging materials, as these guidelines help guarantee adequate protection for electronic components.
Double Boxing Computer Parts
When shipping valuable computer components, double boxing provides an essential layer of protection against damage during transit. You'll need to start by selecting two sturdy boxes – a smaller inner box for your component and a larger outer box with ample space for cushioning materials. Dish-pack boxes can offer exceptional protection for more delicate computer parts.
| Component | Inner Box Protection | Outer Box Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Drive | Anti-static wrap | Packing peanuts |
| Tower | Foam cushioning | Bubble wrap |
| Graphics Card | Anti-static bag | Corner protectors |
| Monitor | Screen protector | Foam inserts |
| Peripherals | Individual wrapping | Crumpled paper |
First, wrap your component in anti-static material and place it in the inner box with at least 3 inches of cushioning on all sides. Seal this box thoroughly with tape in an 'H' pattern. Next, position the inner box inside the larger outer box, surrounding it with additional packing materials to prevent movement. Don't forget to test the package by gently shaking it – if you hear movement, add more cushioning. Finally, seal the outer box securely and label it clearly with "Fragile" and "This Side Up" markings. Remember to tape any hand holes shut on both boxes for extra security.
Custom Foam Insert Solutions
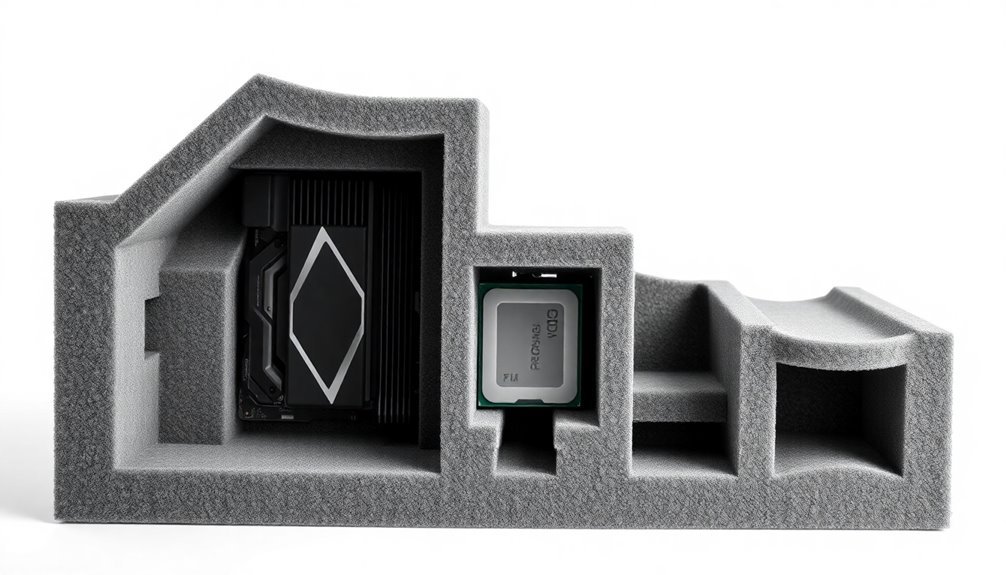
When you're shipping computer components, custom foam inserts with precision-cut designs offer superior protection by eliminating movement and providing exact cushioning for each part.
Companies like Index Packaging provide rapid prototyping services with foam insert samples delivered in just 1-3 days.
You'll want to select anti-static or conductive foam materials for sensitive electronics, while polyethylene foam works well for heavier components like power supplies and cases.
For component-specific protection, you can use CAD-designed inserts that cradle each piece individually, preventing contact between parts while absorbing shock during transit.
Precision-Cut Design Benefits
Modern precision-cut foam inserts represent a game-changing advancement in computer component protection. You'll benefit from computer-guided CNC routing and water jet cutting technologies that create precise, custom-fitted cavities for your sensitive electronics. The high tonnage presses used in fabrication ensure consistently accurate cuts across production runs.
These cutting-edge manufacturing techniques guarantee your components stay securely in place during shipping and handling, with smooth edges that won't generate damaging particulates.
When you're packaging valuable computer parts, precision-cut foam offers three essential advantages:
- Multiple cavity depths accommodate components of varying sizes, from tiny microchips to larger graphics cards
- Customized shock absorption protects against impacts and vibrations that could damage sensitive electronics
- Perfect-fit cavities prevent components from shifting or colliding during transit
The precision-cut approach allows you to choose from various foam materials, including polyurethane and polyethylene, to match your specific protection requirements.
You'll also appreciate how these custom solutions can incorporate your brand colors and logos, adding a professional touch to your packaging. Whether you're shipping individual components or complete systems, precision-cut foam inserts deliver the exact protection your computer equipment needs while maintaining a polished presentation.
Material Selection Guide
Selecting the right foam material for your computer components boils down to three key factors: protection level, environmental conditions, and cost-effectiveness.
For computer components, you'll want to prioritize anti-static and conductive foams to prevent static discharge damage. These specialized materials provide both physical protection and ESD safeguarding for sensitive electronics.
If you're packaging motherboards, graphics cards, or memory modules, don't compromise on using proper anti-static materials.
Consider using multi-layered foam inserts that combine different densities for the best protection. The outer layer should be high-density foam for shock absorption, while inner layers can feature precision-cut cavities that conform to your components' exact dimensions.
For temperature-sensitive parts, expanded polystyrene foam offers excellent thermal insulation.
You'll need to factor in moisture resistance, especially for long-term storage or shipping to humid regions. Custom polyethylene foam inserts with moisture-resistant properties can protect your components from condensation damage.
While premium materials like anti-static foam may cost more initially, they're essential investments that prevent costly component failures. Remember to properly wrap and secure components within the foam cavities to maximize protection during transit.
Component-Specific Protection Methods
Custom foam inserts serve as tailored armor for your computer components, providing precision-fit protection during storage and transit. You'll find these inserts designed with component-specific cutouts that prevent movement and shield against drops, vibrations, and potential collisions.
When you're handling sensitive electronic parts, anti-static and conductive foam options safeguard protection from harmful electrostatic discharge.
For maximum component protection, you'll want to evaluate these essential features:
- Multi-layered foam construction that combines different densities for superior shock absorption and cushioning
- CAD-routed precision cuts that create exact fits for your specific components, eliminating movement during transport
- Material-specific solutions like PE foam for moisture resistance or PU foam for enhanced shock absorption
You can further customize your protective packaging with special additions like adhesive backings or color-coding for easier organization. When you're selecting foam inserts, guarantee they meet industry standards and regulations, particularly for sensitive electronics.
The right combination of materials and design will safeguard your components against damage while maintaining compliance with shipping requirements.
Securing Internal Graphics Cards
Properly securing internal graphics cards requires three essential steps before foam packaging can begin. First, you'll need to disconnect all power sources and carefully remove the card from its PCIe slot while wearing anti-static gloves.
Next, place the card into an anti-static bag that's large enough to accommodate it without forcing or bending the component.
When you're ready to package the graphics card, select a sturdy box that's slightly larger than your wrapped component. Line the bottom with foam padding or bubble wrap, creating a protective cushion.
Place your anti-static-wrapped graphics card in the center, then fill all empty spaces with additional foam, bubble wrap, or packing peanuts to prevent any movement during transit.
Don't forget to label your package as "Fragile" and consider using insurance for valuable shipments. If you still have the original packaging, it's your best option as it's specifically designed for your graphics card.
Before sealing the box, verify that the card can't shift inside, and double-check all seals. Include unpacking instructions for the recipient to safeguard safe handling upon arrival.
For high-value cards, you might want to use professional packing services.
Testing Static Protection Levels
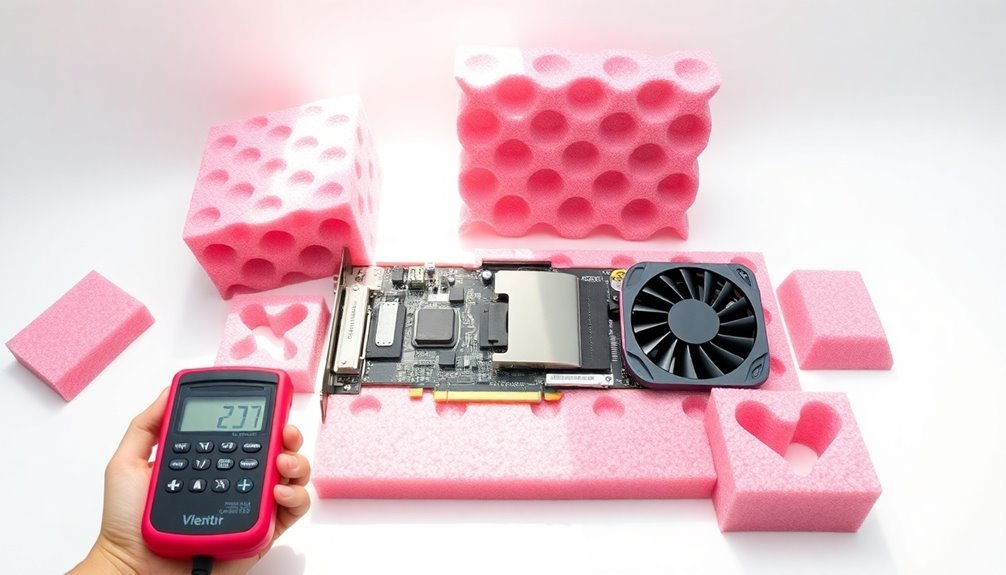

Once you've secured your graphics card in protective packaging, you'll want to verify the static protection levels of your materials. Testing the effectiveness of your ESD protection is vital to guarantee your components remain safe during storage and transport.
You can conduct basic static protection tests using standardized methods that align with IEC 61000-4-2 specifications.
To properly test your foam packaging's static protection levels, follow these essential steps:
- Set up your component in a controlled environment with proper monitoring equipment to detect any potential discharge events or performance issues.
- Use an ESD simulator or testing gun to apply controlled static discharge events at various points around your packaged component.
- Monitor the package's performance across different protection metrics, including its ability to dissipate charges and form an effective Faraday cage.
When testing, you'll need to think about whether you're using conductive, anti-static, or static dissipative foam, as each type offers different protection levels. If you're using conductive foam, it creates a Faraday cage around your products, making it ideal for highly sensitive components that need complete protection. Anti-static foam prevents static buildup but doesn't offer full protection against static transfer, so you might need additional static shielding bags for complete safety. Static dissipative foam combines the benefits of both, allowing charges to dissipate slowly while preventing sudden static shocks.
If you're uncertain about your testing capabilities, think about sending your packaged components to a certified testing facility that can verify compliance with industry standards. Remember that improper testing methods can potentially damage your components, so always follow established testing protocols.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Can Computer Components Safely Remain Stored in Anti-Static Foam Packaging?
You can safely store your computer components in anti-static foam for several years, as the foam maintains its static-dissipating properties and durability over time while protecting against environmental factors and physical damage.
Can Foam Packaging Materials Interfere With Wifi or Bluetooth Components?
You don't need to worry about foam interfering with WiFi or Bluetooth signals. Standard foam packaging materials won't block wireless connectivity since they don't contain metals or conductive elements that typically cause signal interference.
Is Vacuum-Sealed Foam Packaging Safe for Sensitive Electronic Components?
Yes, you'll find vacuum-sealed foam packaging is safe for sensitive electronics. It protects against static, moisture, and physical damage. Just guarantee you're using anti-static or conductive foam that meets industry safety standards.
Should Foam Packaging Be Replaced After Multiple Uses for Shipping?
Yes, you should replace foam packaging after multiple uses since it loses protective properties, shape retention, and cushioning effectiveness. Don't risk component damage by reusing degraded foam that can't properly protect your items.
What Cleaning Solutions Are Safe to Use on Anti-Static Foam Packaging?
You'll need specialized ESD cleaners like StaticCARE or ACL Staticide. Don't use regular household cleaners. You can apply isopropyl alcohol in specific procedures, but it shouldn't be your primary cleaning solution.
In Summary
You'll save yourself significant headaches by implementing these foam packaging best practices for your computer components. Making smart choices about anti-static materials, proper cushioning, and moisture control guarantees your valuable parts arrive safely. Don't skip double boxing or custom foam inserts when shipping expensive components. Remember to test static protection levels and secure internal cards properly before transport.





Leave a Reply