For shipping electronics, you'll want to choose between anti-static foam or conductive foam based on your specific needs. Anti-static foam (typically pink) works well for standard electronic components and smaller items, as it dissipates static charges safely. For more sensitive or expensive electronics, opt for conductive foam, which provides superior EMI shielding and acts like a Faraday cage. You can also consider cross-linked polyethylene foam for exceptional durability and moisture resistance. The right choice depends on your component's sensitivity, size, and shipping requirements – factors that'll determine the level of protection your electronics truly need.
Understanding Electronics Foam Types
For your highest-value electronics or items requiring maximum protection, consider cross-linked polyethylene foam. It's more tear-resistant than standard polyethylene and offers exceptional water resistance and thermal insulation.
You'll benefit from its enhanced durability during long shipments and its ability to protect class-A products. Pink coloring typically indicates proper anti-static treatment of the foam.
All these foams can be manufactured with anti-static properties, ensuring your electronics remain protected from electrostatic discharge throughout shipping and handling.
Anti-Static Vs Conductive Foam
If you're shipping electronic components, you'll need to understand the key differences between anti-static and conductive foam to guarantee proper protection.
While anti-static foam dissipates static electricity and works well for smaller, less sensitive items, conductive foam actively conducts static away from components and provides superior EMI shielding for larger or more sensitive electronics. Anti-static foam has a surface resistance between 10^9 to 10^12 ohms.
Your choice between the two should factor in your component's sensitivity level, size, and whether you'll need the foam for one-time or repeated use.
Key Differences Between Types
Understanding the differences between anti-static and conductive foam helps you choose the right packaging for your electronic components. Anti-static foam works by dissipating static charges, while conductive foam creates a Faraday cage effect to block electromagnetic fields.
You'll find that anti-static foam is made from chemically treated polyethylene or polyurethane, whereas conductive foam contains carbon-filled polyethylene for enhanced protection. Pink anti-static foam provides single-trip protection during transit and is typically non-reusable.
When it comes to performance, conductive foam offers superior electrical protection and EMI shielding compared to its anti-static counterpart. It's also reusable, making it a better long-term investment despite its higher initial cost. You'll notice that conductive foam has lower surface resistivity, which provides better grounding and coupling performance.
For shipping small, sensitive items like CPUs and microprocessors, anti-static foam sheets or egg crate foam will suffice. However, if you're packaging larger, bulkier items that need enhanced electrical protection, you should opt for conductive foam.
Both types should meet EIA-541 packaging standards, and you can get them customized to fit your specific electronic components. Remember that conductive foam also offers better dust sealing and shock absorption capabilities.
When To Use Each
Selecting the right protective foam for electronics shipping requires careful consideration of your component's sensitivity and protection needs.
If you're shipping standard electronic components like circuit boards or computer chips that need basic ESD protection, anti-static foam is your best choice. It's lightweight, non-abrasive, and provides sufficient protection while meeting EIA-541 standards for ESD-sensitive items. Custom precision cutting allows anti-static foam to perfectly cradle your electronics for maximum protection during transit.
For extremely sensitive electronic components or when you need thorough protection, you'll want to opt for conductive foam. It's particularly valuable when you need the Faraday cage effect to shield against electromagnetic fields.
You'll find it's also the better choice for heavier items or when you need long-term packaging solutions, as it offers superior durability and eliminates the need for additional static shielding bags.
Consider your specific requirements carefully. If you need customizable sheets for smaller items, anti-static foam offers excellent flexibility and can be cut to your specifications.
However, if you're looking for repeat use and maximum electromagnetic shielding, conductive foam's higher initial cost is offset by its long-term value and superior protection capabilities.
Protection Level Comparison
Anti-static and conductive foams deliver distinct levels of protection for your electronic components, with key differences in their electrical resistance properties. While anti-static foam offers moderate protection with surface resistance of 10^6 to 10^9 ohms, conductive foam provides superior protection with resistance between 10^3 to 10^5 ohms.
| Feature | Anti-Static Foam | Conductive Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Level | Moderate | High |
| Dissipation Rate | Slow | Fast |
| Static Control | Passes through | Acts as Faraday cage |
You'll find that anti-static foam slowly dissipates charges and allows static electricity to pass through without building up, making it suitable for general electronic components in environments requiring moderate static control. In contrast, conductive foam delivers enhanced protection through faster charge transfer and minimizes static buildup by acting like a Faraday cage, making it ideal for sensitive electronics. The pink dye identification makes it easy to spot and verify you're using the correct protective material for your electronics.
When shipping valuable or highly sensitive components, you'll benefit from conductive foam's superior shielding properties, as it doesn't require additional static shielding bags. While it's more expensive than anti-static foam, it offers better long-term value and can be reused for multiple shipping applications.
ESD Protection Requirements

In accordance with EIA-541 standards, electronic devices require specific ESD protection during shipping to prevent damage from static electricity.
You'll need to select packaging materials that effectively prevent triboelectric charging and dissipate electrostatic charges. Your packaging must also shield sensitive components from harmful electrostatic fields. Pink colored foam helps easily identify anti-static materials during packaging.
When choosing foam materials, you'll need to match the protection level to your device's sensitivity. Anti-static foam offers basic protection with resistance levels between 10^9 and 10^12 ohms, while conductive foam creates a Faraday cage effect with resistance below 10^6 ohms. For controlled discharge capability, static dissipative foam with resistance between 10^5 and 10^9 ohms might be your best choice.
You must guarantee your packaging design complies with ANSI/ESD S541 requirements. Consider using open-cell polyurethane foam for lightweight electronics and closed-cell polyethylene foam for heavier items.
Your packaging should include clear ESD protective markings and meet non-abrasive requirements to protect sensitive surfaces.
Remember to integrate these choices into your organization's ESD control program to maintain consistent protection standards throughout shipping and handling processes.
Foam Density and Protection Levels
While protecting electronic components during shipping, you'll need to match foam density levels to your product's specific requirements. The density of your chosen foam directly impacts its protective capabilities, with ranges typically falling between 10-40+ kg/m³ for EPS foams.
Higher-density foams offer superior impact resistance, which is essential for delicate electronics. If you're shipping items sensitive to moisture, opt for higher-density options, as they're less likely to absorb water. Flexural strength increases significantly with higher density foam choices.
When selecting foam density, consider that steam pressure and temperature during manufacturing affect the final product – higher pressures typically result in lower densities.
For the best protection, you'll want to balance density with thickness. Don't assume that extremely dense foam automatically provides better protection; sometimes, it can be counterproductive. Consider your product's fragility factor when making this decision.
For extremely fragile components, you might need multiple density layers, while moderately rugged items may require only standard-density foam.
Remember that the size and weight of your electronic components should guide your density selection. Smaller, lighter items often work well with lower-density foams, while heavier electronics need denser materials for adequate support and protection.
Custom Foam Solutions

Custom foam solutions stand at the forefront of electronics protection, combining precision engineering with specialized materials like polyurethane and EVA foam. These solutions are designed using advanced software to create precise digital models that guarantee a perfect fit for your electronic devices.
Impact forces are effectively absorbed and dispersed by these custom foam solutions during transit. Through sophisticated cutting methods like water jet and CNC machines, manufacturers can deliver exactingly crafted foam inserts that cradle your valuable equipment.
When you're shipping sensitive electronics, custom foam solutions offer several compelling advantages:
- Your products arrive safely, protected by precisely engineered cushioning that prevents costly damage and maintains your brand's reputation
- You'll reduce waste and improve efficiency with foam designs specifically tailored to your unique packaging needs
- Your customers receive their electronics in pristine condition, leading to higher satisfaction rates and fewer returns
These custom solutions incorporate critical properties like anti-static protection and non-abrasive surfaces, meeting industry standards such as EIA-541. Whether you're shipping consumer electronics, medical devices, or industrial components, you can utilize various foam configurations including trays, shadow boards, and suspension packs.
The combination of precision design and specialized materials guarantees your electronics reach their destination safely and securely.
Moisture Control in Foam Packaging
Moisture poses a significant threat to electronics during shipping, making proper foam packaging with moisture control essential for protection. You'll need to select foams specifically designed to combat moisture-related issues, such as cross-linked polyethylene or specialized vapor barrier foams that prevent moisture penetration.
When choosing moisture-resistant foam packaging, you should consider your shipping environment and the sensitivity of your electronic devices. High-density foams provide better moisture resistance, while antimicrobial treatments can prevent moisture-driven growth.
For marine transport or high-humidity environments, you'll want to combine moisture-resistant foams with additional protective measures like desiccants and sealable barrier bags.
To maximize protection, focus on materials that offer both moisture resistance and thermal insulation properties. Cross-linked polyethylene foam delivers excellent moisture resistance and structural rigidity, while anti-static foam provides dual protection against moisture and static electricity.
Don't forget to guarantee your chosen foam meets relevant moisture control standards and regulations. For sensitive electronic components or medical equipment, you'll need specialized packaging that maintains both integrity and sterility throughout the shipping process.
Temperature Impact on Foam Materials

Temperature fluctuations can substantially impact the performance and protective qualities of foam packaging materials used for electronics shipping. When you're selecting foam for your electronic devices, you'll need to think about how temperature changes affect different materials. Polyurethane and polyethylene foams offer excellent thermal insulation, helping maintain stable temperatures for your sensitive components.
You'll want to be aware of these critical temperature-related effects on foam:
- Your foam materials will expand and contract with temperature changes, which can compromise their protective capabilities
- High temperatures may soften your packaging materials, while cold conditions can make them brittle
- Prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures will degrade your foam's effectiveness over time
For ideal protection, think about using custom foam inserts designed specifically for your electronics. These can incorporate multiple layers of different foam materials, each serving a specific purpose in temperature control.
When shipping temperature-sensitive electronics, EPS foam provides exceptional insulation properties. Remember that proper material selection isn't just about cushioning – it's about maintaining consistent operating temperatures throughout the shipping process to protect your valuable electronic components from damage.
Industry Standards for Foam Selection
Selecting foam materials for electronics shipping requires strict adherence to industry standards and certifications. You'll need to confirm that your packaging materials comply with EIA-541 standards, which govern electrostatic protective packaging materials.
When choosing foam types, you'll find three main categories: anti-static, conductive, and static dissipative foams. Anti-static foams are chemically treated and typically pink in color, while conductive foams contain carbon and create a Faraday cage effect.
For smaller electronics like circuit boards, opt for open-cell polyurethane foams. Larger items like computers work better with closed-cell polyethylene foams.
You'll want to verify that your selected foam meets specific performance characteristics. The density should fall between 2 and 6 pounds per cubic foot for anti-static polyurethane foams.
Your foam must provide adequate cushioning, shock absorption, and moisture resistance while remaining non-abrasive to delicate surfaces.
Don't skip the testing and certification requirements. You'll need to conduct drop tests to determine G-factor ratings and perform ESD testing to verify electrostatic properties.
Regular quality control checks and certifications from recognized organizations like ISO will confirm that your foam packaging consistently meets industry standards.
Cost Analysis of Foam Options
When you're comparing foam packaging options for electronics, you'll find polyethylene foam offers the most cost-effective basic protection.
While polyurethane provides superior cushioning at a higher price point, you can reduce your per-unit costs by purchasing foam materials in bulk, often saving 20-25% on large orders.
Cross-linked polyethylene foam presents a middle-ground option, offering enhanced durability and protection for larger electronics while maintaining reasonable costs compared to polyurethane alternatives.
Price Per Protection Level
Making informed decisions about foam packaging requires careful analysis of price-to-protection ratios for electronics shipping. Open-cell foams offer cost-effective solutions for smaller, delicate electronics, while closed-cell options provide enhanced durability for heavier items at a higher upfront cost.
You'll find that anti-static foams, though more expensive, are essential for protecting components sensitive to electrostatic discharge.
When you're considering protection levels, remember these emotional factors:
- Your reputation depends on delivering undamaged products to your customers
- You can't put a price on losing customers due to inadequate packaging
- Your business's sustainability efforts matter to environmentally conscious consumers
Customized foam solutions might initially seem more expensive, but they'll often save you money in the long run. By optimizing material usage and reducing package dimensions, you'll cut shipping costs and minimize waste.
For sensitive electronics like circuit boards and CPUs, open-cell foam provides sufficient protection while keeping costs down. However, if you're shipping monitors or complete computer systems, investing in closed-cell foam's superior impact resistance is worth the additional expense.
The key is matching the foam's protection level to your specific shipping needs.
Bulk Purchase Cost Benefits
Businesses' bottom lines substantially benefit from bulk foam purchases, with volume discounts often reaching 20-30% off standard pricing. When you order foam sheets in bulk, you'll find significant cost reductions not just in material costs but also in shipping expenses.
These savings compound when you factor in the reduced dimensional weight charges that come from using customized foam inserts to minimize package dimensions.
The lightweight nature of foam packaging translates directly to your shipping costs, potentially reducing them by up to 15%. You'll also benefit from the material's reusability and recyclability, which extends its value over time. The polyethylene foam sheets can be used repeatedly, resisting tears and maintaining their protective properties through multiple shipments.
Your bulk purchase investment pays off through versatile applications across your electronics shipping needs. Whether you're protecting PCBs, sensors, or electrical connectors, you can customize foam inserts to match specific product requirements.
Environmental Considerations for Foam
The environmental impact of foam packaging in electronics shipping presents a complex balance of benefits and drawbacks. While foam offers substantial advantages in protecting electronics and reducing shipping emissions through its lightweight nature, it's crucial to understand its environmental implications for informed decision-making.
When you're selecting foam packaging, consider that many varieties are 100% recyclable and can be reused multiple times, markedly reducing waste. However, you'll need to acknowledge that most foam materials are petroleum-based and can potentially break down into harmful microplastics if not properly disposed of.
To minimize environmental impact, you'll want to:
- Choose eco-friendly alternatives like biodegradable or wood-based foams when possible
- Implement a reuse program to extend the lifecycle of your foam packaging
- Partner with specialized recycling facilities since foam isn't typically accepted in curbside programs
You can further reduce environmental impact by selecting lightweight foams that decrease shipping emissions and opting for materials compliant with environmental regulations. When designing your packaging solution, focus on minimal material use while maintaining adequate protection.
Consider establishing a take-back program to guarantee proper recycling of foam materials after use.
Common Foam Packaging Mistakes
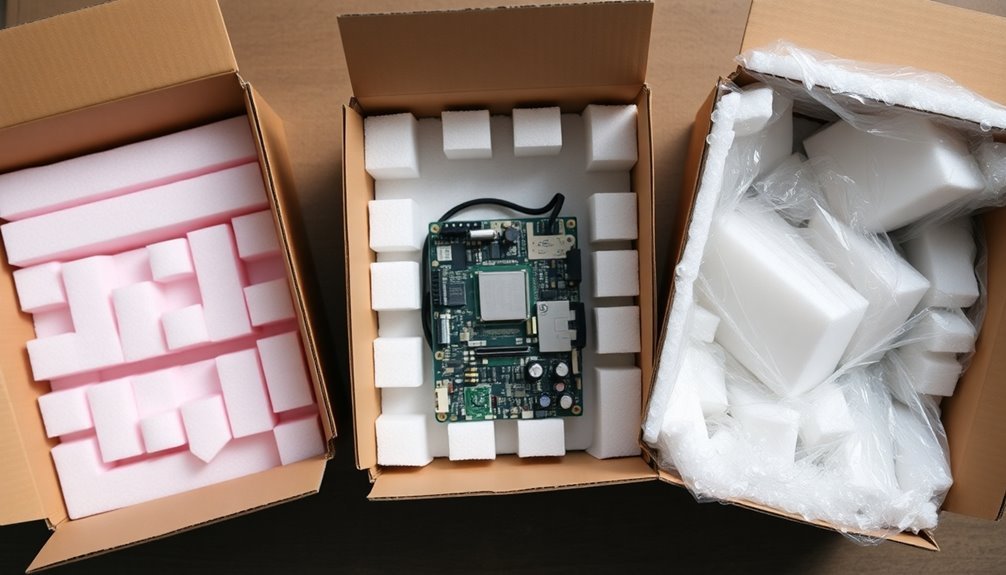

Several critical mistakes in foam packaging can compromise the protection of electronic products during shipping and increase operational costs. One of the most common errors is selecting the wrong type of foam without considering specific product requirements, such as static resistance and compression needs.
You'll find that generic router tools often can't effectively cut all foam types, especially dense polyethylene foam, leading to poor edge quality and compromised protection.
Another significant mistake is using too much foam, which not only increases material and shipping costs but can also distribute impact force along the product's length, potentially causing damage. You're not getting better protection by overusing foam; instead, you're creating reverse logistics issues and unnecessary expenses.
Poor foam application is equally problematic. If you're placing foam along the entire product length or ignoring the product's tensile strength and sensitivity to environmental factors, you're risking damage.
Additionally, using inadequate routing tools and failing to customize foam inserts for specific products can result in subpar protection. Remember to follow packaging material standards, such as EIA-541 for ESD-sensitive items, to guarantee proper protection during shipping.
Testing Foam for Electronics Protection
Testing your foam's performance through standardized drop tests will reveal its true protective capabilities for electronic shipments.
You'll want to conduct drop tests from various heights and angles, documenting any damage to test components to evaluate the foam's shock absorption effectiveness.
Your foam compression analysis must follow ASTM D3574 standards, which measure essential factors like indentation force deflection and compression set that directly impact the foam's ability to protect electronics during transit.
Drop Test Performance Results
When conducting drop tests for electronics packaging, manufacturers must follow strict ISTA 1A standards to guarantee foam materials provide adequate protection during shipping and handling.
You'll need to perform 10 drops from various angles, with heights determined by your product's weight. The test results will show you if your chosen foam effectively absorbs impact and prevents damage to your electronics.
To validate your foam's performance, you'll want to use both physical testing and numerical simulation through Finite Element Method (FEM). This dual approach helps you understand how your packaging foam deforms and absorbs energy during impacts. You'll see detailed data on thermal prestressing effects and dynamic behavior, which you can compare with experimental results.
Don't risk your valuable electronics with untested packaging – one failed drop test could mean thousands in damaged goods.
You'll sleep better knowing your products are protected by foam that's passed rigorous impact testing.
Your customers will thank you for investing in properly tested protective packaging.
Choose between open-cell polyurethane or closed-cell polyethylene foam based on your specific needs, and verify your selection meets EIA-541 Packaging Material Standards for ESD-sensitive items.
Custom-molded options provide the best fit and protection for uniquely shaped electronics.
Foam Compression Analysis Standards
All foam materials used in electronics shipping must undergo rigorous compression analysis to meet industry standards. You'll need to verify that your chosen foam meets the Indentation Load Deflection (ILD) testing requirements, which measure the material's firmness and compression strength using standardized 4-inch thick by 15-inch square samples.
| Test Type | What You Need to Know |
|---|---|
| 25% Compression | Measures force needed to compress foam by quarter depth; values typically range from teens to 70s |
| 50% Compression | Tests foam behavior under increased pressure; critical for heavier electronics |
| Support Factor | Compares 25% to 65% compression; values 1-3 indicate protection level |
| ASTM Standards | Must comply with D3574 for physical properties testing |
When selecting foam for electronics shipping, you'll want to focus on both compression strength and support factor values. The compression tests help determine if your foam can withstand shipping pressures while maintaining its protective properties. For sensitive electronics, you should look for materials that meet ASMA603 standards and demonstrate consistent performance across all compression tests. Higher support factor values indicate better protection against impact and pressure during transit.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Can Foam Packaging Materials Be Safely Reused for Electronics Shipping?
You can safely reuse foam packaging 3-5 times, depending on its type and condition. You'll need to inspect it carefully before each use and verify it hasn't been damaged or exposed to extreme conditions.
Can Foam Packaging Interfere With RFID Tracking During Shipping?
Yes, certain foams can interfere with RFID tracking. You'll want to use anti-static or ESD foam, as conductive foams may block signals. Always test your packaging setup to guarantee proper RFID tag readability during shipping.
Does Colored Foam Indicate Different Levels of ESD Protection?
Yes, foam colors often indicate different ESD protection levels: pink's typically anti-static, blue's static-dissipative, and black's conductive. However, don't rely solely on color – always verify the foam's actual specifications.
What Cleaning Methods Are Safe for Electronics Shipping Foam?
You'll want to use dry cleaning methods like compressed air or gentle brushing. Don't use water or harsh chemicals as they can damage the foam's anti-static properties and compromise its protective qualities.
How Does Altitude Affect the Protective Properties of Shipping Foam?
You don't need to worry about altitude affecting your foam's protective properties. It'll maintain its cushioning and protection regardless of height changes, unlike air-filled packaging that can compress or pop under pressure.
In Summary
When shipping electronics, you'll need to choose the right protective foam based on your specific needs. Anti-static foam is essential for sensitive components, while custom-cut solutions provide the best fit. Don't skimp on density ratings, and always verify ESD protection levels. Remember to take into account both cost and environmental impact, but never sacrifice protection quality. Test your foam packaging before trusting it with valuable electronics.





Leave a Reply