To properly test static protection packaging, you'll need seven essential tools: resistance meters for measuring surface conductivity, ESD combo testers to check footwear and wrist straps, high-voltage ESD simulators for package validation, walking body voltage meters to assess real-world conditions, shielded bag test kits that meet ANSI/ESD standards, digital surface resistance meters with concentric ring probes, and calibration checkerboards to guarantee accuracy. Each tool serves a specific purpose in maintaining ESD safety standards and protecting sensitive electronic components. Understanding how to effectively use these tools will enhance your static control program's success.
Static Protection Testing Fundamentals

In accordance with industry standards, static protection testing combines multiple evaluation methods to guarantee thorough ESD safeguards. You'll need to understand both electrical resistance testing and walking body voltage assessments, as they work together to provide an extensive protection evaluation.
When you're testing electrical resistance, you'll use specialized equipment like resistance meters or megohmmeters following ANSI/ESD STM 7.1 protocols. You'll place one electrode on the floor and measure resistance to ground, confirming readings fall below 1.0 x 10E9 ohms for electronics manufacturing environments. Similar to early detection principles, catching ESD issues during initial testing phases helps prevent costly remediation later.
For communications facilities, PSAPs, flight towers and other end-user environments, the floor should measure > 1.0 x 10E6 and < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms.
You'll want to complement your resistance testing with walking body voltage tests, which measure static generation under real-world conditions. This dynamic assessment helps you verify if your ESD floor performs effectively during actual use.
You'll typically need specialized equipment such as concentric ring probes and digital surface resistance meters to conduct these evaluations properly. The walking test simulates the movement of people on the floor by having a person walk on the floor with special shoes connected to a charge plate meter that measures the electrical resistance, in volts, between the shoes and the floor.
For electronics manufacturing and handling facilities, the floor should generate < 100V. For end-user environments, the floor should measure < 500V. This test should always be performed with the test subject wearing every type of shoes that will be allowed on the floor.
For complete verification, you'll benefit from static control audits performed by third-party consultants. These extensive evaluations examine your entire ESD control program, including floor design, installation, and maintenance practices.
Through this systematic approach, you'll confirm all components meet required protection standards. A static-control audit is a comprehensive evaluation that includes a detailed inspection of the ESD floor, and may also include resistance testing and walking body voltage tests, as well as an evaluation of the effectiveness of the overall ESD control program.
This audit can help to identify any issues with the ESD system or areas of concern that may not be apparent through other testing methods. Due to the nature of the testing, it is more time-consuming and can be more expensive than other test methods.
Surface Resistance Measurement Tools
To accurately measure surface resistance in static protection testing, you'll need specific tools designed for ESD evaluation. ESD surface resistivity meters serve as your primary handheld devices, offering portability and quick measurements across different packaging materials. These meters help you determine whether materials fall within the required resistance limits of less than 1.0 x 10^11 Ω for ESD materials. Testing conducted with these meters helps maintain workplace safety standards in electronics manufacturing environments.
When testing small areas or recessed surfaces, you'll find two-point resistance meters particularly useful. They're ideal for precise point-to-point measurements and can help you assess both surface and volume resistance.
For thorough testing capabilities, you should consider multi-functional ESD meters that can perform various resistance measurements, including resistance to ground (Rtg) and surface resistance testing.
You'll need checker boards to verify your testing equipment remains accurate through regular calibration and certification.
Digital resistivity meters offer you real-time data display and user-friendly operation, making them essential for consistent testing procedures.
When testing packaging materials specifically, you'll want to use concentric ring fixtures, which provide standardized measurements under controlled conditions of 12%±3% RH and 73°F±5°F for 48 hours.
Portable Testing Equipment

You'll find handheld resistance meters essential for quick assessment of static protection packaging in field conditions.
These portable tools, like the ACL 306 Two-Point Resistance Meter and Simco-ION Model FMX-004 Fieldmeter, let you conduct essential measurements without the need for complex lab setups. Many testers are equipped with rechargeable NiMH batteries for extended field operation.
For on-site quality control, you can easily verify your measurements using tools like the ACL 307 Checker Board while maintaining testing accuracy in various environments.
Handheld Resistance Meters
Modern handheld resistance meters serve as essential tools for testing static protection packaging and ESD-sensitive environments. They offer impressive measurement capabilities, with test ranges spanning from 10^3 to 10^12 ohms, making them suitable for various resistance testing needs. Many models include voltage selection options between 10V and 100V for different testing requirements.
Popular models like the METRISO 3000 and Warmbier METRISO B530 come equipped with 5lb probe sets for accurate measurements.
If you're looking for something more compact, the SRM310 and SRM330 provide automatic ranging and color-coded readouts in pocket-sized formats. You can store up to 9801 measurements in some models, allowing for detailed data analysis later.
You'll need the right accessories to maximize your meter's functionality. Choose from 5lb disk electrode probes for point-to-point measurements, two-point probes for surface testing, or concentric ring probes for volume resistance testing.
These tools help you evaluate ESD protection in various applications, from flooring and mat testing to garment compliance verification.
When testing static protection packaging, you can rely on these meters to determine if surfaces are properly dissipative, conductive, or insulative, ensuring your packaging meets ESD protection standards.
Field Testing Solutions
Three essential categories of portable testing equipment dominate the field of ESD protection verification: ESD combo testers, simulator guns, and specialized data logging devices. When you're conducting field tests, you'll need reliable tools that offer thorough testing capabilities while maintaining portability and ease of use.
- ESD combo testers like the PDT800K and GTS900K provide integrated solutions for testing both footwear and wrist straps, featuring RFID capabilities and data logging functions to track your testing history. The ACL 306 meter offers additional portable testing capabilities with its lightweight design and resistance measurement range of 10e3 to 10e12 ohms.
- For packaging validation, you'll find high-voltage ESD simulators such as the 3ctest EDS 20H invaluable. These devices can simulate electrostatic discharges while monitoring temperature and humidity conditions.
- Data logging testers, including the Warmbier series, offer advanced management features that you'll need for documenting and tracking test results in compliance with industry standards.
You can enhance your testing setup with essential accessories like mounting plates, floor mats, and split footplate designs, guaranteeing stable and efficient testing procedures.
When conducting field tests, you'll need to maintain regular testing schedules and guarantee compliance with ANSI/ESD S541 and S20.20 standards while evaluating resistance, conductivity, and dissipative properties of your ESD protection materials.
Common ESD Testing Standards
Several essential standards govern the testing of ESD protective packaging, with ANSI/ESD S541-2008 serving as the primary framework for packaging and materials requirements. You'll need to comply with ANSI/ESD S20.20-2014, which requires traceable test data for all products used in your ESD Protected Area (EPA). Regular audits and certification processes help ensure continued compliance with these standards.
The key testing procedures you'll encounter focus on surface resistance (ANSI/ESD STM11.11-2015), volume resistance (ANSI/ESD STM11.12-2015), and electrostatic decay. You'll need to guarantee your packaging meets specific requirements both inside and outside the EPA, with dissipative or conductive properties for internal use and additional shielding for external applications.
| Test Type | Standard | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Resistance | STM11.11-2015 | Measures surface conductivity |
| Volume Resistance | STM11.12-2015 | Tests through-material resistance |
| Electrostatic Decay | Mil-STD-3010C | Evaluates charge dissipation time |
To properly test your ESD packaging, you'll need specific instruments like ESD guns for discharge simulation, field monitors for static measurement, and resistance testers for surface and volume testing. Don't forget to evaluate environmental factors in your testing protocol, as humidity and temperature can substantially impact results.
Static Decay Testing Methods
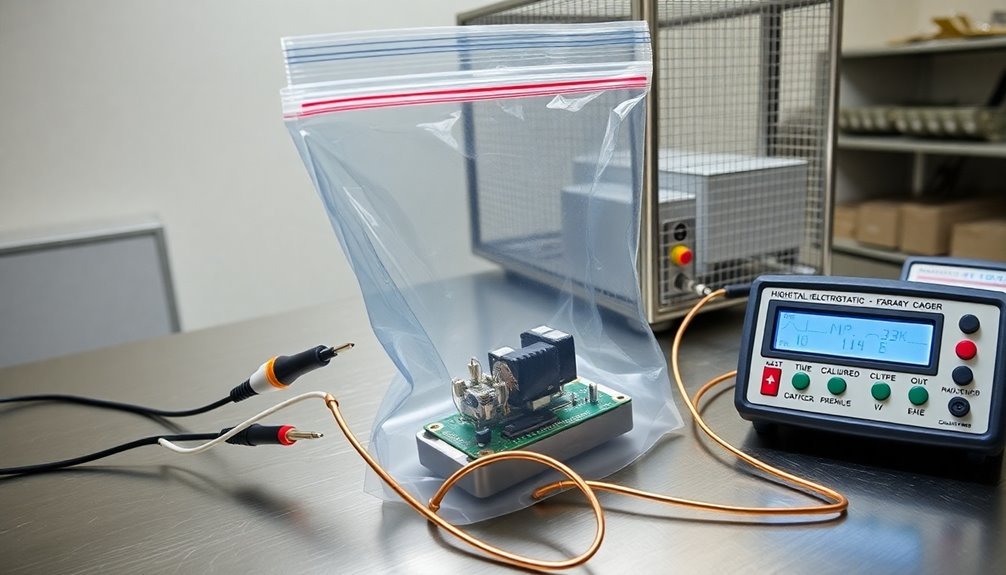
Building on our understanding of ESD testing standards, static decay testing offers precise methods to evaluate how quickly materials dissipate electrical charges. You'll need to follow specific procedures and use specialized equipment to guarantee accurate results when testing static protective packaging materials.
The testing process requires careful attention to environmental conditions, with specimens being preconditioned for 48 hours at 23ºC± 3ºC and 12% ± 3% relative humidity. Test timing devices activate immediately upon specimen grounding to measure decay accurately.
Using a Static Decay Analyzer equipped with a Faraday cage, you'll charge each specimen to 5,000 volts before measuring its decay time to 50 volts or less.
- Follow established standards like Federal Test Standard 101C Method 4046.1 or EIA-541 Appendix F for consistent, reliable results
- Use automatic test procedures with real-time display and analysis software to minimize human error
- Guarantee your testing equipment includes proper fixturing for various material shapes and sizes
- Document compliance tests at different humidity levels to verify material performance across conditions
You'll find this testing vital for R&D, quality control, and certification processes, especially when evaluating static shielding bags and other protective packaging materials for sensitive electronics.
Testing Kits and Applications
Testing kits serve as essential tools for evaluating ESD protective packaging materials in field and laboratory settings.
You'll find thorough systems like the PBT-531 Shielded Bag Test Kit that meets ANSI/ESD STM11.31, IEC 61340-4-8, and MIL-PRF-81705E standards. These kits typically include HBM discharge simulators, fixtures for testing shielded bags, current probes, and oscilloscopes. Maintaining clear documentation standards helps ensure testing procedures are consistently followed and results are properly recorded.
When you're working in electronics or healthcare industries, you'll need to verify that your packaging materials provide adequate ESD protection. Testing kits help you measure surface resistivity, which should fall within the dissipative range of 1×10^4 to 1×10^11 Ω/sq.
You can choose from various options like the Warmbier METRISO® 3000 and B530 ESD Audit Kits for thorough testing, or the Warmbier ESD Starter Kit for basic measurements.
The kits you'll use must comply with key standards such as ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340. You can customize your testing kit based on specific needs, and most are designed to be portable for convenient field use.
Static Shielding Test Equipment

While safeguarding electronic components requires reliable protection, static shielding test equipment helps you verify that your packaging meets critical standards like ANSI ESD.2020 and IEC 61340-5-1.
You'll need to test your static shielding bags using a portable test kit that delivers a 1000-volt discharge through a capacitance arm, ensuring they retain less than 20 nanojoules as specified by S11.4.
To properly evaluate your static protection materials, you'll find several essential testing components:
- Surface resistance meters that measure conductive, dissipative, and insulative properties of your packaging materials
- Combo testers like the CT-8900 that evaluate both wrist straps and heel grounders while storing digital results
- Portable test equipment that allows you to conduct on-site testing of ESD packaging materials with quick, reliable results
- Static meters that measure static fields and verify the integrity of your Faraday cage protection
You can choose from providers like MRO Essentials, Static Solutions, and Antistat for your testing needs. These companies offer both virtual and on-site testing services, along with annual NIST-certified calibration to maintain your equipment's accuracy.
Resistance Meters and Checkerboards
You'll find that handheld resistance meters offer precise surface testing with their metal spring-loaded pogo pins and LED logarithmic scales, making them ideal for quick measurements in static-sensitive environments.
Multi-point measurement systems enable you to test various spots on packaging materials while maintaining compliance with ANSI/ESD standards for surface and volume resistance testing.
To guarantee continued accuracy in your ESD testing program, your resistance meters need annual calibration and proper maintenance under controlled temperature and humidity conditions.
Accurate Surface Testing Methods
Two primary methods stand out for accurately testing the surface resistance of ESD protective packaging: resistance meters and checkerboard testing. You'll need resistance meters to measure both point-to-point resistance (Rtt) and resistance to ground (Rtg), which help classify materials as conductive, dissipative, or insulative.
For large surface areas, you can employ the checkerboard method, dividing the testing area into systematic sections for thorough evaluation.
When testing ESD protective packaging, follow these essential steps:
- Select appropriate testing equipment: Use hand-held resistance meters or complete resistivity meter kits designed specifically for ESD material evaluation.
- Verify compliance with standards: Confirm your testing methods align with industry standards like ESD STM11.31 and ANSI/EOS/ESD S11.11-2001.
- Conduct surface resistance measurements: Test multiple points across the material's surface to establish consistent readings and identify any irregularities.
- Document results accurately: Record whether materials fall within acceptable ranges – conductive materials should measure 10^4-6 Ω, while dissipative materials should measure up to 10^12 Ω.
Multi-Point Measurement Systems
Building on our understanding of surface testing methods, multi-point measurement systems offer advanced capabilities for thorough ESD protection evaluation. You'll find extensive solutions like the Earth-Rite MULTIPOINT II that provide active static grounding monitoring across multiple points in your EX/HAZLOC processes.
When you're testing packaging materials, you'll need tools like the ACL 306 Two-Point Resistance Meter, which gives you portable resistance readings using spring-loaded pogo pins. To verify your measurements' accuracy, you should use the 307 Checker Board, which requires annual certification from a metrology lab.
These systems won't indicate a positive ground status unless the electrical resistance stays at 10 Ohms or less. You'll benefit from fail-safe relays that activate if resistance exceeds permissive thresholds or if the software stops running.
The systems' CAN bus and intrinsically safe power design help you minimize cabling variations and costs.
For field technicians and production operators, these multi-point measurement tools are essential in maintaining ESD-safe environments. You can efficiently verify ESD protection across various applications, from drum mixing to filling processes, while ensuring compliance with resistance thresholds between 10^4 and 10^11 Ohms.
Annual Calibration Requirements
Accurate ESD testing depends on properly calibrated measurement tools. You'll need to verify your resistance meters and other testing equipment undergo annual calibration to maintain reliability in your ESD protection program. This requirement aligns with ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards and helps you maintain compliance while guaranteeing accurate measurements of your static protection packaging.
When it comes to calibration requirements, you should follow these essential steps:
- Schedule annual calibration services through manufacturers or certified calibration laboratories that are accredited for DC resistance measurements.
- Use appropriate calibration standards that match your testing needs, selecting from various sizes and verifying they're certified and traceable.
- Perform calibrations in controlled environments, preferably within a Faraday cage to minimize electrical interference.
- Maintain detailed documentation of all calibration certificates, including measurement data and uncertainties.
If you're working in critical environments like clean rooms, you may need to increase your verification frequency beyond the annual requirement.
Remember that continuous monitoring systems require semi-annual checks, and all calibration activities should be integrated into your broader ESD control program, including proper staff training for handling ESD-sensitive items.
Quality Control Testing Procedures

Through rigorous standardized procedures, quality control testing for static protection packaging guarantees materials meet strict performance requirements.
You'll need to follow ANSI/ESD S541 standards while conducting tests in controlled environments with specific humidity levels of 12%±3%RH and temperatures of 73°F±5°F for at least 48 hours.
You must use concentric ring fixtures and electrometers to measure both surface and volume resistance, confirming they don't exceed 1.0 x 10^11 Ω.
When testing static shielding properties, you'll need to verify that materials provide protection below 20 nJ. For electrostatic decay, you'll measure the time it takes for charges to dissipate, which shouldn't exceed 2.0 seconds according to Mil-STD-3010C Method 4046.
Before testing, you'll need to properly precondition your samples in environmental chambers. It's vital to maintain accurate documentation of all test results, and you must verify they're traceable to accredited laboratories.
Remember that consistent testing methods aren't just about compliance – they're vital for maintaining supply chain integrity and preventing counterfeit materials from entering your operations.
ESD Package Testing Requirements
Manufacturers must adhere to stringent ESD package testing requirements outlined in ANSI/ESD S20.20 and ANSI/ESD S541 standards. You'll need to guarantee your testing environment maintains specific conditions of 12%±3% relative humidity and 73°F ±5°F for at least 48 hours before conducting any tests.
Your packaging materials must undergo thorough evaluation to verify their protective capabilities against electrostatic discharge.
Here's what you'll need to test for:
- Surface and volume resistance measurements to confirm your materials can effectively dissipate static charges
- Electrostatic decay rates to verify how quickly your packaging eliminates harmful static buildup
- Charge retention properties to guarantee your materials don't store potentially damaging static electricity
- Static shielding effectiveness to confirm your packaging can block external discharge energy below 20 nJ when exposed to 1kV HBM discharge
You'll want to use specialized testing equipment like concentric ring fixtures, electrostatic test chambers, and electrometers to gather accurate data. Your test results must meet industry standards and customer specifications for compliance.
Remember to maintain detailed records of all test procedures and results for quality assurance documentation.
Preventive Testing Best Practices
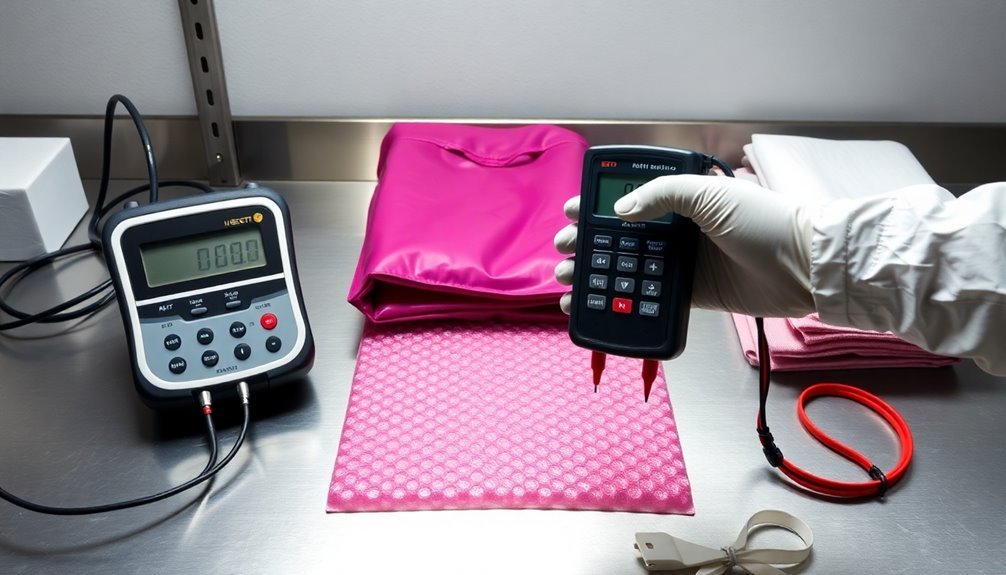
To maintain quality control and identify potential issues early in your packaging inventory, especially for static protection packaging, you need to implement several key practices:
Consistent Testing Schedule
You'll want to start with a consistent testing schedule that covers your entire packaging inventory. This ensures that all packaging materials are regularly evaluated for their performance and compliance with industry standards.
Calibration and Maintenance of Testing Equipment
Your testing equipment needs regular calibration checks and maintenance to guarantee accurate results. This is crucial for meeting industry standards for static protection packaging.
Documentation of Test Results
Make sure you're documenting all test results, including dates, equipment settings, and specific measurements. This creates a reliable audit trail and helps track packaging performance over time.
Example Testing Methods
For ESD control packaging, several specific testing methods are employed. These include:
- Surface Resistance; inside and outside of bags per ANSI/ESD STM11.11-2015 at <1.0 x 10^11O.
- Volume Resistance; inside of the bag to plate per ANSI/ESD STM11.12-2015 at <1.0 x 10^11O.
- Electrostatic Decay per Mil-STD-3010C, Method 4046-2013 (5kV to 0 volts) at a 2.0 second limit.
- Charge Retention (Faraday Cup) per ESD Adv.11.2-1995 at <1.0 nC.
- Static Shielding; 12%RH and 50%RH per ANSI/ESD STM11.31-2012 at <20 nJ.
Periodic Testing
The frequency of testing should be defined in your written ESD control plan. It is user-defined and can vary based on the critical nature of the ESD sensitive items handled and the risk of failure for the ESD protective equipment and materials. For example, daily wrist strap checks may be sufficient in some applications, while other materials may require more or less frequent monitoring.
Comprehensive Testing Strategy
The testing process should be flexible and iterative. It involves regularly reviewing and updating testing processes to align with new technologies or regulations, gathering and analyzing customer feedback and field performance data, and maintaining detailed records of all testing activities, results, and subsequent actions.
Regular Testing Schedule Implementation
Consistency in preventive testing forms the backbone of effective static protection packaging programs. You'll need to establish a systematic approach that integrates various testing methods while maintaining detailed documentation of all activities and results.
By implementing regular assessments of your packaging materials, seams, and closures, you're creating a robust defense against ESD-related failures.
To implement an effective testing schedule, follow these key steps:
- Set up a calendar-based testing routine that covers all critical areas within your facility, focusing on locations where ESD-sensitive products are handled and stored.
- Combine multiple testing methods to evaluate packaging performance under different environmental conditions, ensuring thorough protection throughout the supply chain.
- Document all testing procedures, results, and areas requiring attention, creating a traceable record for audits and continuous improvement.
- Review and update your testing protocols regularly to incorporate new technologies and maintain compliance with industry standards.
Remember to gather feedback from customers and field performance data to refine your testing approach.
Equipment Calibration Requirements
Building on a regular testing schedule, proper equipment calibration guarantees the accuracy and reliability of your ESD protection measurements. You'll need to maintain your testing equipment according to ANSI/ESD STM11.11 standards and certify all calibration checks are performed under controlled conditions of 12% ±3% RH and 73° ±5° F for at least 48 hours.
Your calibration requirements should focus on these key components:
| Equipment Type | Calibration Frequency | Critical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Electrometers | Quarterly | Resistance Range |
| Ring Fixtures | Semi-annually | Surface Resistivity |
| ESD Testers | Monthly | Discharge Time |
| Ground Monitors | Weekly | Resistance to Ground |
| Environmental Meters | Monthly | Temperature/Humidity |
You must maintain detailed calibration records and implement proper ESD control measures during testing. This includes using appropriate grounding techniques and ESD-safe materials. When calibrating, verify that your equipment meets the resistance limits for different packaging materials: conductive (< 1.0 x 10^4 ohms) and dissipative (≥ 1.0 x 10^4 to < 1.0 x 10^11 ohms). Don't forget to stay current with the latest ESD standards and testing methodologies to certify your calibration procedures remain compliant.
Document Test Results Properly
When implementing preventive testing practices for static protection packaging, proper documentation serves as the foundation for quality control and regulatory compliance. You'll need to maintain detailed records of all testing activities, results, and subsequent actions while verifying your documentation follows standardized protocols for consistency and repeatability.
To properly document your test results, follow these essential steps:
- Record detailed information about the test environment, including temperature, humidity, and other relevant conditions that could affect the testing outcome.
- Use standardized forms and templates to capture all test procedures, observations, and measurements consistently across different testing sessions.
- Store test data securely in both digital and physical formats, facilitating easy retrieval for future reference, audits, or comparative analysis.
- Analyze and interpret results objectively, documenting any deviations from expected outcomes and implementing corrective actions when necessary.
Remember to regularly review your documentation processes to verify they're meeting current industry standards and regulatory requirements. You should also maintain clear traceability of your testing samples and data, making it easier to verify compliance and conduct failure analyses when needed.
This systematic approach to documentation will help you maintain quality control and support continuous improvement in your static protection packaging.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should ESD Testing Tools Be Recalibrated for Optimal Accuracy?
You'll need to recalibrate your ESD testing tools annually at minimum, but increase frequency to every 6 months for heavily used equipment. Always follow manufacturer's guidelines and perform daily verification checks between calibrations.
What Environmental Conditions Can Affect the Reliability of ESD Tests?
You'll find that temperature extremes, humidity levels, environmental exposure (like dust and radiation), and uncontrolled testing conditions directly impact your ESD test reliability. Each factor can substantially alter your test results.
Can Damaged ESD Packaging Be Repaired or Must It Be Replaced?
You shouldn't attempt to repair damaged ESD packaging. It is crucial to replace it immediately as repairs can't restore the original protective properties and would compromise your components' safety. Always opt for new packaging.
How Long Does a Typical Complete ESD Testing Certification Process Take?
You'll need around 9-12 months to complete your ESD certification process, including meeting experience requirements, gathering endorsements, completing training, and taking the eight-hour exam. Don't forget to submit your test questions.
What Are the Cost Differences Between Basic and Advanced ESD Testing Equipment?
You'll find basic ESD testing equipment costs between $650-$1,600, while advanced equipment ranges from $1,640-$2,400. The price difference mainly reflects enhanced features, precision, and thorough testing capabilities in advanced models.
In Summary
You'll get the most value from your static protection testing by implementing a consistent quality control program using the right combination of tools and methods. Make sure you're following current ESD standards and regularly calibrating your testing equipment. When you're diligent about preventive testing and monitoring surface resistance, you'll effectively protect sensitive components and maintain packaging integrity throughout your operation.





Leave a Reply