Your ESD control audit must include five essential steps. First, you'll need to define the scope and document compliance requirements across all protected areas. Next, verify personnel training records and assess competency levels against ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards. Third, test and calibrate all equipment while checking grounding systems for proper functionality. Then, conduct a thorough workspace environmental assessment to identify potential static generation sources and control measures. Finally, implement risk assessments and develop corrective action plans. Understanding these critical components will help you establish a more extensive ESD control strategy.
Defining ESD Audit Scope
Defining the scope of an ESD audit isn't just about choosing what to examine – it's about creating a thorough framework for evaluation.
You'll need to specify which departments and functions you'll audit, determine the time period, and decide how deeply you'll investigate each area. Regular compliance verification reports should document all findings to trigger necessary improvements. Your scope should clearly outline objectives while considering the relevant regulatory framework, including standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340-5-1.
You must include all ESD Protected Areas (EPAs) where sensitive components are handled and guarantee you're covering all departments with ESD control measures.
Don't forget to examine training areas and evaluate the equipment, materials, and grounding systems used throughout your facility.
Your audit scope should encompass different types of evaluations, from program management assessments to workplace surveys.
You'll want to incorporate quality process checking and compliance verification to guarantee your ESD control procedures are being followed.
Remember to specify your sampling techniques and testing equipment requirements – they're essential for consistent results.
Include plans for corrective actions based on your findings, as this will help drive continuous improvement in your ESD control program.
Personnel Training Documentation Review
Your personnel training documentation review needs to focus on two critical areas: verifying complete training records and evaluating employee competency levels.
You'll want to examine records for both initial and recurring ESD training sessions, ensuring they meet ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards and include proper signatures, dates, and training content details.
To assess employee competency, you'll need to check that objective assessment methods are in place, such as written tests, practical demonstrations, or hands-on evaluations of ESD handling procedures. The employee knowledge level evaluation should be included as part of the comprehensive ESD audit process.
Training Records Verification Process
Maintaining accurate training records stands at the core of an effective ESD control program's documentation process. You'll need to guarantee your training plans clearly document all procedures for recording personnel training, covering everything from ESD fundamentals to specific program details and individual roles.
You must establish a robust verification system that includes various training methods and tools, from live instruction to interactive programs. It's crucial to maintain a central repository for all educational materials, making it easier to keep your employees updated with the latest information. Implementing specialized training modules for different job disciplines ensures comprehensive coverage across all organizational levels.
To verify training effectiveness, you'll need to implement objective evaluation techniques and conduct regular compliance audits. Don't forget to track and analyze trends to identify areas where retraining might be necessary. Your verification process should include sampling techniques and statistical analysis to guarantee thoroughness.
Make sure you're following ISO 9000 and ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards in your documentation process. You'll want to develop an all-encompassing Compliance Verification Plan that includes different audit types, from program management to workplace checks.
Remember to use detailed checklists during audits to maintain consistency and support continuous improvement efforts.
Employee Competency Assessment Methods
A robust employee competency assessment system forms the foundation of effective ESD control training documentation.
You'll need to verify that your training program covers essential elements including static electricity fundamentals, ESD Control Program Plan details, and specific procedures while adapting content for cultural differences across facilities.
Your assessment methods should incorporate diverse training tools, from live instruction to interactive computer-based programs. Certification and testing have proven to enhance material retention and employee motivation.
Make sure you're maintaining a central repository for educational materials and utilizing demonstrations to illustrate ESD events' impact.
You'll want to supplement these with ongoing reminders through bulletin boards and newsletters.
To evaluate competency effectively, you must implement objective assessment techniques to track comprehension and analyze training needs.
You should share quality and reliability data with employees while regularly observing their compliance with ESD control procedures.
Don't forget to document all aspects of training, including initial and recurrent sessions.
Ensure you're keeping detailed records of training participation and materials used.
You'll need to conduct regular quizzes or exams to assess understanding and perform audits to verify compliance, measuring success against identifiable performance goals.
Equipment Testing Requirements

You'll need properly calibrated equipment that meets strict ESD testing standards to conduct effective audits and guarantee accurate measurements.
Equipment options range from basic testers to analyzers costing up to $12,967 to meet various testing requirements.
Your basic toolkit must include calibrated electrostatic field meters, resistance meters, and ground testers that comply with industry standards for ESD measurement accuracy.
Make sure all testing devices undergo regular calibration checks and include current calibration certificates to maintain testing validity and meet compliance requirements.
Equipment Calibration Standards
Three critical elements define equipment calibration standards in ESD control: accuracy, compliance, and documentation. You'll need to verify your test equipment maintains accuracy through regular calibration that traces back to national or international standards. All calibrations must be performed by certified laboratories to maintain measurement integrity.
You must comply with ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340-5-1 standards for your ESD test equipment calibration. The frequency of calibration depends on your equipment's usage and manufacturer specifications, which you'll need to document in your compliance verification plan. Some devices require daily verification, while others need annual calibration – stick to these schedules strictly.
You're required to maintain detailed calibration records for audit purposes. Your documentation should include calibration certificates with equipment details, calibration dates, and traceability information. Keep these records secure yet accessible, as they're essential for demonstrating compliance during audits. Essential tools like resistance meters and testers must be properly maintained to ensure accurate field testing results.
Without proper calibration standards and documentation, your ESD control program risks failure, and you won't meet certification requirements. Make sure you're tracking calibration schedules and maintaining thorough records to identify equipment due for recalibration.
ESD Testing Device Requirements
Proper ESD testing equipment must meet specific voltage and discharge requirements for accurate testing and compliance. You'll need a device that can handle contact discharge voltages from 1 to 8 kV, with a rise time between 0.7 and 1 nanosecond. Your testing equipment should maintain a holding time of at least 5 seconds, with typical storage capacitance of 150 pF and discharge resistance of 330 ohms.
When selecting your ESD testing device, you'll want to guarantee it complies with international standards like IEC 61000-4-2. Your setup must include an ESD generator, test table, and both horizontal and vertical coupling planes. Electronic failures account for approximately 30% of device malfunctions due to ESD events. Don't forget proper grounding and resistance components for accurate measurements.
You'll need to verify and calibrate your equipment regularly. Use a voltmeter or voltage divider to check voltage levels, and conduct current waveform verification during annual calibration. Your verification setup should include an ESD target and adapter, 20 dB attenuator, and an oscilloscope with bandwidth exceeding 1 GHz.
To minimize interference, perform testing in a shielded chamber or move your test area away from environmental noise sources. Remember to maintain annual calibration schedules to guarantee your testing equipment remains reliable and accurate.
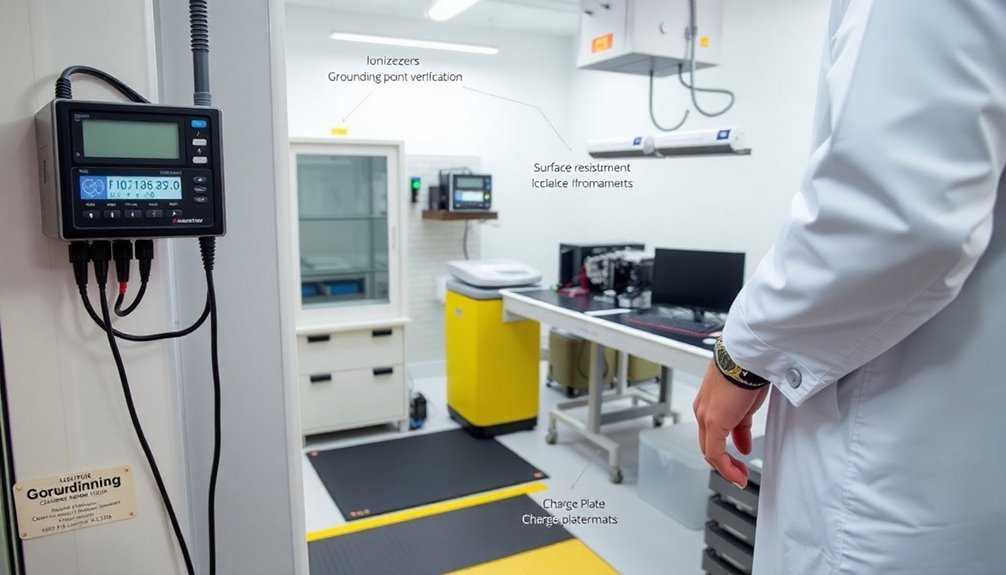
Workspace Environmental Assessment
A thorough workspace environmental evaluation forms the foundation of an effective ESD control program. You'll need to analyze multiple critical components, starting with facility grounding systems. Make certain you're checking for proper equipotential bonding of conductive surfaces and performing regular inspections of all grounding connections.
When reviewing your workspace, you'll need to identify and document all ESD-sensitive areas where static-sensitive components are handled. You must evaluate existing control measures and look for potential static generation sources. Don't forget to verify that your ESD-protected areas are clearly marked and properly maintained. Specialized software and equipment should be utilized to monitor ESD events throughout the facility.
| Evaluation Area | What to Check | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Grounding | Continuity & Resistance | Test & Document Results |
| Surfaces | Static Dissipative Properties | Measure Surface Resistance |
| Personnel | ESD Garments & Straps | Verify Daily Testing |
| Equipment | Ionizers & Monitors | Calibrate & Maintain |
| Environment | Humidity & Temperature | Monitor & Control |
Your evaluation should include verification of ESD-safe worksurfaces, proper ionization systems, and protective equipment usage. You'll need to guarantee your storage solutions are designed to prevent static generation, and implement a regular maintenance schedule for all ESD control equipment.
Control Program Documentation Analysis

You'll need to scrutinize quality control records to guarantee proper documentation of all ESD control measures and test results.
Your assessment should verify that compliance documentation meets industry standards and regulatory requirements, including proper signatures, dates, and detailed procedural notes.
When examining control test data, you must confirm that all measurements are accurately tracked, properly logged, and stored in an organized system that allows for easy retrieval and analysis.
Quality Control Records Assessment
Maintaining detailed quality control records forms the backbone of an effective ESD control program. You'll need to guarantee these records include audit results, training documentation, and test equipment calibration data. They serve as vital evidence of your conformity to technical requirements and help you track trends for implementing corrective actions.
When evaluating quality control records, you must verify they're easily accessible and well-documented, avoiding simple checklist dependencies. You'll want to focus on three key audit types: program management audits using surveys, quality process checking through regular visual and electrical inspections, and workplace audits for compliance verification.
You should analyze trend charts and detailed records to trigger necessary process adjustments. If you discover deficiencies during audits, implement corrective actions promptly, which may include retraining staff or revising procedures.
Make sure your records support continuous improvement efforts by providing clear data for statistical analysis. Regular compliance verification audits, often conducted monthly, will help you identify areas for optimization and guarantee your ESD control program maintains its effectiveness through proper documentation and systematic review.
Compliance Documentation Standards
Building on proper record-keeping practices, the documentation standards for your ESD control program must follow strict protocols outlined in ANSI/ESD S20.20-2014.
You'll need to guarantee your documentation includes both administrative and technical requirements while maintaining alignment with your internal quality system standards.
Your compliance documentation should detail all approved ESD protective products, specific test methods, and any deviations from referenced standards.
You must clearly document your verification procedures, including measurement requirements, testing limits, and frequency schedules.
When you're establishing these standards, make sure to incorporate extensive guidelines for personnel training and verification procedures that demonstrate how you're following the plan.
Don't forget to document your sampling techniques and statistical analysis methods for compliance verification.
You'll need to maintain detailed records of all audit findings, corrective actions, and test results.
Your documentation should include specific checklists tailored to your ESD control requirements and clearly outline the reporting procedures for any discrepancies.
Remember to keep all records readily accessible for management review and guarantee they provide clear evidence of your program's conformity to established standards.
Control Test Data Tracking
In post-audit activities, you'll prepare a detailed report summarizing findings and recommended actions.
Monitor the implementation of corrective measures and conduct follow-up audits to guarantee sustained compliance.
You should regularly analyze trends and update your ESD control program based on new findings and industry developments.
Static Charge Measurement Procedures
Reliable static charge measurement demands precise techniques and specialized equipment for accurate results. You'll need to use an electrostatic fieldmeter for non-contact measurements, positioning the probe 1-5mm from the surface.
Don't attempt these measurements with a standard multimeter, as they require instruments with high input impedance.
When using a fieldmeter, you're measuring the force between induced charges in the sensor and the object's surface charge. You'll need to record both the initial peak voltage and its decay rate.
The fieldmeter operates through a charge-discharge process, using a corona source to charge a floating electrode that discharges to the earth-electrode at regular intervals.
For the most accurate measurements, you'll want to use the Faraday cage method. Place your charged object inside the insulated inner electrode, which induces a charge proportional to the object's charge.
You can then measure the potential difference between inner and outer electrodes without losing any charge during measurement.
Remember that your ESD control program requires regular compliance verification audits, typically monthly, to ascertain all equipment and materials meet specified limits.
Grounding Systems Verification

While grounding systems form the backbone of any ESD control program, you'll need to verify these systems through systematic testing and monitoring. Start by checking that all equipment grounding conductors create proper paths to bring ESD protective materials and personnel to the same electrical potential.
You must verify that your chosen grounding methods, whether wrist straps or foot grounders, comply with industry standards. Test the resistance to ground of all worksurfaces, including their ground snaps and cords. You'll want to measure the surface to groundable point resistance and ascertain all ESD protective surfaces connect to the common point ground.
For operator grounding, implement daily wrist strap checks and regular testing of foot grounders when used with ESD flooring systems. Maintain your grounding systems by conducting regular inspections for wear and contamination. Clean worksurfaces with approved ESD cleaners and perform quarterly testing of electrical outlets to confirm proper wiring.
Don't forget to document any non-conformities you find and address them promptly. Using continuous monitors will help you test wrist strap and static mat connections throughout the workday, ascertaining consistent protection against ESD damage.
Protective Materials Inspection
A thorough inspection of ESD protective materials forms the foundation of your control program's effectiveness.
You'll need to systematically evaluate all surfaces, equipment, and packaging materials that come into contact with ESD-sensitive devices. Start by checking your workstations' dissipative properties, including tables and shelving units, guaranteeing they maintain proper electrical resistance levels.
Your protective materials inspection should focus on these critical areas:
- Check all packaging materials, including bags, boxes, and containers, to verify they're ESD-compliant and in good condition.
- Inspect transport devices like trolleys and containers for dissipative properties and signs of wear.
- Verify that all tools used in ESD-protected areas meet compliance requirements.
- Test floor surfaces and confirm that cleaning materials won't compromise their dissipative properties.
Don't forget to document all your findings and implement corrective actions immediately when you spot deficiencies.
Regular verification measurements help guarantee your protective materials maintain their effectiveness over time. If you're using sampling techniques, make sure they're statistically valid and representative of your entire operation.
Remember that proper maintenance of these materials directly impacts your ability to protect sensitive components.
Risk Assessment Methods

Developing thorough risk assessment methods serves as the cornerstone of an effective ESD control program. You'll need to start by reviewing industry standards and evaluating workplace conditions to identify potential ESD risks in your facility.
Make certain you're assessing existing control measures and developing a detailed audit plan to guide your assessment process.
When you conduct your risk analysis, you should perform on-site evaluations and measure electrostatic charges where necessary.
Don't forget to collect data on your ESD control practices, including maintenance records and training documentation. You'll want to analyze your grounding systems and identify any potential hazards and their root causes.
In the evaluation phase, you'll need to classify non-conformities by severity and evaluate how well your current controls are working.
It's crucial to verify compliance with industry standards and document any deviations you find.
Finally, prioritize your recommendations based on impact and urgency, and develop an action plan to address the identified risks.
You should regularly track trends and analyze data to guarantee your ESD control program remains effective and compliant over time.
Corrective Actions Implementation
Once you've identified ESD control issues through your audit, implementing effective corrective actions becomes your next critical task.
You'll need to carefully assess each finding's classification to determine the appropriate response level, as major non-conformances require immediate action while minor ones can be addressed within your regular improvement cycle.
To implement corrective actions effectively, you must follow a structured approach that guarantees thorough resolution of identified issues.
Start with root cause analysis and develop specific solutions that directly address the problems you've found.
- Document each non-conformance thoroughly, including its classification, location, and potential impact on your ESD control program.
- Develop detailed action plans with specific steps, responsibilities, and deadlines for implementation.
- Prioritize your corrective actions based on risk level and resource availability.
- Verify the effectiveness of implemented solutions through follow-up assessments and data collection.
Remember to maintain extensive documentation of all corrective actions and their outcomes.
This documentation isn't just for record-keeping – it'll help you track progress, demonstrate compliance to auditors, and identify patterns that might indicate systemic issues requiring broader solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Calibration Checks Be Performed on ESD Audit Testing Equipment?
You should calibrate your ESD audit testing equipment at least every 12 months, but check it every 6 months if it's frequently used. Don't exceed 2 years between calibrations for any testing equipment.
What Specific Certifications Should ESD Auditors Possess Before Conducting Facility Assessments?
You'll need EOS/ESD Association certification, ANSI/ESD S20.20 training, and IEC 61340-5-1 competency. You must complete ESD Auditor training and maintain valid certification that's renewed every two years through recertification courses.
Can Remote Audits Effectively Replace On-Site ESD Control Inspections?
While you can't fully replace on-site ESD inspections with remote audits, you'll find they're effective as supplementary tools. They're best used in combination with traditional inspections for thorough ESD control assessment.
How Do Seasonal Changes Affect ESD Audit Results and Measurements?
You'll notice significant variations in your ESD audit results across seasons. Lower winter humidity increases static risks, while summer's higher humidity improves readings. Temperature changes also affect your ESD protective materials' performance.
What Software Tools Are Recommended for Tracking and Analyzing ESD Audit Data?
You'll want to use specialized ESD management software like ESdat for tracking audit data. It offers essential features like data visualization, trend analysis, statistical processing, and automated reporting for effective compliance monitoring.
In Summary
You've got to maintain a thorough ESD control program by following through with all audit requirements. Make certain you're regularly reviewing personnel certifications, testing equipment calibration, and verifying grounding systems. Don't forget to inspect protective materials and workspace conditions. Document your findings, assess risks, and implement corrective actions promptly. Your diligence in following these audit steps guarantees continued ESD protection effectiveness.





Leave a Reply