Always wear a properly fitted ESD wrist strap against your skin and connect it to designated grounding points. Don't handle sensitive components without first grounding yourself. Use anti-static footwear with conductive soles that work with your facility's flooring system. Maintain room humidity between 40-60% to prevent static buildup. Store components in anti-static bags and handle them by their edges. Test grounding connections daily and keep your workspace clean with ESD-safe products. Check your anti-static equipment regularly, including straps and mats. Follow ESD-protected area protocols strictly. Document all safety procedures. These foundational steps will help you establish a thorough anti-static safety routine.
Wear ESD Wrist Straps Properly

Getting serious about ESD protection starts with proper wrist strap usage in data centers. You'll need to wear your ESD wrist strap directly against your skin, not over clothing, to guarantee proper grounding. Make sure it's snug but comfortable, as you'll likely wear it for extended periods while working with sensitive equipment.
Connect your wrist strap securely to a designated grounding point or ESD mat, and don't rely on wireless straps, as they don't meet industry standards. Choose brightly colored straps for better visibility and to demonstrate your compliance with ESD procedures. These wrist straps incorporate conductive materials to safely dissipate static charges from your body.
Remember, these straps are mandatory in ESD protected areas and play a vital role in preventing static discharge that can damage expensive equipment.
You'll need to test your wrist strap regularly using an ESD test station to verify it's functioning correctly. If your facility has continuous monitoring systems, they'll alert you to any grounding issues immediately.
Don't hesitate to replace your strap if it shows signs of wear or damage. By following these guidelines, you're protecting sensitive electronic components and helping maintain uninterrupted data center operations while meeting ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
Ground Yourself Before Handling Equipment
Every data center technician must ground themselves properly before handling sensitive electronic equipment. Your first step should be to locate the nearest ground bus bar or designated grounding point in your work area.
You'll need to establish a direct connection to the facility's grounding system before touching any servers, switches, or other sensitive components. The Signal Reference Grid provides a low-impedance pathway that helps protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference.
When you're working on raised floors, make sure you're using static discharge grounding points specifically designed for these areas. Don't skip the grounding process even if you're in a hurry – it's essential for both your safety and the protection of valuable equipment.
You'll want to verify that your connection to the grounding system is secure and that you're maintaining constant contact throughout your work session.
If you're handling particularly sensitive equipment, you should use isolated grounding points to minimize interference. Remember that proper grounding isn't just about preventing static discharge – it's also vital for protecting yourself against potential electrical hazards.
Make sure you understand your facility's specific grounding protocols and always follow established safety procedures. If you're unsure about proper grounding techniques, don't hesitate to consult your facility's grounding experts or review your training materials.
Choose Anti-Static Footwear Solutions

Selecting the right anti-static footwear is crucial for protecting sensitive electronic equipment in your data center. You'll need to choose footwear specifically designed with conductive outsoles that can rapidly discharge static electricity to the ground. Look for options made from high-quality split leather, which offers both durability and reliable static dissipation properties.
When selecting your anti-static footwear, you'll need to think about your data center's specific flooring type. Even with ESD-protective flooring installed, wearing standard shoes can generate dangerous static charges. Professional installation of your facility's flooring system is essential to ensure proper conductivity between shoes and floor surface.
Your footwear must work in conjunction with your facility's conductive flooring system to effectively control static buildup.
You'll want to maintain your anti-static footwear regularly to guarantee top performance. Check the conductive properties periodically and replace worn-out shoes that no longer provide adequate protection.
Remember that your footwear needs to perform consistently across varying humidity levels while meeting industry safety standards and regulations. If you're unsure about compliance requirements, consult ASHRAE guidelines for data centers, which provide specific recommendations for moderately conductive flooring systems and appropriate footwear solutions.
Monitor Room Humidity Levels
Beyond protective footwear, maintaining proper humidity levels stands as a fundamental aspect of data center safety. You'll need to keep relative humidity (rH) between 40% and 60% to prevent both static electricity buildup and condensation that can damage your equipment.
To effectively monitor humidity, you'll want to deploy several tools throughout your data center. Install humidity sensors in hot zones and near air conditioning systems to detect any failures quickly. Consider using desiccant dehumidifiers for more efficient moisture control.
Use both dry and wet bulb thermometers to measure ambient air temperature and moisture content, while keeping track of dew point temperatures to prevent condensation issues.
Make sure you're regularly calibrating your measurement equipment for accurate readings and maintaining your HVAC systems for peak performance. You should set up monitoring tools at the rack level, particularly in areas with extreme conditions.
Don't forget to optimize airflow using access flooring systems for proper air distribution.
Use ESD-Safe Storage Containers

Three essential types of ESD-safe storage containers should be part of your data center's safety protocol: bins, shelves, and totes. These containers prevent static charges from building up and protect your sensitive electronic components from potentially devastating ESD damage.
You'll want to use ESD-safe bins for storing smaller components like PCBs, ICs, and resistors. They're available in various sizes and come with or without lids, depending on your needs. The stackable design of these containers helps optimize valuable floor space in your facility.
For larger equipment storage, install ESD-safe shelving units that protect your hardware from both electrostatic discharge and environmental hazards.
ESD totes are particularly useful when you need to clean components or keep them dust-free during transport.
To maximize the effectiveness of your ESD-safe storage solutions, implement proper grounding strategies and maintain a cleanroom environment. Replace common items like trash cans with their ESD-safe versions to reduce static buildup throughout your facility.
Leading tech companies like Meta, Apple, and Microsoft rely on these storage solutions to protect their sensitive equipment and maintain data center efficiency.
When handling components, always use ESD-safe equipment and tools to minimize the risk of static-related damage.
Maintain Clean Workstation Surfaces
Maintaining clean surfaces throughout your workstation stands up against both static discharge and equipment contamination. You'll need to establish a regular cleaning schedule using non-abrasive materials and appropriate cleaning solutions that won't generate static or conduct electricity. Make sure you're using ESD-safe cleaning products specifically designed for sensitive electronic environments.
Start by dusting your workstation surfaces daily with anti-static cloths to prevent particle buildup. Electrostatic attraction can cause dust to cling persistently to surfaces, making thorough cleaning essential. Install ESD mats at your workstation and guarantee they're properly grounded before beginning any hardware handling tasks.
When cleaning, work methodically from top to bottom, including walls and overhead areas that can collect dust and contribute to contamination.
Don't forget to vacuum your workspace regularly using ESD-safe equipment to remove dust and dirt particles that can affect your equipment's performance. You should also inspect your work area daily for any signs of contamination or static-generating materials.
If you're working in a data center environment, coordinate with facility managers to maintain proper environmental controls, including temperature, humidity, and air filtration systems.
Remember to test your anti-static measures regularly to guarantee they're functioning correctly and providing adequate protection.
Handle Components With Care
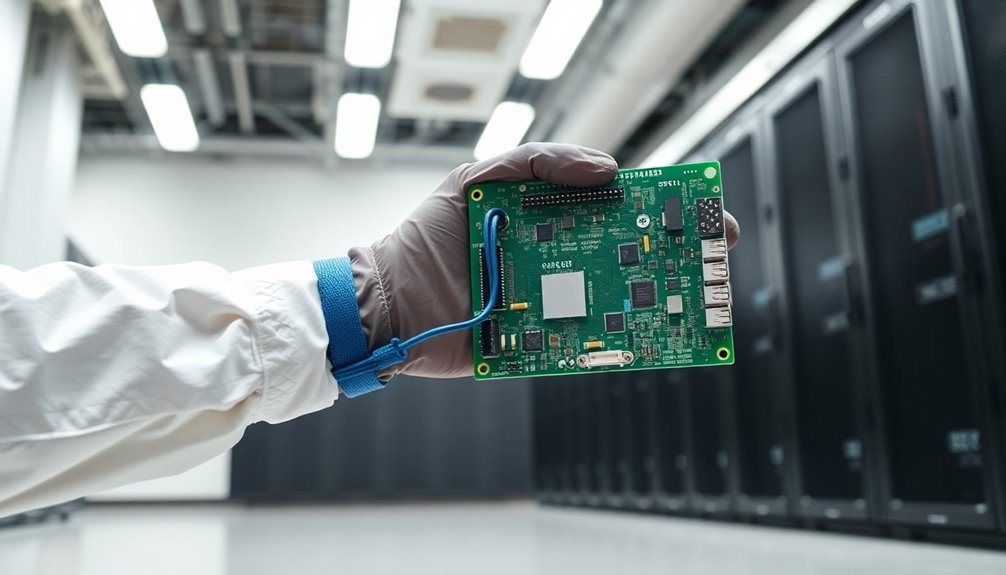
You'll need to wear a properly grounded ESD wrist strap whenever you're handling sensitive data center components to prevent static discharge damage.
Always use both hands when moving or installing components to maintain stability and reduce the risk of accidental drops or impacts.
Following safety standards and regulations is essential when handling data center equipment to ensure both personnel and equipment protection.
Keep components in their original anti-static packaging until you're ready to install them, and return unused items to protective containers immediately after handling.
Wear ESD Wrist Straps
Safety in data centers begins with proper ESD protection, and wearing an ESD wrist strap is essential when handling sensitive electronic components. You'll need to guarantee your wrist strap is properly fitted and connected to a grounding point through the anti-static coiled cord. Always test your wrist strap using an ESD Test Station before starting work to verify it's functioning correctly. ESD events can damage sensitive electronics with as little as 25 volts of discharge, making proper grounding critical.
Choose the right type of wrist strap for your needs, considering factors like comfort and duration of use. If you're a regular data center worker, invest in a high-quality fabric or metal adjustable strap. For temporary visits, disposable bands will suffice.
| Wrist Strap Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric | Daily Use | Comfortable, durable, washable |
| Metal Adjustable | Heavy Use | Expandable links, long-lasting |
| Hypoallergenic | Sensitive Skin | Nylon/stainless steel construction |
| Disposable | Visitors | Single-use, cost-effective |
Remember to maintain your wrist strap properly and replace it if you get high fail readings during testing. Your strap's resistance should stay below 35 megohms to meet ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards. Don't compromise on ESD protection – it's vital for preventing costly equipment damage and system failures.
Use Both Hands Always
A firm, steady grip with both hands is crucial when handling sensitive data center components. You'll need to handle all electronic equipment by their edges while keeping your movements controlled and deliberate. Using both hands provides better stability and reduces the risk of accidentally dropping or damaging components.
When handling components, you'll want to position yourself properly at your workstation to avoid overreaching. Make sure all items are within easy reach, and you're wearing your ESD-safe gloves if you're dealing with sharp edges.
Remember to work only on designated static-free surfaces that have been properly cleaned and grounded. You should always maintain contact with the edges of components, never touching pins or leads directly.
Before handling any equipment, make certain you've removed all static-generating items from your workspace and replaced them with ESD-safe alternatives. Keep your movements steady and controlled, using both hands to distribute the weight evenly.
This two-handed approach isn't just about preventing drops – it's also about maintaining consistent control throughout the handling process. When moving larger components, coordinate your movements carefully and maintain awareness of your surroundings to prevent accidents.
Transport in Protective Packaging
Three essential protective packaging methods help safeguard sensitive data center components during transport. You'll need to use anti-static bags, ESD foam, and conductive metallized packaging to protect your sensitive equipment from electrostatic discharge that could cause immediate or latent damage.
When you're transporting components, make sure you're using the right type of protective packaging for each item:
- Use anti-static bags with Faraday cage properties for circuit boards, hard drives, and GPUs to shield them from external static charges.
- Apply ESD foam specifically for components with exposed pins to prevent both mechanical damage and static discharge.
- Select metallized bags with appropriate closure types (zipper, heat-seal, or self-sealing) based on your security and handling needs.
Don't risk damaging expensive equipment by using improper packaging materials. Static-shielding packaging isn't just an option – it's essential for maintaining component integrity and preventing costly replacements.
You'll save time and money by investing in proper ESD-safe storage solutions. Remember that proper packaging extends component life and guarantees they'll arrive at their destination in ideal working condition.
Always keep your ESD-protective materials readily available and in good condition.
Check Grounding Points Daily
You'll need to verify all grounding connections in your data center at the start of each shift using approved testing equipment.
Make it a habit to visually inspect every grounding point for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections that could compromise your antistatic protection.
Double-check that all equipment maintains proper ground connectivity by testing resistance levels and ensuring solid contact between components and grounding straps.
Test Ground Connections Daily
Regular ground testing forms the cornerstone of data center safety and reliability. You'll need to conduct daily tests on ground connections to prevent equipment damage and maintain system stability.
Using specialized equipment like the Fluke 1625-2, you can perform various testing methods including stakeless and selective testing to guarantee your grounding system remains effective.
When testing ground connections daily, focus on these critical aspects:
- Check all equipment connections using the two-point ground resistance test to identify potential weak points or loose connections
- Conduct visual inspections of grounding points while using thermal imaging to detect any overheating issues
- Verify that all protective equipment and insulated tools are in proper condition before performing any tests
Don't skip your daily ground testing routine, as it's vital for preventing intermittent issues and protecting sensitive equipment from data loss.
If you discover any irregularities during testing, report them immediately and guarantee repairs are made by certified personnel.
Remember that proper grounding isn't just about equipment protection – it's essential for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing electrical hazards that could lead to injury or loss of life.
Visual Inspection of Points
Building upon your daily ground testing routine, visual inspections serve as your first line of defense against potential grounding issues. You'll need to systematically check all grounding points, including main bonding connections, equipment frames, and common bonding networks (CBN). Use calibrated tools and follow industry standards like ANSI/TIA-942 and IEEE guidelines during your inspections.
| Inspection Point | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Main Bonds | Corrosion, loose connections, damaged conductors |
| Equipment Frames | Secure attachments, proper labeling, wear signs |
| CBN Connections | Tight bolts, clean surfaces, intact conductors |
| Rack Systems | Proper grounding, secure connections, wear patterns |
During your visual checks, you'll want to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage that could compromise the grounding system's integrity. Use a torque wrench to verify that bolted connections maintain proper tightness, and employ thermal imaging to detect potential overheating issues. Don't forget to document your findings and address any concerns immediately to maintain network efficiency and protect mission-critical equipment. Regular visual inspections help you stay compliant with safety requirements while ensuring business continuity.
Proper Connection Verification
Maintaining up to and beyond standard safety protocols requires daily verification of all grounding connections in your data center environment. You'll need to routinely check the tightness of bolted electrical connections using a calibrated torque wrench, following manufacturer specifications or NEC Table 100.12 guidelines.
Don't skip point-to-point resistance testing between your main grounding system and electrical equipment frames.
When verifying connections, confirm you're following these critical steps:
- Inspect all grounding points visually for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose components
- Test electrical continuity throughout racks and cabinets, confirming paint has been properly scraped or paint-piercing hardware is correctly installed
- Verify proper bonding at system anchorage points and check the stability of all connections
You should use thermal imaging to identify potential overheating issues before they lead to failures.
Remember that only certified electricians should handle these verification procedures, and you'll need to document all inspections.
Pay special attention to grounding bus bars and continuous copper ground rings, as these serve as central connection points for your grounding infrastructure and require consistent monitoring for peak performance.
Follow ESD-Protected Area Guidelines
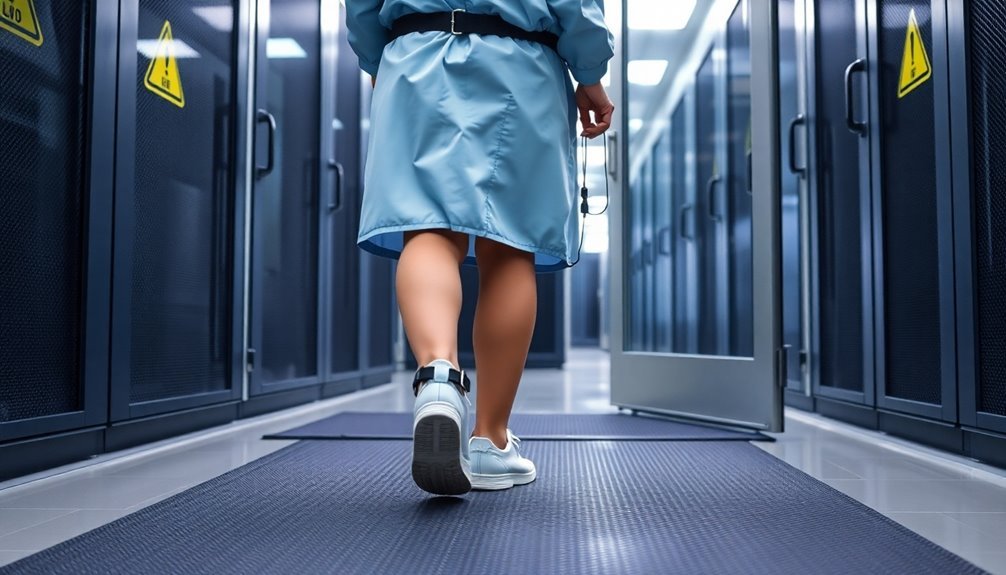

Successfully implementing ESD-Protected Area (EPA) guidelines requires strict attention to safety protocols and clear boundaries.
You'll need to guarantee your EPA zones are clearly marked with black and yellow demarcation tape or physical barriers, and install proper signage to prevent unauthorized access.
Make sure you're using only ESD-safe equipment within your protected areas. This includes workstations, chairs, tables, and anti-static flooring or mats.
You'll need to regularly test all equipment to verify it maintains ESD safety standards, and promptly remove any non-compliant items from the zone.
Your compliance measures should include wearing anti-static wrist straps and ESD-safe clothing whenever you're working in EPA areas. You'll also need to properly ground all equipment and personnel.
If you're handling sensitive components, always do so within these controlled environments.
Don't forget to participate in regular ESD safety training sessions and follow established entry protocols.
Your facility's ESD coordinator will conduct periodic audits to guarantee ongoing compliance.
Inspect Anti-Static Equipment Regularly
Regular inspections of your anti-static equipment form the backbone of any effective ESD protection strategy. You'll need to conduct thorough checks monthly or after each use, depending on your data center's specific policies.
During these inspections, verify that all equipment meets essential standards like ASHRAE, ISO 14644, and IEST certification requirements.
Make sure you're documenting every inspection for future reference and maintaining detailed records of any issues found. Pay particular attention to expiration dates on anti-static consumables and equipment, as expired materials won't provide adequate protection.
Test the functionality of all anti-static devices regularly to confirm they're working as intended.
Key areas to focus on during your inspections include:
- Ground connections and wiring integrity of all anti-static equipment
- Wear patterns on anti-static floor mats and other static-dissipative surfaces
- Condition of anti-static clothing and PPE issued to personnel
Remember to calibrate your anti-static testing equipment according to manufacturer guidelines, and immediately replace any faulty items. Don't wait until equipment fails – proactive maintenance and regular calibration will help prevent costly static discharge incidents that could damage sensitive components.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Anti-Static Clothing Be Replaced?
You'll need to replace your anti-static clothing after 100 effective washings. However, you should inspect it regularly for wear and tear, and replace it sooner if you notice any degradation in its protective properties.
Can Static-Sensitive Equipment Be Safely Transported Between Different Data Centers?
Yes, you can safely transport static-sensitive equipment between data centers by using ESD-safe containers, maintaining proper humidity levels, and ensuring all handlers wear antistatic gear. Always use climate-controlled vehicles for transportation.
What Emergency Procedures Should Be Followed After an ESD Incident?
After an ESD incident, you'll need to immediately notify management, isolate the affected area, assess damage, guarantee personnel safety, document the incident, and follow your facility's escalation procedures for appropriate emergency response actions.
Are Wireless Devices Allowed in Static-Controlled Areas?
You can use wireless devices in static-controlled areas, but you'll need proper authorization and must follow strict protocols. Always verify that your device complies with ESD safety measures and facility-specific guidelines.
How Do Seasonal Changes Affect Static Control Measures?
You'll need to adjust your static control measures seasonally. During dry winters, increase humidity and grounding practices, while in humid summers, you'll focus more on maintaining proper air circulation and dehumidification systems.
In Summary
You'll find that following these antistatic safety measures isn't just about protecting equipment – it's about maintaining your data center's reliability and longevity. Make these practices part of your daily routine, and you'll minimize the risk of ESD damage that can silently destroy sensitive components. Remember, it only takes one static discharge to cause expensive failures, so don't skip these essential precautions.





Leave a Reply